A SON OF GOD Savitri Devi
... convince a minimum number of disciples capable of carrying on his work. His teaching "suitable for our own times," met little response in his. Those who could easily have gathered it from his lips and transmitted it to posterity in all its details, were not moved to do so. And we, who would have don ...
... convince a minimum number of disciples capable of carrying on his work. His teaching "suitable for our own times," met little response in his. Those who could easily have gathered it from his lips and transmitted it to posterity in all its details, were not moved to do so. And we, who would have don ...
Building The Great Pyramid At Giza: Investigating
... lift the blocks. Scholars believe that such “machines” were some type of crane. Another Greek historian, Diodorus of Sicily, wrote, three hundred years later, that the Egyptians used ramps to move the blocks (Brier 2007, 23). Whatever the model, one can assume that Hemienu chose the one that minimiz ...
... lift the blocks. Scholars believe that such “machines” were some type of crane. Another Greek historian, Diodorus of Sicily, wrote, three hundred years later, that the Egyptians used ramps to move the blocks (Brier 2007, 23). Whatever the model, one can assume that Hemienu chose the one that minimiz ...
Pharaoh Manual pdf
... its muddy banks all manner of vegetation grows, even some small farms that some in your city have planted. Your family has lived and died along the river for generations, eking out an existence from what the land has to offer. Yet, change is in the hot, arid air. A charismatic leader has arisen. His ...
... its muddy banks all manner of vegetation grows, even some small farms that some in your city have planted. Your family has lived and died along the river for generations, eking out an existence from what the land has to offer. Yet, change is in the hot, arid air. A charismatic leader has arisen. His ...
Science Of - students of thought
... Come Up With Are Illogical And They Are Simply Guessing, Which I, Nayya: Malachizodok York-El Will Prove To You Further In This Scroll. At The End Of This Scroll, You Will Have A Clearer Picture Of The Ta-Merra (Egyptians Also Called Khemet, Khamites, Hamites, Mizrymites And Many Other Names) And Th ...
... Come Up With Are Illogical And They Are Simply Guessing, Which I, Nayya: Malachizodok York-El Will Prove To You Further In This Scroll. At The End Of This Scroll, You Will Have A Clearer Picture Of The Ta-Merra (Egyptians Also Called Khemet, Khamites, Hamites, Mizrymites And Many Other Names) And Th ...
Boundless Study Slides
... • stelae Stone or wooden slabs, generally taller than they are wide, often erected for funerals commemorative purposes and decorated with images or text. • sunk relief A type of artwork in which an image is made by cutting the relief sculpture itself into a flat surface. • tenon A projecting member ...
... • stelae Stone or wooden slabs, generally taller than they are wide, often erected for funerals commemorative purposes and decorated with images or text. • sunk relief A type of artwork in which an image is made by cutting the relief sculpture itself into a flat surface. • tenon A projecting member ...
Narmer Palette Narmer Mace Head
... palette’s obverse side and the White Crown of the South on the palette’s reverse side. This suggests that when the palette was made, Egypt was either already unified or perhaps had just been unified. The images of decapitated prisoners on the obverse side and defeated foes on both sides certainly su ...
... palette’s obverse side and the White Crown of the South on the palette’s reverse side. This suggests that when the palette was made, Egypt was either already unified or perhaps had just been unified. The images of decapitated prisoners on the obverse side and defeated foes on both sides certainly su ...
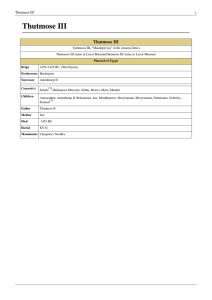
Thutmose III
... were directed against the Phoenician cities in Syria and Annals of Tuthmoses III at Karnak depicting him standing before against Kadesh on the Orontes. In Thutmose's the offerings made to him after his foreign campaigns. twenty-ninth year, he began his fifth campaign where he first took an unknown c ...
... were directed against the Phoenician cities in Syria and Annals of Tuthmoses III at Karnak depicting him standing before against Kadesh on the Orontes. In Thutmose's the offerings made to him after his foreign campaigns. twenty-ninth year, he began his fifth campaign where he first took an unknown c ...
Radiological evaluation of the evisceration tradition in ancient
... also used to plug and seal the embalming incision, anus, and vagina of the deceased in many cases (Raven and Taconis, 2005). Solid and solidified (once fluid) resinous materials have been included in Egyptian burials since the Predynastic Period, and were likely the product of the conifers and Pistaci ...
... also used to plug and seal the embalming incision, anus, and vagina of the deceased in many cases (Raven and Taconis, 2005). Solid and solidified (once fluid) resinous materials have been included in Egyptian burials since the Predynastic Period, and were likely the product of the conifers and Pistaci ...
THE CAIRO DAHSHUR BOATS A Thesis by PEARCE PAUL
... Tool marks on throughbeam 3 and deck planks in section 4 (room D) of GC 4926....................................................................................................... 107 ...
... Tool marks on throughbeam 3 and deck planks in section 4 (room D) of GC 4926....................................................................................................... 107 ...
Document
... pharaoh’s body for the afterlife and then installed his mummified body in the tomb. ...
... pharaoh’s body for the afterlife and then installed his mummified body in the tomb. ...
The Great Pyramids of Egypt - Vb-Tech
... Teti's cult places are enduring, later the pyramid complexes surrounding the main ...
... Teti's cult places are enduring, later the pyramid complexes surrounding the main ...
Hatshepsut Summary - The Bored of Studies Community
... four classes. The upper class included the government officials, nobles, and priests. The middle class included the scribes, skilled craftsmen, trades people, teachers, artists, and soldiers. The peasants mostly farmers, labourers, and servants made up the lower class, which was the largest class. L ...
... four classes. The upper class included the government officials, nobles, and priests. The middle class included the scribes, skilled craftsmen, trades people, teachers, artists, and soldiers. The peasants mostly farmers, labourers, and servants made up the lower class, which was the largest class. L ...
Diplomová práce/The thesis
... transporting heavier loads until the Hellenistic Period 4. The transport of very heavy loads, groups of people, herds of cattle or grain was ensured by specialized boats. Moreover, from at least the Fifth Dynasty the Egyptians built sailing ships for sea navigation5. The wheeled chariots, pulled by ...
... transporting heavier loads until the Hellenistic Period 4. The transport of very heavy loads, groups of people, herds of cattle or grain was ensured by specialized boats. Moreover, from at least the Fifth Dynasty the Egyptians built sailing ships for sea navigation5. The wheeled chariots, pulled by ...
The King Herself What motivated Hatshepsut to rule ancient Egypt
... So began one of the most intriguing periods of ancient Egyptian history. At first, Hatshepsut acted on her stepson's behalf, careful to respect the conventions under which previous queens had handled political affairs while juvenile offspring learned the ropes. But before long, signs emerged that Ha ...
... So began one of the most intriguing periods of ancient Egyptian history. At first, Hatshepsut acted on her stepson's behalf, careful to respect the conventions under which previous queens had handled political affairs while juvenile offspring learned the ropes. But before long, signs emerged that Ha ...
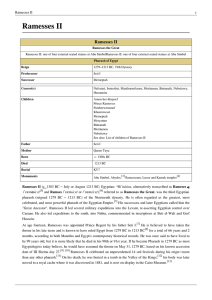
Ramesses II
... Further information: Battle of Kadesh The Battle of Kadesh in his fifth regnal year was the climactic engagement in a campaign that Ramesses fought in Syria, against the resurgent Hittite forces of Muwatallis. The pharaoh wanted a victory at Kadesh both to expand Egypt's frontiers into Syria and to ...
... Further information: Battle of Kadesh The Battle of Kadesh in his fifth regnal year was the climactic engagement in a campaign that Ramesses fought in Syria, against the resurgent Hittite forces of Muwatallis. The pharaoh wanted a victory at Kadesh both to expand Egypt's frontiers into Syria and to ...
The pyramids - mundoegipcio
... he Egyptians believed in the afterlife and thought that they were necessary to maintain the pharaoh´s body for this second life. They mummify the body and they put it on the monuments, called pyramids. The pyramids also contained many treasures, because they hope that, in the second life, they will ...
... he Egyptians believed in the afterlife and thought that they were necessary to maintain the pharaoh´s body for this second life. They mummify the body and they put it on the monuments, called pyramids. The pyramids also contained many treasures, because they hope that, in the second life, they will ...
The Pyramids, the Pharaohs and their Water World.
... as such that was worshipped, but the inherent power of rejuvenation and recreation. Compared to other river civilisations, it is a striking and noteworthy fact that the Nile was not worshipped as a supreme deity, particularly since the whole of Egypt and all living there were dependent upon this lif ...
... as such that was worshipped, but the inherent power of rejuvenation and recreation. Compared to other river civilisations, it is a striking and noteworthy fact that the Nile was not worshipped as a supreme deity, particularly since the whole of Egypt and all living there were dependent upon this lif ...
Decoding the Secrets of Eqyptian Hieroglyphs
... could organize farmers to begin digging irrigation canals so that more crops could be grown. Then, the pharaoh could collect even more taxes, which required writing. ...
... could organize farmers to begin digging irrigation canals so that more crops could be grown. Then, the pharaoh could collect even more taxes, which required writing. ...
Integrated ART Lesson Ancient ART: The Pyramids The STEP
... would be disturbed by grave robbers. They chose a site on the west side of the Nile River because they believed that the home of the dead was toward the setting sun. The burial chambers were placed under the exact centers of the pyramids. Passageways, which were built angling down from the sides and ...
... would be disturbed by grave robbers. They chose a site on the west side of the Nile River because they believed that the home of the dead was toward the setting sun. The burial chambers were placed under the exact centers of the pyramids. Passageways, which were built angling down from the sides and ...
THE SPHINX
... The sphinx is built of soft sandstone and would have disappeared long ago had it not been buried for so long. The body is 200 feet (60m) in length and 65 feet (20m) tall. The face of the sphinx is 13 feet (4m) wide and its eyes are 6 feet (2m) high. Part of the uraeus (sacred cobra), the nose and th ...
... The sphinx is built of soft sandstone and would have disappeared long ago had it not been buried for so long. The body is 200 feet (60m) in length and 65 feet (20m) tall. The face of the sphinx is 13 feet (4m) wide and its eyes are 6 feet (2m) high. Part of the uraeus (sacred cobra), the nose and th ...
7. Exodus 1-17
... who had gone down to Egypt, Exodus tells us that “there arose up a new king over Egypt, which knew not Joseph” (8). Thought Exodus does not give us the names of any Pharaohs, the situation described aligns with the transition from the Hyksos’ reign to the return of Egyptian control under Kamose (155 ...
... who had gone down to Egypt, Exodus tells us that “there arose up a new king over Egypt, which knew not Joseph” (8). Thought Exodus does not give us the names of any Pharaohs, the situation described aligns with the transition from the Hyksos’ reign to the return of Egyptian control under Kamose (155 ...
Tutankhamun Catalog - The Origins Museum Institute
... as divine, treated not as a king but as a god. The entire industry of the state, including its art and architecture, was primarily concerned with ensuring the pharaoh’s eternal life after death. At the close of the 6th Dynasty (some 800 years before Tutankhamun’s birth), the Old Kingdom came to an e ...
... as divine, treated not as a king but as a god. The entire industry of the state, including its art and architecture, was primarily concerned with ensuring the pharaoh’s eternal life after death. At the close of the 6th Dynasty (some 800 years before Tutankhamun’s birth), the Old Kingdom came to an e ...
Name: Date: ______ Class: ______ Famous Pyramids of Egypt
... Some believe that his pyramid at Giza was built by slaves but this is not true. One hundred thousand (100,000) people worked on it for three months of each year. This was the time of the Nile's annual flood which made it impossible to farm the land and most of the population was unemployed. He provi ...
... Some believe that his pyramid at Giza was built by slaves but this is not true. One hundred thousand (100,000) people worked on it for three months of each year. This was the time of the Nile's annual flood which made it impossible to farm the land and most of the population was unemployed. He provi ...
Welcome to Presentation Plus!
... upheavals that led the Egyptians to lose their empire. • Ramses II, who reigned from 1279 to 1213 B.C., regained some of the empire. • New invasions by the “Sea Peoples” then ended the Egyptian Empire once and for all. The New Kingdom collapsed in 1085 B.C. (pages 47–51) Click the mouse button o ...
... upheavals that led the Egyptians to lose their empire. • Ramses II, who reigned from 1279 to 1213 B.C., regained some of the empire. • New invasions by the “Sea Peoples” then ended the Egyptian Empire once and for all. The New Kingdom collapsed in 1085 B.C. (pages 47–51) Click the mouse button o ...
The “Children of Israel” (cont.)
... upheavals that led the Egyptians to lose their empire. • Ramses II, who reigned from 1279 to 1213 B.C., regained some of the empire. • New invasions by the “Sea Peoples” then ended the Egyptian Empire once and for all. The New Kingdom collapsed in 1085 B.C. (pages 47–51) Click the mouse button o ...
... upheavals that led the Egyptians to lose their empire. • Ramses II, who reigned from 1279 to 1213 B.C., regained some of the empire. • New invasions by the “Sea Peoples” then ended the Egyptian Empire once and for all. The New Kingdom collapsed in 1085 B.C. (pages 47–51) Click the mouse button o ...