* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genes and Behaviour
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Broken windows theory wikipedia , lookup
Anti-social behaviour order wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Mentalism (discrimination) wikipedia , lookup
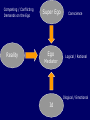
Explaining Mental Disorder The study of mental disorder involves: Definition: What do we mean by mental disorder? Classification: How do we distinguish between different mental disorders? Explanation: How do we understand mental disorder? Treatment: How do we treat mental disorder? Different Approaches to Explaining Mental Disorder No completely dominant approach. Different Approaches to Explaining Mental Disorder All of the approaches we will explore assume that the proximal cause of behaviour and experience is biological. The approaches emphasize different distal causes. Different Approaches to Explaining Mental Disorder Most psychologists today do not propose linear, one dimensional causal explanations Approaches to Explaining Mental Disorder Biological / Neuroscience Perspective Psychodynamic Perspective Cognitive Perspective Behavioural Perspective Sociocultural Perspective Humanistic / Existential Perspective Interpersonal Perspective Biological / Neuroscience Perspective the functioning of the brain and other biological systems Behaviour Genetics Behaviour Genetics studies the extent to which mental disorder is caused by genetics. The “nature-nurture” debate explores the role of genes vs. the environment. Behaviour Genetics Three different methods are used: family studies twin studies adoption studies Family Studies Examine family members of an individual with a mental disorder to see what percentage of relatives also have the disorder. Twin Studies Monozygotic twins (MZ) share exactly the same genotype. Dizygotic twins (DZ), have 50% of their genes in common. Adoption Studies Attempt to remove environmental influence that DZ and MZ twins share by studying twins that have been separated at birth. Adoption Studies Adoptions studies still do not control for all environmental factors because: People with the same genes seek out and elicit the same kinds of environments. Outgoing vs. Shy Energetic vs. Passive Genes and Behaviour Summary It is most helpful to think of how genes and environment interact to produce disorders. Interactions, or “that depends” What is the influence of X? that depends on Y. The Diathesis-Stress Model Individuals inherit tendencies to express certain traits or behaviours, which are then expressed or activated under conditions of stress. The reciprocal Gene-Environment Model Genes may actually increase the probability that an individual will experience a stressful event. Evaluating the Biological Approach Effective treatment does not mean we understand causation Side effects of biological treatments Correlation does not mean causation the disorder could cause the biological correlate a third factor might cause both the disorder and the biological correlate The Psychodynamic Explanation of mental disorder Psychodynamic Model mental mechanisms emphasis on childhood experiences emphasis on unconscious motives Freud and the “Classical” Psychodynamic model Unconscious: most mental activity takes place outside of awareness the unconscious contains passively and actively forgotten information The Structure of the Mind according to Freud Id basic primitive biological drives or instincts Ego develops to help the Id find adaptive ways to fulfill it’s desires and cope with reality Superego internalized moral standards of parents does not consider what is realistic only what is abstractly ideal Competing / Conflicting Demands on the Ego Reality Super Ego Ego Mediator Conscience Logical / Rational Illogical / Emotional Id The Ego’s Defense Mechanisms Ego defense mechanisms involve distorting or denying internal and external reality. Repression Repression is the basis of all defense mechanisms. Impulses that are unacceptable to the ego are pushed into the unconscious Sublimation Sublimation is the most adaptive defense mechanism Sublimation is the transformation of Id impulses into more socially acceptable forms. Anxiety Anxiety is a signal that the ego’s controls are at risk of being overcome by the id or the superego. The Psychodynamic Explanation of mental disorder Disorder occurs when the ego is not able to adequately balance the Id, Superego and reality. The Psychodynamic Explanation of mental disorder Poor ego defense leads to anxiety Rigid ego defense leads to constricted behaviour and impoverished relationships. Ego collapse leads to a flooding of id impulses. Evaluating the Psychodynamic Approach First well developed approach to mental disorders that did not consider mental disorder as a biological or a moral, religious problem. Difficult to subject many of the ideas to empirical testing. Gender and cultural bias in original Freudian ideas The Cognitive Explanation of mental disorder “Men are disturbed not by things but by the views they take of them” Epictetus Cognitive Appraisal Stimulus--->Appraisal---> Response evaluation of stimulus based on memories, beliefs, and expectations Cognitive Appraisal Appraisals are determined by: Competencies (acquired skills) Perception/Understanding Expectancies Values Plans and Goals Cognitive Appraisal Attribution is an example of an appraisal belief about the cause of an event global/specific stable/unstable internal/external Information Processing Selective Attention what information we take in from the environment (Schizophrenia, depression, anxiety) Schema how we organize and understand the information we take in (self schemas) Evaluating the Cognitive Approach Does it explain causes or describe symptoms? (Why do people have maladaptive beliefs?) If an individual could change their thoughts then they would not have a problem. Changing beliefs or views about the world may not be the best solution in some situations. Behavioural Approach mental disorder is the result of “learning” or environmental experience The Background of Behaviourism Learning Pavlov the process whereby behaviour changes in response to the environment The conditioned Reflex Watson study only what can be observed “Little Albert” The Background of Behaviourism Thorndike The Law of Effect Skinner Radical Behaviorism predict and influence behaviour by focusing on environmental contingencies Respondent (Classical) Conditioning UCS -----> UCR the unconditioned or unlearned stimulus causes an unconditioned or unlearned response UCS -----> UCR CS -----> CR after conditioning the conditioned stimulus causes a conditioned response Operant Conditioning The organism does something or “operates” on the environment. The likelihood of a response is altered by its consequences. Punishment and Reinforcement Reinforcement any consequence of a behaviour that increases the probability of the behaviour occurring again Punishment any consequence of a behaviour that decreases the probability of the behaviour occurring again Learning Mechanisms Extinction Generalization Discrimination Shaping Behavioural Explanation of Mental Disorder Abnormal behaviour, or mental disorders are the result of various environmental experiences (learning or conditioning) eg Dog Phobia respondent conditioning negative reinforcement eg Depression extinction Behavioural Explanation of Mental Disorder Less inclined to use Diagnostic Labels symptoms have different functional roles in different people Less focused on the past, more focused on present environmental factors Sociocultural Approach mental disorder is the result of social and political factors Sociocultural Approaches Mental disorder is a social label or a social construction. Social Construction Social Concept the boundary between what is and is not a mental disorder is not “natural” but “cultural” (think back to mental disorder defined as a norm violation) Social Construction Social Role the “cause” of a mental disorder is the fact that an individual is fulfilling or carrying out a social role this role has a function for the individual, and/or society as a whole Three umpires are sitting around over a beer, and one says, “There’s balls and there’s strikes, and I call ‘em the way they are.” Another says, “There’s balls and there’s strikes, and I call ‘em the way I see ‘em.” The third says, “There’s balls and there’s strikes, and they ain’t nothin’ until I call ‘em.” Anderson, 1990 p. 75 Humanistic / Existential Approach Natural vs. Human Science Importance of ‘Understanding’ and entering into subjective world of client Emphasis on uniqueness of each person rather than general patterns Agency Contrast with determinism Authenticity, Freedom, and Responsibility Humanistic Approach ‘Acorn’ Theory Potential and Uniqueness Fulfill possibilities Self actualization