* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ed Founds Week 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
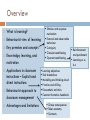
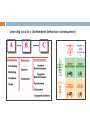
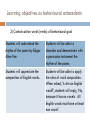
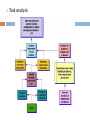
BEHAVIOURIST APPROACHES TO LEARNING AND TEACHING Education Foundations, Sec., Week 5, Semester 1, 2012 Overview Stimulus and response mechanism External and observable behaviour Contiguity Classical conditioning Operant conditioning What is learning? Behaviourist view of learning Key premises and concepts Knowledge, learning, and motivation Applications in classroom Learning objectives Task breakdown instructions – Explicit and Modelling and thinking aloud direct instructions Practice and drilling Kinaesthetic activities Behaviourist approach to Constant formative feedback classroom management Group consequences Advantages and limitations Token economy Contracts Reinforcement and punishment Learning as ab-c What is learning? The parrot’s learning to count/ greet Learning to smoke Learning the lyrics of the Sesame Street song Learning to ride a bike Learning English, maths, history, … Learning the times tables / a formula / an algorithm Learning about thinking, learning, and self Learnt helplessness … Permanent change rather than temporary Assimilation or adaptation Due to experience rather than natural maturation Definitions of learning and underlying epistemologies Behavioural, psychological, or psychical? Conscious and rational, subconscious, or holistic? Behaviourist view of learning Change in behaviour Subject to active control and shaping by external factors Outcome-orientation Key premises and concepts Psychology as the science of stimulus and response “Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select— doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief and, yes, even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talents, penchants, tendencies, abilities, vocations, and race of his ancestors” (Watson,1930, p.82). John B. Watson (1878-1958) Focuses on objectively observable and measurable actions and behaviour “The mentalistic problem can be avoided by going directly to the prior physical causes while bypassing intermediate feelings or states of mind. The quickest way to do this is to confine oneself to … only those facts which can be objectively observed in the behavior of one person in its relation to his prior environmental history. If all linkages are lawful, nothing is lost by neglecting a supposed nonphysical link” (Skinner, 1976, p.23). Burrhus F. Skinner (1904-1990) Contiguity principle Learning by association Formation of S-R relation Classical conditioning Pavlov’s dog experiment Involuntary (emotional or physiological) association / responses Unconditioned association: Neutral stimulus Unconditioned stimulus Unconditioned response Conditioned association: Conditioned stimulus Conditioned response Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936) What are the UCS, UCR, CS, and CR in this ad? Operant conditioning Behaviour as operants rather than respondents Thorndike’s cats Skinner’s pigeons Reinforcement Positive Negative Schedule Continuous Intermittent – fixed or unpredictable a) Interval b) ratio Punishment Learning as a-b-c (antecedent-behaviour-consequence) Knowledge, Learning, and Motivation Knowledge: a repertoire of behaviours or behavioural capacities Learning: formation of appropriate S-R association Motivation: schedules of positive and negative reinforcement Behaviourist principles of classroom instruction Explicit and direct instructions Clear communication of learning objectives (Kizlik, 2012; Linder-Crow, 2000) 1)objective Focus on student rather Good than theobjective teacher Bad statements statements To acquaint students with Students will be able to behaviourist learning identify 3 behaviourist theories learning principles To familiarise students with Students will be able to neo-behavourist learning describe neo-behaviourist theories learning theories Learning objectives as behavioural antecedents 2) Contain action words (verbs) of behavioural goal Students will understand the rhythm of the poem by Edgar Allen Poe. Students will be able to describe and demonstrate with a percussion instrument the rhythm of the poem. Students will appreciate the composition of English words. Students will be able to apply the rules of word composition. When asked, ‘Is cttn an English word?’, students will reply, ‘No, because it has no vowels. All English words must have at least one vowel.’ Task breakdown Task analysis Task analysis Behaviour modelling Skinner’s pigeons video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=erhmslcHvaw&feature=re lated Thinking aloud and justify thinking rationale Explicit teaching video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6h4q-bok644 Practice and drilling (first 1.5 minutes) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3cwODCQ9BnU&feature =related Using kinaesthetic movements to help retention http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yStzJjLXdxM Using paper folding to do multiplication by fractions Monitoring and constant formative feedback Formative feedback video (2 minutes) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zY0U7axgdHY&feature =related Behaviourist approach to classroom management Group consequences Token economy programs Rewards or punishments given to a class /group as a whole for adhering to or violating rules of conduct Good behaviour game Tokens earned for academic work and positive classroom behaviour can be exchanged for desired reward. Contracts Agreement between teacher and student specifying behaviour and its reward or punishment Advantages of behaviourist instructions Effective strategies for teaching action sequences that need to be automated Widely applied in teaching young students and students with LD Effects in eliminating SES-related differences of school achievement Limitations Dependence on extrinsic forms of reinforcement Neglect of complex thinking processes leading to behavioural performance References Kizlik, B. (2012) How to write learning objectives that meet demanding behavioural criteria, www.adprima.com/objectives.htm Linder-Crow, J. (2000) Writing behavioural leaning objectives and assessment, http://www.apa.org/ed/sponsor/about/faq/objectives.pdf Skinner, B. F. (1976) About Behaviorism, Vintage Books, New York. Watson, J. B. (1930) Behaviorism, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.