* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 02_tcom5272_lan
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Telephone exchange wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
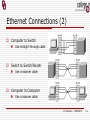
Spanning Tree Protocol wikipedia , lookup
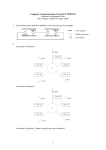
TCOM 5272 Telecomm Lab Dr. Mostafa Dahshan OU-Tulsa 4W 2nd floor 660-3713 mdahshan@ou.edu M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 1 Acknowledgements Some notes and figures in this presentation are imported from Notes by Dr. Anindya Das Textbook supplemental material CCNA Intro Exam Certification Guide M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 2 M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 3 Ethernet/802.3 Most common LAN architecture Used to transport data between devices connected to the same delivery medium Uses a data frame broadcast method Frame is sent to the entire bus, intended destination processes the frame, while all other devices discard it M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 4 Ethernet 802.3 (2) Negative effects of a shared LAN broadcast delivery of all frames CSMA/CD: collisions are inherent distance limitation requires using repeaters to extend M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 5 Repeaters Connect two or more cable segments Retransmit incoming signal to all other segments Cable segment is run within IEEE specifications Ethernet segment in star-bus network Repeater hub is a multiport repeater M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 6 Repeaters (2) Filter out signal disturbance caused by EMI and RFI Amplify and reshape incoming signal Retime the signal (in Ethernet applications) Reproduce the signal on all cable runs M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 7 Repeaters (3) Benefits of Using a Repeater a layer 1 device that cleans up and boosts the signal extends the coverage area of a LAN segment Negative Effects of Using a Repeater increases the collision domain size increases the broadcast domain size can’t filter traffic based on Layer 2 or 3 addressing M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 8 Half-Duplex Ethernet Only one host can transmit at a time because the NIC needs to listen for collisions The NIC provides several circuits. Most important are: receive (RX), transmit (TX), and collision detection bandwidth usage = 50% to 60% M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 9 Collision Domains Group of Ethernet devices connected by repeaters (or repeater hubs) Only one device can transmit at a time Simultaneous transmissions result in a collision M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 10 Full-Duplex Ethernet Transmission and the reception at the same time Requires using two pairs of wires in the cable and a switched connection between each node Connection is considered point-topoint and is collision free M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 11 Full-Duplex Ethernet (2) Because both nodes can transmit and receive at the same time, there are no negotiations for bandwidth 100% of bandwidth is available: 10 Mbps increases to 20 Mbps of potential throughput 10 Mbps TX & 10 Mbps RX M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 12 Ethernet Connections Computer NIC Pins 1,2 Transmit Data Pins 3,6 Receive Data Hub/Switch/Router Pins 1,2 Receive Data Pins 3,6 Transmit Data M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 13 Ethernet Connections (2) Computer to Switch Use straight-through cable Switch to Switch/Router Use crossover cable Computer to Computer Use crossover cable M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 14 LAN Segmentation By segmenting a LAN fewer devices are sharing the same bandwidth Improved performance of a shared media LAN Each segment is considered its own collision domain M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 15 Bridges Network devices connecting LAN segments Extend LAN when maximum connection limit reached Example: the 30-node limit on an Ethernet bus Extend a LAN beyond the length limit Example: beyond 185 meters for thinnet segment Segment LANs to reduce data traffic bottlenecks Prevent unauthorized access to a LAN M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 16 Segmenting with Bridges Bridges “learn” a network’s segmentation by building address tables that contain: Bridge interface that will reach that device Each device’s MAC address M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 17 Bridge Operation Three frame scenarios Destination on same segment as source Bridge drops frame, since no forwarding needed Destination on another segment known to bridge Bridge transmits frame to the known segment only Destination segment not known to bridge Bridge transmits frame to all segments but source M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 18 Broadcast Domains Group of devices that can receive layer2 broadcasts Ethernet address FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Devices can communicate to each other without going through a router M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 19 Segmenting with Switches A switch is simply a multi-port bridge, making forwarding decisions based on MAC addresses Like a bridge, segmenting a LAN with a switch creates more collision domains Replacing hubs with switches therefore decreases congestion and increases available bandwidth M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 20 Segmenting with Switches (2) A switch can microsegment a LAN creating collision-free domains but still be in the same broadcast domain. Switch creates a virtual circuits, allowing many users to communicate in parallel M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 21 Switches VS Bridges Switches operate at higher speeds Switches are capable of creating virtual LANs (VLANs) through microsegmentation Bridges switch use software; switches typically switch using hardware (called the “switch fabric”) Bridges use store-and-forward, Switches can use cut-through switching which switches the packet as soon as the destination MAC is read M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 22 Spanning Tree Protocol Defined by the IEEE 802.1d standard Bridges frames in networks with more than two bridges Sets up a system of checks performed by bridges Two motivations for using spanning tree algorithm Ensure a frame does not enter infinite loop Causes congestion that may intensify to broadcast storm Forward frames along the most efficient route Efficiency based on distance and utilization of resources M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 23 Spanning Tree Protocol (2) Create one-way path around network (use bridge data) Establish maximum number of hops for maximum route Enable bridges to send frames along best route M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 24 Spanning Tree Protocol (3) Example: Why STP? Larry sends a frame to Bob Bob is powered off Bob’s address unknown Frames forwarded by each switch to all ports The frames will loop forever! Archie Bob Larry M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 25 Virtual LANs Logical grouping of network devices Similar to splitting a switch into separate logical switches Each VLAN forms a separate broadcast domain Devices in different VLANs cannot communicate without a router or a layer 3 protocol (e.g. IP) M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 26 Virtual LANs (2) VLAN 1 VLAN2 M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 27 Trunking A VLAN spanning multiple switches Devices in a VLAN can be connected to different switches M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 28 Trunking (2) VLAN1 VLAN1 Trunk VLAN2 VLAN2 M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 29 Ethernet Addressing MAC Address: 6 bytes (48 bits) First 3 bytes Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) Each mfc has its own OUI Address Types Unicast: single device Multicast: Multiple devices 0100.5Exx.xxx Broadcast: All Devices FFF.FFF.FFF M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 30 Address Resolution Protocol Used to translate IP addr to MAC addr Used between devices on the same broadcast domain Each device maintains a cached table of IP to MAC address mappings M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 31 Address Resolution Protocol (2) ARP works as follows The inquiring device sends a broadcast message (addr: FFF.FFF.FFF) The destination device responds with its MAC address to the inquiring device M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 32 M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 33 Exp 1: Common Network Utils ping traceroute (Windows: tracert) nslookup netstat route (more details next class) arp telnet M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 34 Exp 2: Access Switch Console Use the Cisco Catalyst 1900 switch Connect a serial cable to the switch console port Use PC with terminal software to access the console To use the command line interface, type K Type ? To see available commands M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 35 Exp 3: Ethereal Packet Sniffer Use Ethereal to capture and analyze packets in the following scenarios Access a website with and input form (e.g. www.google.com) Capture packets from your own PC and other PCs in the same LAN When PCs are connected by a hub When PCS are connected by a switch M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 36 Exp 4: ntop Traffic Monitor Start ntop on a PC Connected with a hub Connected with a switch Generate some network traffic View ntop reports and record your observations M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 37 Exp 5: RouterSim Use the CCNA Network Visualizer 5.0 to familiarize yourself with the Cisco Catalyst 1900 switch M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 38 M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 39 Homework 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Write (in your own words) a summary about each of the utilities used in Experiment 1 Use ping to measure Round Trip Time (RTT) for 10 messages of size 64, 256, and 4096 bytes. Graph the message size versus RTT for two hosts on a LAN (two workstations in the lab) and two nodes on a WAN (for instance, your lab workstation and a host outside the OU campus). Discuss the effects of distance, message size, and their relationship with bandwidth and latency. Use the traceroute utility on your lab workstation to find the route to a. b. c. a host in another city in Oklahoma a host on the east or west coast of the United States a host in Canada or Mexico Next, using the traceroute utilities at the site www.traceroute.org, find the routes between two hosts on different continents. Trace the route again between these two hosts after at least an hour. Analyze your recorded results. Briefly discuss why ping would not necessarily provide an accurate estimate of the round trip time for packets exchanged by two hosts on the Internet? Use the Ethereal software to capture one traffic session generated while using the ping and tracert commands. Report your results. M. Dahshan - TCOM5272 40