* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download terminal branch of Popliteal artery
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
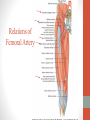
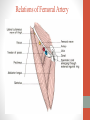
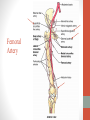
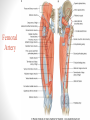
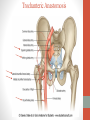
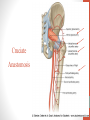
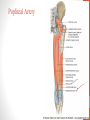
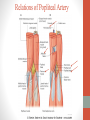
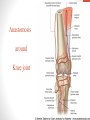
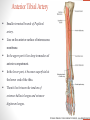
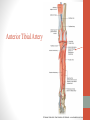
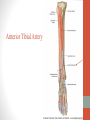
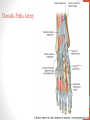
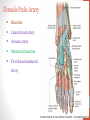
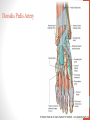
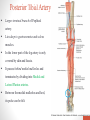
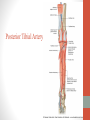
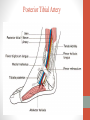
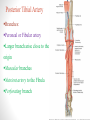
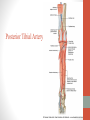
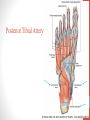
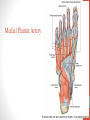
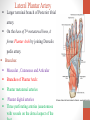
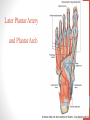
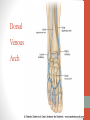
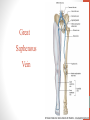
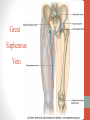
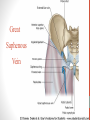
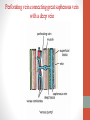
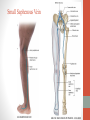
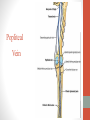
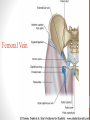
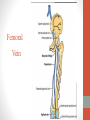
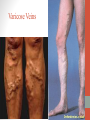
Blood Supply of the Lower Limb Dr. Safaa Dr. Sama-ul-Haque Objectives Describe femoral artery and its relations. Enlist the branches of femoral artery. Define the trochanteric and cruciate anastomosis. Describe popliteal artery, its relations and branches. Discuss the arterial anastomosis around the knee joint. Discuss the anterior tibial artery, its relations and branches. Define Dorsalis pedis artery. Objectives Discuss the posterior tibial artery, its relations and branches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Describe the formation of great saphenous vein and enlist its tributaries. Discuss the formation of small saphenous vein and enlist its tributaries. Describe the formation of popliteal vein and femoral veins. Femoral Artery Enters thigh by passing behind inguinal ligament. Continuation of External iliac artery. Ends at the opening in the adductor Magnus muscle and continuous as Popliteal artery. Relations: Anteriorly: Skin , Fascia and Sartorius Posteriorly: Psoas Major Laterally: Femoral Nerve Medially: Femoral vein Relations of Femoral Artery Relations of Femoral Artery Femoral Artery Branches: Superficial circumflex iliac artery Superficial epigastric artery Superficial external pudendal artery Deep external pudendal artery Descending genicular artery Femoral Artery Branches: Profunda femoris artery Large branch enters the medial compartment of thigh. Ends by becoming 4th perforating artery. Branches: Medial femoral circumflex artery Lateral femoral circumflex artery 1st, 2nd and 3rd perforating arteries. Femoral Artery Femoral Artery Trochanteric Anastomosis Anastomosis between the branches of internal iliac and femoral arteries. Main supply to the head of Femur. Branches forming anastomosis: Superior gluteal artery Inferior gluteal artery Medial femoral circumflex artery Lateral femoral circumflex artery Trochanteric Anastomosis Cruciate Anastomosis Anastomosis between the branches of internal iliac and femoral arteries. Branches forming anastomosis: Inferior gluteal artery Medial femoral circumflex artery Lateral femoral circumflex artery First Perforating artery In occlusion of the proximal part of the femoral artery, blood passes through the cruciate & trochanteric Anastomosis. Cruciate Anastomosis Popliteal Artery Continuation of Femoral artery. Ends at the lower border of the Popliteus muscle by dividing into Anterior and Posterior tibial arteries. Relations: Anteriorly: Popliteal surface of femur, Knee joint & Popliteus muscle. Posteriorly: Popliteal vein & Tibial nerve Popliteal Artery Relations of Popliteal Artery Branches of Popliteal Artery Muscular branches Articular branches Terminal branches Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Anastomosis around Knee joint Anastomosis between the branches of femoral, popliteal, anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Branches forming anastomosis: Branch of femoral artery Descending genicular Articular branches of Popliteal artery Superior genicular (lateral & medial) Inferior genicular (lateral & medial) Small branches of anterior and posterior tibial arteries Anastomosis around Knee joint Anterior Tibial Artery Smaller terminal branch of Popliteal artery. Lies on the anterior surface of interosseous membrane. In the upper part it lies deep to muscles of anterior compartment. In the lower part, it becomes superficial at the lower end of the tibia. Then it lies between the tendons of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus. Anterior Tibial Artery Anterior Tibial Artery Anterior Tibial Artery In front of ankle joint, the artery becomes the Dorsalis pedis artery. Branches: Muscular branches to the muscles of anterior compartment Anastomotic branches Around Knee and Ankle joints Dorsalis Pedis Artery Also called Dorsal artery of the foot. Continuation of anterior Tibial artery. Terminates by joining the lateral plantar artery and completes the plantar arch. On dorsum of the foot it lies between the tendons of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus. Its pulsation can be felt here. Dorsalis Pedis Artery Dorsalis Pedis Artery Branches: Lateral tarsal artery Arcuate artery Metatarsal branches First dorsal metatarsal artery Dorsalis Pedis Artery Posterior Tibial Artery Larger terminal branch of Popliteal artery. Lies deep to gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. In the lower part of the leg artery is only covered by skin and fascia. It passes behind medial malleolus and terminates by dividing into Medial and Lateral Plantar arteries. Between the medial malleolus and heel, its pulse can be felt. Posterior Tibial Artery Posterior Tibial Artery Posterior Tibial Artery Branches: Peroneal or Fibular artery Larger branch arise close to the origin Muscular branches Nutrient artery to the Fibula Perforating branch Posterior Tibial Artery Branches: Muscular branches to muscles of posterior compartment Nutrient artery to the Tibia Medial plantar artery Medial plantar artery Anastomotic branches Around Ankle joint Posterior Tibial Artery Posterior Tibial Artery Medial Plantar Artery Smaller terminal branch of Posterior tibial artery. Supply medial side of the big toe. Branches: Muscular Cutaneous Articular Medial Plantar Artery Lateral Plantar Artery Larger terminal branch of Posterior tibial artery. On the base of 5th metatarsal bone, it forms Plantar Arch by joining Dorsalis pedis artery. Branches: Muscular , Cutaneous and Articular Branches of Plantar Arch: Plantar metatarsal arteries Plantar digital arteries Three perforating arteries (anastomose with vessels on the dorsal aspect of the Later Plantar Artery and Plantar Arch Areas of Lower Limb Arteries Pulsation Veins of the Lower Limb Veins of the Lower Limb Superficial veins Lie in the superficial fascia Having Thick muscular wall Deep veins Accompany the arteries Having Thin muscular wall Superficial Veins of the Lower Limb Dorsal Venous Arch Great Saphenous Vein Small Saphenous Vein Deep Veins of the Lower Limb Venae Comitantes Popliteal Vein Femoral Vein Veins of the Lower Limb Superficial Veins of the Lower Limb Dorsal Venous Arch Lies on the dorsum of the foot. The blood from the whole foot drains into this arch via digital veins and communicating veins. Drains on the medial side into the Great Saphenous vein Drains on the lateral side into the Small Saphenous vein Dorsal Venous Arch Great Saphenous vein Longest vein in the body. Drains medial side of the dorsum venous arch. Passes upward in front of medial malleolus. Then runs upward in superficial fascia over the medial side of the leg. Passes behind the knee and curves forward around the medial side of the thigh. Great Saphenous vein It contains 10-20 valves. Connected to small saphenous vein behind knee. Perforating veins connect the great saphenous vein with the deep veins. Passes through saphenous opening. Finally drains into femoral vein Great Saphenous Vein Great Saphenous Vein Great Saphenous Vein Great Saphenous Vein Tributaries: Subcutaneous tributaries Superficial circumflex iliac vein Superficial epigastric vein Superficial external pudendal vein Accessory vein Tributaries of Great Saphenous Vein Perforating vein connecting great saphenous vein with a deep vein Small Saphenous vein Drains lateral side of the dorsum venous arch. Passes upward behind lateral malleolus. Reaches middle of the back of leg. Then it pierces deep fascia. In the lower part of popliteal fossa ends in the popliteal vein. Contains numerous valves. Small Saphenous Vein Tributaries: Numerous small veins from the back of the leg. Communicating veins with deep veins of the foot. Anastomotic branches that join the great saphenous vein. Small Saphenous Vein Deep Veins of the Lower Limb Venae Comitantes Deep veins accompany the arteries are called venae comitantes. The deep plantar venous arch gives medial and lateral plantar veins. Medial and lateral plantar veins forms posterior tibial vein behind the medial malleolus. Peroneal vein drain into posterior tibial vein. Venae comitantes of anterior and posterior tibial arteries unite in the popliteal fossa to form the popliteal vein. Popliteal Vein Formed by the venae comitantes of the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Ends at the adductor hiatus and continuous upward as Femoral vein. Tributaries: Veins accompany arteries. Small saphenous vein. Popliteal Vein Femoral Vein Continuation of popliteal vein at adductor hiatus. Enters in the intermediate compartment of femoral sheath. Then passes behind inguinal ligament and continuous as External Iliac Vein. Femoral Vein Femoral Vein Tributaries: Great saphenous vein Tributaries corresponding to the perforating branches of the profunda femoris artery. Medial and lateral femoral circumflex veins. Femoral Vein Varicose Veins Thank You