* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
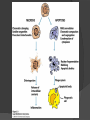
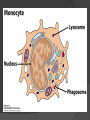
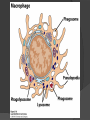
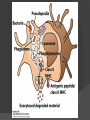
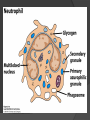
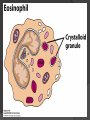
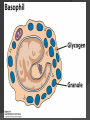
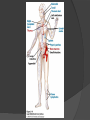
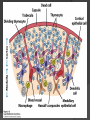
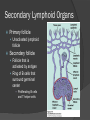
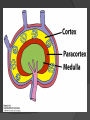
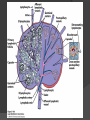
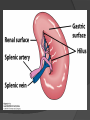
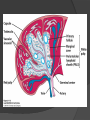
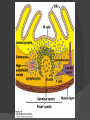
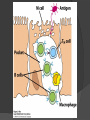
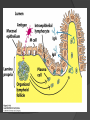
Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of the Immune System Dr. Capers Kindt • Goldsby • Osborne Kuby IMMUNOLOGY Sixth Edition Chapter 2: Cells and Organs of the Immune System Copyright © 2007 by W. H. Freeman and Company Hematopoiesis All blood cells arise from Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSC) Study of these cells is difficult ○ Scarce ○ Difficult to grow in vitro Hematopoiesis Early in hematopoiesis, stem cell differentiates to either ○ Lymphoid progenitor cell ○ Myeloid progenitor cell - Progenitor cells have lost ability for self renewal and are committed to particular cell lineage Organized hierarchy Most of proliferation takes place in differentiated precursors (that are NOT self-renewing) rather than hematopoietic stem cell Lowers chance of cancer Hematopoiesis Regulated at gene level ○ Transcription factors play important roles in hematopoiesis ○ Studies using “knockout” mice - Gene inactivated, if RBC or a particular WBC fails to develop, it is concluded that protein was involved in development of that cell Hematopoietic Homeostasis Erythrocyte ○ Average life span: 120 days ○ Phagocytosed by macrophages in spleen WBC - LEUKOCYTES ○ Life spans from 1 day to 20-30 years Apoptosis – programmed cell death Normal WBC WBC going through apoptosis Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes ○ 20-40% of WBC ○ 3 populations - B cells - T cells - Natural Killer Cells Lymphocytes B cells and T cells Adaptive immunity Small lymphocytes Those that have not interacted with antigen are called naïve Interaction with antigen – proliferation into effector cells (i.e. plasma cells) and memory cells Lymphocytes B and T cells Lymphocytes B Lymphocytes (B cells) Site of maturation ○ Bursa of fabriscus in birds ○ Bone marrow in mammals Display membrane-bound immunoglobulin (antibody) Once antigen is encountered: Differentiation - Plasma cells – antibody can be secreted, die within 12 weeks - Memory B cells – same membrane-bound antibody as parent B cell, longer life span Lymphocytes T Lymphocytes (T cells) Site of maturation ○ Thymus T cell receptor ○ Only recognize antigen that is bound to cell membrane proteins called major histocompatibility complex (MHC) ○ Once antigen in encountered with MHC: Differentiation - Effector T cells - Memory T cells 2 subpopulations T helper (TH) T cytotoxic (TC) And now T regulatory (Treg) Lymphocytes T helper cells ○ CD4 glycoprotein ○ “help” activation of B cells, TC cells, macrophages in immune response Lymphocytes T cytotoxic cells CD8 glycoprotein Recognition of MHC-antigen complex initiates differentiation into effector cell called cytotoxic T lymphocyte Eliminates infected cells or cancerous cells Lymphocytes T regulatory cells CD4 and CD25 glycoproteins Help suppress the immune system Lymphocytes Natural Killer Cells Innate immune response Large, granular Recognize tumor or virus-infected cells CD16 – which can recognize a region of antibody that has attached to cell infected by virus Other Leukocytes Mononuclear phagocytes Monocytes circulate in blood and then migrate into tissue and differentiate into specific macrophage Macrophages Intestinal macrophages in gut Alveolar macrophages in lung Histiocytes in connective tissue Kupffer cells in the liver Mesangial cells in the kidney Microglial cells in the brain Osteoclasts in bone Activated macrophages are more effective than resting ones Other Leukocytes Mononuclear phagocytes ○ Complex antigens are phagocytized, the resulting phagosome fuses with a lysosome ○ The digested antigen is then eliminated through exocytosis - Some of it is presented on membrane on MHC ○ Phagocytosis is enhanced when antibody is attached to the antigen - Antibody acts as opsonin: molecule that binds to both antigen and phagocyte Macrophage and bacteria Other Leukocytes Granulocytes ○ Neutrophils ○ Eosinophils ○ Basophils Other Leukocytes Granulocytes – Neutrophils Multi-lobed nucleus, light granules 1st to arrive at site of inflammation High #’s is 1st indication of infection Phagocytize Generate antimicrobial agents Other Leukocytes Granulocytes – Eosinophils Phagocytize Play a role in parasitic organisms Other Leukocytes Granulocytes – Basophils Nonphagocytic Play a role in allergic reactions Other Leukocytes Mast cells Play important role in development of allergies Other Leukocytes Dendritic cells Long membranous extensions, look like dendrites on nerve cells Antigen presentation 4 major groups: Langerhans DC Interstitial DC Monocyte-derived DC Plasmacytoid-derived DC Follicular dendritic cells Involved with B cell maturation Organs of the Immune System Primary ○ Thymus and bone marrow ○ Place of maturation of lymphocytes Secondary ○ Lymph nodes, spleen, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues such as gut-associated lymphoid tissues ○ Mature lymphocytes interact with antigen Primary Lymphoid Organs Bone marrow Lymphocytes arise there, T cells go to thymus to mature B cells mature here 90% of plasma IgG and IgA comes from B cells in the bone marrow Primary Lymphoid Organs Thymus ○ T cell development and maturation ○ Bilobed organ above heart - Surrounded by capsule and divided into lobules - Outer part of lobule is cortex, inner is medulla - Network of epithelial cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages ○ Thymus will induce death of those T cells that can’t: - Recognize self-MHC molecules - Those that interact with MHC molecules too strongly (could produce autoimmune disorder) ○ Function decreases with age Lymphatic System Interstitial fluid (the portion that doesn’t enter venous system) is returned to circulatory system by lymphatic vessels Largest lymphatic vessel – thoracic duct ○ Enters left subclavian vein ○ Lymph from right arm and right side of head enters through right lymphatic duct, drains into right subclavian Antigen is carried by lymph to lymph nodes Secondary Lymphoid Organs Primary follicle Unactivated lymphoid follicle Secondary follicle Follicle that is activated by antigen Ring of B cells that surround germinal center Proliferating B cells and T helper cells Secondary Lymphoid Organs Lymph Nodes Encapsulated 3 regions: ○ Cortex B cells, macrophages, dendritic cells Primary follicles ○ Paracortex T cells, dendritic cells ○ Medulla Plasma cells secreting antibody Secondary Lymphoid Organs Spleen Filters blood, traps blood-bourne antigens ○ Important in systemic infections Blood enters through splenic artery Encapsulated Structure: ○ Projections from capsule form trabeculae ○ Compartments: Red pulp - Macrophages, red blood cells White pulp - Surrounds branches of splenic artery - Forms PALS (periarteriolar lymphoid sheath) - Primary follicles rich in B cells Secondary Lymphoid Organs Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue MALT Organized areas along digestive, respiratory, and urogenital tracts Very well organized areas in intestine are referred to as Peyer’s patches Includes tonsils and appendix