* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
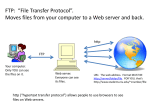
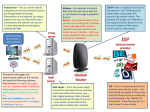
Getting Connected CECS 5030 with Cathie Norris, Jennifer Smolka & Gerald Knezek The Internet Today Worldwide network of networks Government agencies, educational institutions, hospitals, and commercial organizations The Internet Today Phenomenal growth - 1 million/month End of 2001 – 500 million users Largest connection of networks in the world How the Internet Works Local connection via modem, leased-line, ISDN, etc. Router at provider’s point-of-presence How the Internet Works Small providers buy from big providers NorthwestNet NorthwestNexus Big providers interconnect with each other MCI MCI AT&T Sprint AT&T NWNET NWNEXUS The Internet uses TCP/IP Share common protocol TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol “/” means it operates at two levels TCP IP The Internet uses TCP/IP Created more than thirty years ago by the Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) TCP/IP is the still the basis for the Internet The Internet uses TCP/IP IP Address – unique identifier IP resides in the Network Layer TCP resides in the Transport Layer TCP/IP Network Protocols Internet Protocol (IP) • Every computer on the Internet has a unique number which is the destination point • Where you are and how I get there Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) • How is my data getting between you and me TCP/IP Application Protocols Terminal Emulation (Telnet) HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Domain Name Service (DNS) TCP/IP in the OSI Model Seven Layer Open System Interconnect Model Application Presentation Session Transport Network Logical Link Physical FTP, Telnet SNMP TFTP NFS TCP UDP ARP IP LLC Ethernet, WAN, Token Ring, FDDI TCP/IP in the OSI Model Application Presentation Session Transport Network Logical Link Physical FTP, Telnet SNMP TFTP NFS TCP UDP ARP IP LLC Ethernet, WAN, Token Ring, FDDI Internet Protocol (IP) IP is a connectionless service that provides basic datagram delivery services. IP takes care of addressing, or making sure the routers know what to do with your data when it arrives. Internet Protocol (IP) Not everything is sent over the Internet is not sent as a BATCH – or complete file Sent over as packet of smaller pieces 256 characters or 512 characters (maybe longer) Internet Protocol Every computer on the Internet has a unique address. Information sent across IP networks is broken up into bite-sized pieces, called packets. The information within a packet is usually between 1 and about 1500 characters long. IP Envelopes DATA From: 192.112.36.5 To: 128.174.5.6 IP Packet Internet Protocol Some addressing information goes at the beginning of your message; this information gives your network enough information to deliver the packet of data. Internet addresses consist of four numbers each less than 256. 192.112.36.5 128.174.5.6 Internet Protocol IP Addresses Class A Networks: 128.x.x.x Class B Networks: 146.79.x.x Class C Networks: 192.100.10.x IP addresses are running out - Extensions to the current IP address protocol will be required - IPng Transmission Control Protocol Reliable TCP takes the information you want to transmit and breaks it into pieces. TCP numbers each piece so receipt can be verified and the data can be put back in the proper order. Acknowledgments TCP Packet Encapsulation DATA Bytes 1 to 500 To: 128.174.5.6 TCP Packet From: 192.112.36.5 To: 128.174.5.6 IP Packet SLIP and PPP Extensions of IP over voice-grade modem lines: Serial Internet Protocol (SLIP) Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Allow internet access from the PC in your home by dialing up over modems to an Internet host. TCP/IP Applications/Services Terminal Emulation (Telnet) File Transfer Protocol (FTP) HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Domain Name Service (DNS) Terminal Emulation (Telnet) Telnet is the login and terminal emulation program for TCP/IP environments Primary function is to allow users to log into remote host systems Requires username and password How to Telnet Open your DOS prompt Type telnet Your telnet window opens... Uses for Telnet Today Use of Telnet has diminished in recent years Still being used to: Connect to routers Remote management of servers Access to home system while traveling File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Important for building web pages Primary mode of moving complete file from one computer to another FTP is a program for transferring files in TCP/IP environments (ASCII or Binary) File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Client – when you want information Server – when you have the information Typically, a user at a client computer downloads files from a remote server FTP Terms: DOS GET (MGET): You are downloading a file (or files) from another computer to your desktop PUT (MPUT): You are uploading a file (or files) from your desktop to another computer File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Must logon to server Requires username and password to access normal file system Anonymous FTP allows access to anyone to a special file system (e.g. ftp.microsoft.com) FTP Terms: DOS CD: Change Directory Move up or down the directory structure MD: Make Directory New storage space FTP Transparent Often FTP commands are transparent through your browser or through a FTP program like WS FTP. HyperText Transfer Protocol Primary application protocol that underlies the world wide web Provides user access to the files that make up the web Anywhere – anyplace – anytime HyperText Transfer Protocol Defines HOW they get there, not what they look like Files can be in many different formats (text, graphics, audio, video, etc.) Hypertext markup language (HTML) is the standardized language for creating web pages Simple Mail Transfer Protocol SMTP is the electronic mail transfer protocol used in TCP/IP environments Provides a store-and-forward mail capability between host computer mail systems on the network MIME (Multimedia Internet Mail Exchange) has become the standard for document attachments Domain Name Service DNS is a TCP/IP service that maps network address numbers, for example, 123.456.789, to an easy to remember name, such as: www.microsoft.com Internet and TCP/IP applications such as telnet, FTP and SMTP access DNS to locate names you’ve specified and resolves them to a numeric address and inserts it into a message for transport. Domain Name Service The address information is stored at many locations in a hierarchical structure, not at one central depository Each site has a domain server that maintains information about the local nodes Node Node Central Hub Node Node Client/Server Architectures Two-tier “Fat” Client: User Interface + Application Database Server Example: File servers, SQL Servers Client/Server Architectures Three-tier “Thin” Client: User Interface only Application Server Database Server Examples: Mail servers, Business applications Client/Server Architectures Application Programming Interfaces SQL, ODBC APPC TP Monitors RPC Interface Definition Languages DCE CORBA Microsoft OLE References From Networking 101 Jim Cabral, Puget Technology Group, Inc. & Tammy Ruth, Children’s Hospital and Medical Center www.pugettech.com cabralje@pugettech.com truth@chmc.org