* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PP Presentation Chapter 12
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
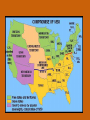
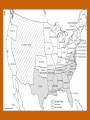
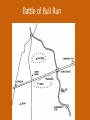
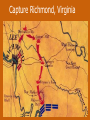
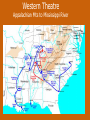
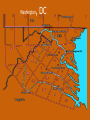
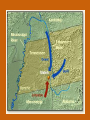
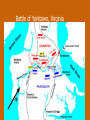
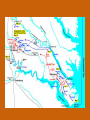
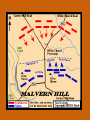
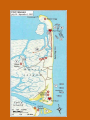
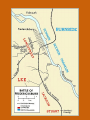
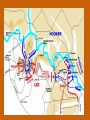
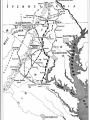
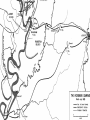
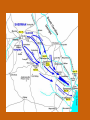
Chapter 12 – Section 1 The Union Dissolves CRITTENDEN COMPROMISE John Crittenden U.S. Senator – Kentucky (favor slavery) Compromise extended the Missouri Compromise line westward John Crittendon CRITTENDEN COMPROMISE REJECTED President Lincoln rejected the plan because it extended slavery into the west. Fort Sumter Charleston, South Carolina Even though the fort was located in the deep South the Union (North) controlled it Conflict between the South and North over the control of the fort South gained control over the fort after bombing it for 34 hours Fort Sumter Confederate States in 1861 Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas STRENGTH OF THE NORTH Population is 22 million Industrialized (controlled 85% of the industry in the U.S.) Transportation – Railroad – North controlled (important for moving troops) Naval – U.S. Navy remained loyal to the North – built new ships for war STRENGTHS OF THE SOUTH Defensive War – only had to protect their territory in the south Military leadership – had the best generals 9 million people (3.5 million were slaves) COMPARING THE ARMIES NORTH SOUTH President Abraham Lincoln President Jefferson Davis Capital – Washington, Dc Capital – Richmond, Virginia 2.7 million soldiers 750,000 soldiers 3,500 Indians (knew the land) 5,500 Indians (knew the land) 180,000 Blacks No Blacks could fight (fearful of revolting) Washington, D.C. Richmond, Virginia Abraham Lincoln Union President Jefferson Davis President Lincoln’s order to attack the South General Irwin McDowell (North) Ordered to march to Richmond, Virginia Capture Richmond and end the conflict General Irvin McDowell MANASSAS JUNCTION (THE FIRST BATTLE OF BULL RUN) North attempted to march 100 miles west to capture Richmond, Virginia (South’s capital) South attempted to capture Washington, D.C. Confrontation at Bull Run (30 miles from D.C.) between both sides (35,000 soldiers from the North and 35,000 soldiers from the South fought) General “Stonewall” Jackson from the South stopped the North from advancing to Richmond – victory for the South Battle of Bull Run Battle of Bull Run Stonewall Jackson – Confederate General at Bull Run Joseph E. Johnston Confederate General at the Battle of Bull Run Robert E. Lee – Confederate General and advisor for Jefferson Davis – Confederate President George B. McClelland heads the Union forces after Bull Run Section 2 The North and the South Face Off 3 – PART STRATEGIES FOR THE NORTH Capture Richmond, Virginia Gain control of the Mississippi River Naval blockade of the South (Anaconda Plan) Capture Richmond, Virginia Control the Mississippi River Naval Blockade (Anaconda Plan) Blockade the Atlantic Coast North divided most of the action in the Civil War into 2 arenas Eastern Theatre Western Theatre EASTERN THEATER - EAST OF THE APPALACHIAN MOUNTIANS Western Theatre Appalachian Mts to Mississippi River Western Theatre STRATEGIES OF WAR - SOUTH Capture Washington, D.C. Winning foreign support from (G.B & France) South felt that G.B. & France needed their cotton. G.B. and France had a surplus of cotton. Washington , DC MILITARY EXPERIENCE FOR BOTH SIDES (North and South) Uniforms Illnesses – influenza, pneumonia, typhoid No anesthesia Temporary Hospital Bed Disease and Infections Influenza, Pneumonia, and Typhoid pain-killers used during surgery None Andersonville, Georiga - Prison Camp HOME FRONT - NORTH Women – replaced male workers in factories, on the farms, bankers, and morticians Aid Societies were established (volunteer group) Freeman’s Aid Commission – females taught former slaves Women in the Civil War HOME FRONT - SOUTH Parades and barbeques Raffles and auctions HOMEFRONT – NORTH – MEDICAL CARE “Nuns of the battlefield” – Ireland and Germany Elizabeth Blackwell – 1st female licensed doctor Clara Barton – founder of the Red Cross U.S. Sanitary Commission – Civilian Aid - medical OPPOSITION TO WAR South Conscription – farmers, working class “Rich man’s war and a poor man’s fight OPPOSITION TO WAR North Union draft New York riots Copperheads Suspension of civil liberties by Lincoln Section 3 Fighting the War BATTLE OF SHILOH Tennessee North victory (S) surprised (N) (N) has a counterattack Casualties (N) 13,000 (S) 10,000 North gained advantage in the control over the Mississippi River valley BATTLE OF NEW ORLEANS Louisiana North victory Union ships bomb (S) fort for 6 days (S) surrenders (S) losses: 50,000 square miles of territory, 1000 miles on the Mississippi River & city of New Orelans (S) losses 2 state capitals, Jackson MS and Baton Rouge, LA, city of New Orleans Morale of the South dropped BATTLE OF YORKTOWN Virginia South victory (N) General McClellan meets (S) President Lincoln tells to attack (N) McClellan refused because his troops are outnumber (S) held this area until the spring George B. McClelland - Union General Battle of Yorktown, Virginia BATTLE OF SEVEN PINES Virginia North victory After waiting it out in the Battle of Yorktown. (N) McClellan over ran the (S) (S) retreats towards their capital, Richmond, Virginia 2 sides battle at this site (S) General Robert E. Lee retreats Robert E. Lee – Confederate General and advisor for Jefferson Davis – Confederate President SEVEN DAYS’ BATTLE Virginia South victory (S) Generals Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson attack the (N). Battle last 7 days Robert E. Lee – Confederate General and advisor for Jefferson Davis – Confederate President Stonewall Jackson – Confederate General at Bull Run BATTLE OF ANTIETAM (Creek) Maryland North victory Bloodiest single day battle Casualties: (S) 13,000 (N) 12,000 (S) escaped back to the Virginia President Lincoln announces the Emancipation of Proclamation after this battle Emancipation Proclamation January 1, 1863 President Lincoln freed the slaves in the rebelling states How can he do this? BATTLE AT FORT WAGNER Charleston, South Carolina North victory (N) attacks at the fort (N) used 6000 troops 1st time the Union uses African Americans (N) suffered heavy losses but the (S) eventually evacuated the fort BATTLE OF FREDERICKSBURG Virginia South victory (S) General Robert E. Lee and his 75,000 troops controlled the hills overlooking the city of Fredericksburg Casualties: (N) 12,000 (S) 5,000 Battle of Chancellorsville Virginia South victory Battle in the forest (S) Generals Lee and Jackson attacked from 2 sides – several days of fighting (S) General “Stonewall” Jackson was shot in the arm and died 8 days later Section 4 The Final Phase BATTLE OF GETTYSBURG Pennsylvania Union victory President Lincoln makes the famous Gettysburg Address after the battle (reminded people of the democratic ideals) Gettysburg Address Address made by President Lincoln after the Battle of Gettysburg Address was made at the Gettysburg cemetery Mourned the loss of 23,000 Union soldiers and 28,000 Confederate soldiers Gettysburg Address Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth, upon this continent, a new nation, conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that "all men are created equal“ Etc. BATTLE AT VICKSBURG Mississippi North victory (N) gains control over the Mississippi River Cut off Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas If the (S) had not surrendered they would have starved to death UNION GENERAL GRANTS STRATEGY IN 1864 War of attrition – used (N) large number of soldiers and industrial resources to fight until the (S) runs out of men, supplies, and will General Ulysses Grant UNION GENERAL SHERMAN’S STRATEGY IN 1864 Total War – destroying the (S) economic resources and demoralizing them TERMS OF SURRENDER South surrenders at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia Officers keep their side arms All soldiers would be fed Soldiers keep their horses and mules Not tried for treason