* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch8 Power Point - Eyes
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
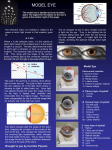
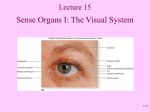
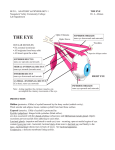
Chapter 8 – Special Senses Eye sphere – 1 inch in diameter – only see 1/6 of eyeball External Structure Eyelids – protection Come together at medial and lateral canthus Eyelashes along border Tarsal glands – lubricate eye External Structrure cont. Conjunctiva – lines eyelids and covers outer surface of eyeball Ends at edge of cornea Secretes mucous for lubrication Conjunctivitis – pink eye External Structure cont. Lacrimal glands – above lateral end of eye Release tears which move across eye into lacrimal canals → lacrimal sac → nasolacrimal duct → empties into nasal cavity Tears also contain antibodies and lysozymes Cleanses and protects External Structure cont. Extrinsic (external) muscles – 6 Lateral rectus – laterally Medial rectus – medially Superior rectus – elevates Inferior rectus – depresses Superior oblique – elevates and lateral Inferior oblique – depresses and lateral Internal Structure Tunics = coats; humors = fluids Sclera – outermost – aka fibrous tunic Thick, white Central anterior is clear = cornea Where light enters Internal Structure cont. Vascular tunic Choroids – posteriorly – dark Prevents light from scattering Ciliary body and ciliary zonule – hold lens in place Iris – has opening called pupil Muscles control diameter – regulates light Internal Structure cont. Sensory tunic Retina – stops at ciliary body Contains photoreceptors – rods and cones Pass signals through bipolar and ganglion cells to optic nerve → optic cortex = vision Are all through retina except where optic nerve leaves – called the optic disk (blind spot) Internal Structure cont. Rods – more dense at edge Allow peripheral vision Allow to see at night Cones – more dense in center Allow color vision 3 types – different wavelengths Missing cones = colorblindness Fovea centralis – pit next to optic disc Contains only cones Point of sharpest vision Internal Structure cont. Lens – focuses light on retina Divides eye into 2 chambers Anterior (aqueous) segment Contains aqueous humor – clear, watery Provides nutrients to lens and cornea Reabsorbed through scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm) Blocked sinus = glaucoma – increase of intraocular pressure Internal Structure cont. Posterior (vitreous) segment Contains vitreous humor – gel like Keeps eye from collapsing in – maintains intraocular pressure Cataracts – lens becomes milky Light Pathway Refraction – bending of light – occurs when light passes through substances with different densities Occurs as light moves through cornea, conjunctiva, aqueous humor, lens, pupil, vitreous humor, retina Lens changes shape – causes more/less bend in light Greater bulge (convexity) – more bending Flatter – less bending Eye at rest is set for distant vision About 20ft and no change is necessary Closer and lens must bulge – accommodation Ciliary body contracts – lens becomes convex Vision Emmetropia – “harmonious vision” Myopia – nearsightedness – “short vision” Light is focused in front of retina Eyeball is too long or cornea is too curved Correction = concave lenses Hyperopic – farsightedness – “far vision” Light focuses behind retina Eyeball is too short Correction = convex lenses Visual fields & pathways to brain Nerves leave eye via optic nerve At optic chiasma some (medial) fibers cross Optic tracts – contain fibers from both eyes Joint neurons in thalamus and are sent to occipital lobe of brain Allows binocular vision because the visual fields overlap Eye reflexes Photopupillary reflex – pupil constriction due to bright light Accommodation papillary reflex – constriction for viewing close objects Development Vision is the only sense not fully functional at birth. No tears until 2 weeks Newborn sees in gray tones 5 months – close focus, following moving objects By 5 – color vision well developed, depth perception 6/7 – emmetropia About 40 – presbyopia may occur – type of farsightedness