* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Napoleon Lecture
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord wikipedia , lookup
Causes of the French Revolution wikipedia , lookup
French Revolutionary Wars wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Amiens wikipedia , lookup
War of the Fifth Coalition wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
Hundred Days wikipedia , lookup
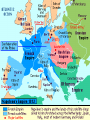
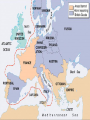
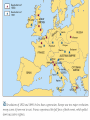
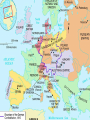
Opening Question (12.13) Put these events in chronological order… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Death of Robespierre Tennis Court Oath Storming of the Bastille Execution of Louis XVI Napoleon’s Coup D’etat Directory is created Start of the Reign of Terror Declaration of the Rights of Man created Formation of the French Republic The Rise and Fall of Napoleon “Napoleonic Era” 1799-1814 His legacy and impact on Europe 12.3.09 Lets Review French Revolution Starts with Third Estate forming as the National Assembly 1. 2. 3. 4. Tennis Court Oath Storming of the Bastille (July 14th 1789) Declaration of the Rights of Man (Aug. 1789) Louis XVI is taken into Paris by commoners Trial and Error gov’ts Constitution of 1791 (lasted less than a year) French Republic (1792-1795) Extremist (Jacobins take power and start “Reign of Terror”) Directory (1795-1799) Not very effective (5 Directors fight for power) Instability leads Generals to have more power over the army – especially a popular one… Ends with the rise of Napoleon to power Who was Napoleon Bonaparte? Born in 1769 in Corsica (island in Mediterranean Sea) - noble status Received scholarship to elite military school at age 15 officer at 16 Became a general during the Revolution 1796 – put in charge of French Army in Austria and Italy Turned things around and won big victories Made him popular with people 1799 returns to Paris amid military/political chaos Takes advantage of the situation… Napoleon’s rise to power “I found the crown of France in the gutter and I picked it up with my sword” quoted from Napoleon Coup D’etat (1799)– a sudden and unconstitutional overthrow of the government Why did it happen? Threat of foreign nations Desire for stability yet did not want a return to the old regime Napoleon’s Rule 1799-1804 (Consulate) Napoleon is first consul (more like a dictator though) A new Constitution is put up to a plebiscite (vote by people) and it passes Centralized government to give himself complete power Puts his loyal military commanders in charge Sets up departments (states) that answer to him How did he rule??? Suppresses all opposition to his government Paris newspapers go from 73 to 13 and then to 4 (all government controlled) He was a constant working on both military and politics affairs Only took short breaks to eat small meals for a few minutes Return to the Church 1801 – Concordat (Agreement w/ Catholic Church) Agreed to settle dispute with Catholic Church Church officials paid by French state (Protestant ones too… religious toleration) Pope Pius VII supports Napoleon’s regime Napoleon as Emperor Another Plebiscite is put to people This on would make Napoleon Emperor (1804) People vote yes and Pope crowns Napoleon and his wife Josephine Napoleon now looks to conquer Europe Napoleonic Code (1804) Believed in many ideals of French Revolution Took all privileges away from Nobility, church officials, and rich people Set up a single unified code of law for France Ensured property rights for all men Religious freedom Mandatory high school (Lycee) for all boys Protected the rights of all men set them up as equals before the law Suppressed freedom of speech and women’s rights though Napoleon’s conquest Drafted large number of men for his Grand Army (under his direct control) Reorganizes the army, based on merit and achievement French Republic already conquered Italy and the Netherlands Napoleon defeats the Austrians, Prussians and Russians at several major battles Seems invincible – helps him maintain control In every area he conquers he does two things 1. Puts the Napoleonic Code into effect 2. Puts a relative on the throne of that country Napoleon’s conquest Napoleon conquers Spain, Germanic states, Italy, and Austria Basically controls continental Europe No one had this much control of Europe since the Roman Empire about 1500 years before Napoleon goes after Britain too Loses naval invasion in 1805 British Gen. Horatio Nelson leads Brits (dies in battle) “Continental System” – 1806 Blockade of Britain by Napoleon Not popular with other European nations (Why?) France and Europe under Napoleon Napoleon sets up Napoleonic Code in every region he conquers 1. Abolishes serfdom and feudalism everywhere 2. Gives Civil Rights to Jewish people and other religious minorities (religious freedom) 3. Builds roads, schools, public works, etc… Raises taxes and uses draft too in these areas 4. Introduces new military tactics all over Europe (modernize warfare) Prussia makes reforms in military to keep up 5. Organizes Germanic and Italian States Unintentionally leads to rise in nationalism Nationalism spreads to every region of Europe End of Day Question (12/13) Why is the Napoleonic Code so important to the history of Europe? How did change the mindsets and lives of people in not only France, but many other European countries as well? Next Class we will discuss Napoleon’s downfall… and the return to order of Europe Napoleon’s Downfall starts Peninsular Wars (1808-1814) Between Spain and France Napoleon send 100,000 troops to invade Portugal (British aid Portugal) Napoleon put his bro Joseph on the Spanish throne (1808) Spanish people fight for their freedom Spanish people revolt and win with British help Napoleon commits 250,000 troops there for 6 years Hurts French economy badly Spanish set up a limited monarchy and include many ideals from the French Revolution Think about the Spanish peasants that fought in the war… Napoleon goes after Russia 1812 – Russia starts to trade with Britain Napoleon gets angry and decides to attack Russia Recruits 600,000 person army (Grand Army) and marches into Russia “Scorched-Earth Policy” – Russians retreat and burn everything of use down in the process French reach Moscow and nothing is left Oct. 19th 1812 – Napoleon orders retreat (Winter is coming…) French are attacked all the way back Loss of 400,000 men to sickness, starvation, fighting, and capture Cripples Napoleon’s army and then Russia decides to invade French territory The rest of Europe smells blood!! European nations unite for revenge Leipzig Alliance (Britain, Russia, Austria, and Prussia) Beat France at Battle of Leipzig in Oct. 1813 Napoleon’s allies and satellite states desert him Capture Paris in March 1814 Napoleon is removed from power by the French Senate Allies force Napoleon to give up crown and banish him to island of Elba, Italy Louis XVIII is given the throne and most of Napoleon’s reforms are kept intact Napoleon will not go away (The Hundred Days) Louis XVIII is not too popular Has to flee country when Napoleon returns March 20th 1815 – Napoleon returns and marches French army into Paris Reinstates his army officers and takes back power People support him as he marched towards Paris June 18th – Napoleon forces meets European forces under British lead at the Battle of Waterloo (in present day Belgium) Napoleon loses and the British banish him to St. Helena island in the off the coast of Africa (he dies 6 years later @ 52 – 1821) Effects of Napoleonic Era Napoleon could not keep power once he lost on the battle field 750,000 French Soldiers died 400,000 from other French controlled countries New form of government (military state) Changed France and Europe forever Introduction of modern forms of democracy, Republicanism, terrorism, nationalism, and military dictatorship Napoleon’s legacy More secular societies No more absolute monarchy in France or Spain Increase in Nationalism throughout Europe Democratic ideals spread through Europe Spread the legal reforms of the French Revolution Imagine the ideals of the Revolution hitting everywhere in Europe End of feudalism in Europe New freedom to many former serfs New ideas scare European powers Congress of Vienna (1815) Attempt by other European Nations to restore order and security to Europe after the Napoleonic Era 3 major principles 1. Compensation for countries that suffered under Napoleon (both money and land) 2. Restore balance of power (no country too powerful) Even kept France powerful 3. Rule of Legitimacy – all former ruling families restored to power Also protected the status of smaller states New alliances aimed at maintaining peace Concert of Europe was created International group of states to keep safety in Europe Holy Alliance was created Russia w/ Prussia and Austria (new system of relations) British and others in western Europe refuse to join New Political Ideals form in 1800’s Conservatism 1. Believed in restoration of old order in Europe Wanted to keep things the same Believed that only the ones of the highest status should rule – (Brings stability) 2. Appealed to Monarchs and Nobility Liberalism in the 1800’s – (like conservatism today) 1. Wanted change but not full equality Believed economic inequality was natural Wanted the ideals and reforms of the Revolution 2. Appealed to Wealthy Merchants and Businessmen Believe in free enterprise and democracy Rise of capitalism, they want power to match their wealth End of Day Question (1.6.09) Looking at the two philosophies we have just discussed, which one do you believe will become more influential and powerful, conservatism or liberalism? Why?