* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Foundation Knowledge and Skills
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Specialty drugs in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
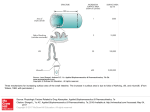
Chapter 11: Basic Biopharmaceutics, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics Learning Outcomes Define biopharmaceutics Describe 4 processes of pharmacokinetics Describe factors that affect medication absorption Describe process & factors of distribution phase Describe 2 most common types of drug interactions Define pharmacodynamics Describe process & factors of elimination phase Learning Outcomes Describe steps for medication to exert effect Describe potential problems that can occur when product formulation is disrupted absorption, distribution, metabolism, or elimination is altered how these alterations can affect pharmacodynamics of medication Key Terms Absorption First-pass metabolism Bioavailability Half-life Biopharmaceutics Loading dose Clearance Metabolism Cytochrome P450 Metabolite Dissolution Pharmacodynamics Drug interaction Pharmacokinetics Elimination Therapeutic level Excretion Volume of distribution Biopharmaceutics Study of manufacture of medications Common formulations Choice of routes Precursor steps of absorption Disintegration Dissolution Pharmacokinetics ADME Absorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination Absorption Amount of medication that enters bloodstream only absorbed medication has pharmacologic effect bioavailability is percentage of dose that reaches bloodstream Factors amount of drug dissolved dosage form route of administration First-pass Metabolism Following oral ingestion med metabolized before reaching main bloodstream through either intestine wall or liver result-lower percentage reaches main systemic circulation Routes of Administration Rectal, inhalation, sublingual avoid first-pass metabolism Medications given intravenously 100% bioavailability Distribution Phase Follows absorption Medication may leave bloodstream & enter tissues remain in the blood, bound to protein Medication bound to blood proteins (albumin) is inactive does not exert any pharmacologic effect reversible-drug may be released from protein & distributed into tissues Therapeutic Level Desired effect with minimal side effects Concentration of drug in blood measured to help guide appropriate therapy determines whether a change in therapy is needed Examples of medications whose levels are measured phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproic acid, phenobarbital digoxin gentamicin, tobramycin, vancomycin Volume of Distribution Extent drug distributes to various body tissues/spaces Medications with large volume of distribution have lower blood concentration Medications with small volume of distribution have a higher blood concentration Factors that affect extent of distribution highly protein bound high affinity to body fat Loading dose is used when medications have large volume of distribution Metabolism Breakdown of drugs (not all drugs susceptible) drug molecule is changed or altered metabolite Drugs may travel directly to kidneys excreted Liver is major organ in which drug metabolism occurs Small intestine-significant metabolism occurs Other organs-limited metabolism kidneys lungs Enzyzmes Protein substances (enzymes) metabolize drugs Cytochrome P450 (CYP) family of enzymes Drug metabolites Metabolites may or may not be pharmacologically active be used as active form of pro-drugs be toxic Excretion Removal of drug or metabolite from body fluid Kidneys filtering process –drug eliminated into urine without being metabolized metabolites - water soluble-susceptible to excretion by kidneys Bloodstream liver cellbile ductsmall intestine Drug clearance=elimination rate Half-life (T1/2,) is time for 50% of drug to be eliminated Drug Interactions Impact of drug/food product on amount or activity of another drug Altered drug metabolism in liver Inhibition of enzyme activity Induction of enzyme activity Common drug-food interaction grapefruit juice (CYP enzyme inhibitor) injested with nifedipine (metabolized by CYP) results in hypotensive episodes Variables in Pharmacokinetics Speed of gastrointestinal tract constipation or diarrhea Diseases of kidney and liver cirrhosis Reduced elimination prolonged half-life Changes in cardiac output changes in delivery of drugs via bloodstream low cardiac outputdecreased blood flow to kidneys & liver decreased clearance of medications Kidney Disease Renal failure hemodialysis kidney transplant Causes of kidney damage blood pressure high blood cholesterol diabetes Detection: blood levels of creatinine Doses adjusted based on degree of renal impairment Liver Disease Cirrhosis decreased ability to metabolize certain medications Detected by measuring aspartate aminotransferase (AST) alanine aminotransferase (ALT) bilirubin albumin Reduced elimination & clearance of some drugs Albumin reduced reduced protein binding Advanced Age Medications must be used cautiously in elderly Reduced kidney function Estimate patient’s creatinine clearance dose reduction may be needed for some drugs avoid drug accumulation & toxicity Reduced liver function watch for toxicity Topical medications less drug is absorbed Pregnancy Increased blood volume? … hypothesized Drugs may be cleared through kidneys more quickly May need higher doses of some medications Some over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are unsafe avoid aspirin in last 3 months of pregnancy safety of herbal, botanical, & dietary supplements? Pediatrics Medications are often dosed based on body weight accurate weight important Higher relative volume of distribution for some drugs Refer to pediatric references/manufacturer’s guidelines Pharmacist evaluates drug doses adjusted based on weight & other factors Pharmacodynamics What drug does to body Pharmacodynamic responses increase in bone mass with bisphosphonates decrease in BP with antihypertensive agents Pharmacologic effect sequence of events absorption distribution bind to targeted receptor causing cascade of events that leads to drug’s response