* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro-comp
Name mangling wikipedia , lookup
Abstraction (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Programming language wikipedia , lookup
Program optimization wikipedia , lookup
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Reactive programming wikipedia , lookup
Go (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Parallel computing wikipedia , lookup
Assembly language wikipedia , lookup
Object-oriented programming wikipedia , lookup
Java (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
History of compiler construction wikipedia , lookup
Java ConcurrentMap wikipedia , lookup
Interpreter (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Structured programming wikipedia , lookup
University of Hail
College of Computer Science & Engineering
Computer Science and Software Engineering Department
ICS 102
Computer Programming
ICS 102
Computer Programming
Chapter1 : Introduction
Components of a Personal Computer
Questions :
- what are the input devices ?
- what are the output devices ?
ICS102: Computer Programming
3
Motherboard
A motherboard, provides the electrical
connections by which the other components
of the system communicate and hosts the
central processing unit as well as other
subsystems and devices .
4
Motherboard example : Acer E360
ICS102: Computer Programming
5
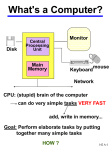
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) or
processor is the portion of a computer system
that carries out the instructions of a computer
program and is the primary element carrying
out the computer's functions.
Example: (3 + 2) = 5
In an addition operation, the arithmetic
logic unit (ALU) will be connected to a
set of inputs and a set of outputs. The
inputs provide the numbers to be added,
and the outputs will contain the final
sum .
3
5
2
ICS102: Computer Programming
6
Memory
Memory refers to computer components, devices, and recording
media that hold digital data used for computing for some interval of
time.
There are mainly three types of memory :
CPU memory
◦ Registers
◦ Cache
Main memory (RAM):
◦ Data has to be in main memory so that CPU can access it
◦ Volatile: lost when program exits; computer shuts off
Hard Disk, CD, etc.
◦ This is where you keep the data for long-term storage
ICS102: Computer Programming
7
Main Memory …
Address
1002
1003
1004
1005
Cell
Memory is divided into
Many memory locations (cells)
Each memory cell has a
numeric address, which
uniquely identifies it
Each cell contains a data
value, e.g. 22
ICS102: Computer Programming
8
Main Memory …
ICS102: Computer Programming
9
Main Memory …
The word “Hello.” stored in 6 memory cells
ICS102: Computer Programming
10
Memory units : Bits and Bytes
Bit -- most basic unit of memory
◦ 1 or 0, on or off
1 Byte = 8 bits
In a computer, data values are stored as a sequence of bits
1004
2
1004
00000010
1005
7
1005
00000111
ICS102: Computer Programming
11
Program / CPU / Memory Interaction
Example:
◦ Input read a number from keyboard
◦ Add 1 to it
◦ Output it on screen
Keyboard
1
RAM
1
1
CPU
2
RAM
2
2
Monitor
ICS102: Computer Programming
12
Software
Software
is the programs and data that
a computer uses.
Both programs and data are saved in
computer memory in the same way.
1-13
Computer Software
Types of software
Software
1-14
Software
Application Programs
Systems Programs
Word processors
Game programs
Spreadsheets
Data base systems
Graphics programs
Web browsers
Operating system.
Networking system.
Programming
language software.
Web site server.
Device drivers.
1-15
What is programming?
What is a program?
A (software) program is a list of instructions
intended to a computer
A program has inputs and outputs
Each instruction tells the computer to do
something (an action, a calculation, a
comparison)
ICS102: Computer Programming
17
Program Execution
A program tells the CPU how to manipulate and/or
move information
Programming is about processing information
◦ Take some input,
◦ manipulate it in some way, and
◦ produce a particular output
Program
Inputs
Manipulation
Outputs
ICS102: Computer Programming
18
Example 1 : Recipe for Scrambled Eggs
Ingredients (Inputs) : two eggs,
tablespoon of oil, salt
Instructions (program):
◦ Add oil to pan
◦ Heat pan on stove
◦ Crack eggs into pan
◦ Add salt
◦ Mix until light and flakey
Output: scrambled eggs
ICS102: Computer Programming
19
Example 2 : Currency Exchange
Task : convert an amount of money in some currency (e.g. US
Dollars) to another one (e.g. Saudi Riyals).
Input:
◦ Amount
◦ Source Currency
◦ Desired Currency
Instructions
◦ Look up in table current exchange rate for the
selected currencies
◦ Calculate result as amount * exchange rate
• Output: result
ICS102: Computer Programming
20
Programming language
A programming language is the language used to
write programs
A programming language employs a set of rules
that dictate how the words and symbols can be
put together to form valid program statements
A programming language has a syntax and
semantics
In this course we focus on Java programming
language.
ICS102: Computer Programming
21
Java
• Java is a programming language originally
developed by James Gosling at Sun
Microsystems
• It was first released in 1995.
• The language derives much of its syntax
from C and C++.
• But has a simpler object model and fewer
low-level facilities than C and C++.
ICS102: Computer Programming
22
Programming Language Hierarchy
High-Level Language (HLL)
Assembly Lanuage
Machine Language
Hardware
The highs and lows of programming
languages ...
High-Level Language (HLL) Machine Language
◦ closest to natural language (lowest level)
◦ words, numbers, and math
◦ natural language for
symbols
hardware
◦ not directly understood
◦ just 0s and 1s
by hardware
◦ directly understood
◦ Java, C/C++, COBOL,
by hardware
FORTRAN, BASIC, Lisp,
Ada, etc.
Assembly Language (middle level)
a more or less human readable version of
machine language
words, abbreviations, letters and numbers
easily translated from human readable to
machine executable code
Getting from Source to Machine Code
“Compiler”
a program that translates HLL source code to machine
(object, or executable) code.
“Assembler”
a program that translates assembly source code to machine
(object, or executable) code.
Compilers vs. Assemblers vs. Interpreters
Compilers and Assemblers
◦ translation is a separate user step
◦ translation is “off-line,” i.e. not at run time
Interpreters
◦ interpretation (from source to object code) is not a separate
user step
◦ translation is “on-line,” i.e. at run time
Source
Code
Compiler,
Assembler, or
Interpreter
Object
Code
Java Program Translation
Data for Java Program
Java Program
Intermediate Code:
“Byte Code”
◦ similar to assembly code,
but hardware independent
Interpreter translates from
generic byte code to
hardware-specific machine
code
Java Compiler
Byte-Code
Program
Java
Virtual
Machine
Byte-Code Interpreter
Machine-Language
Instructions
Computer Execution
of Machine-Language Instructions
Output of Java Program
Byte-Code and the Java Virtual Machine
The Java compiler translates Java programs into
byte-code, a machine language called the Java Virtual
Machine
◦ Once compiled to byte-code, a Java program can be used
on any computer, making it very portable
1-29
Portability of Java
Classical model :
Java model :
ICS102: Computer Programming
30
Program terminology
Code: A program or a part of a program
Source code (or source program): A program written
in a high-level language such as Java
◦ The input to the compiler program
Object code: The translated low-level program
◦ The output from the compiler program, e.g., Java bytecode
1-31
Portability of Java
Write once, run anywhere :Because applications written in
the Java programming language are compiled into machineindependent bytecodes, they run consistently on any Java
platform .
32
A Java Program
A Java Program
A Java program consists of
one or more classes
A Java class consists of one or
more methods
A Java method consists of one
or more statements
Java
classes
Java
Methods
33
A Java Program
A Java program resides in one or more files.
The file name of a Java program has extension .java.
One of the classes of a Java program is called the driver
class.
The name of the driver class must be the same as the name
of its Java file. (Java is case sensitive. So EX1 is different from
ex1.)
The driver class must contain a method called main. The
execution of Java program starts from the main method of
the driver class.
34
Example of a Java Program
35
Example of a Java Program
Class name
Main method
Class body
Instruction
36
Example of a Java Program
Also notice:
Curly braces { }
ICS102: Computer Programming
37
Example of a Java Program
Also notice:
Curly braces { }
Parentheses ( )
38
Example of a Java Program
Also notice:
Curly braces { }
Square brackets [ ]
Parentheses ( )
39
Example of a Java Program
Also notice:
A pair of braces { }
define a block
ICS102: Computer Programming
40
Compiling and running a program
Type in your program
Save the program
◦ Store all your files in one directory for now
◦ Give the program the same name as the class
Compile the program
◦ this produces a .class file
◦ Translates the program into something the computer can
understand and execute (Java bytecode)
Run the program
Observe the result and adjust the program if necessary
ICS102: Computer Programming
41
Edit
Public class firstPtog
/*
This program is an …
*/
Public class
/*
Text Editor
public static void main…
/* Program statements g …
System.out.print(“Wel …
}
}
firstProg.java
ICS102: Computer Programming
42
Compile - With Errors
Public class firstPtog
/*
This program is an Arit
*/
public static void main
/* Program statements g
System.print(“Welcome
}
Compiler
}
firstProg.java
Errors and Warnings
------------------Error : The method print(
String) is undefined for
Type System
ICS102: Computer Programming
43
Compile - Success
Public class firstPtog
/*
This program is an Arit
*/
public static void main
/* Program statements
System.out.print(“Welcome”);
}
Compiler
}
firstProg.java
001011010001011101
1011010001011101110
101000101110111010110100010
111011101011010001011101110
101101000101110111010110100
010111011100010111011101011
010001011101110010111011101
011010001011101110010111011
101011010001011101110010111
011101011010001011101110010
111011101011010001011101110
0101110
firstPtog.class
ICS102: Computer Programming
44
Run Program
Fred
1
firstProg
Welcome to the Arithm
The date is Monday Sep
What is your name?Fred
Well Fred, after a day
The cube appears to be
You find a Green door,
The door closes behind
There is a feel of mat
ICS102: Computer Programming
45