* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
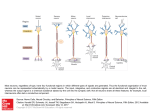
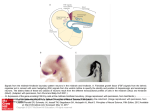
Chapter 3 The Development and Plasticity of the Nervous System The Structural Development of the Human Nervous System Brain development begins at the point of conception when the ovum is fertilized by a sperm resulting in the formation of a zygote. After the zygote divides the resulting developing human is called: • Embryo – next 6 weeks • Fetus – at week 9 and for the remainder of the pregnancy Eight cell zygote Development of the Nervous System: The Human Embryo Layers of cells in the embryo: • Ectoderm forms the nervous systems as well as the epidermis and parts of the eyes and ears • Mesoderm forms connective tissue, muscle, blood, blood vessels • Endoderm forms the linings of the body Throughout the embryonic and fetal period different cell types are created; the process is called differentiation. Structural Development: Formation of Nervous System Embryonic layers thicken to become: • Neural Plate is the name for the thickened ectodermal layer. • Neural folds push up to form a space called the neural groove. • Neural tube forms from the neural groove in 23 days. The brain and spinal cord develop from it. 3 Vesicle Stage 5 Vesicle Stage Structural Development: Differentiation of the Brain Structural Development: The Developing Spinal Cord Alar plate - gives rise to sensory neurons and interneurons of the spinal cord’s dorsal horn. Basal plate - forms ventral portion of the spinal cord where motor neurons originate and the interneurons of the ventral root form Sympathetic and Parasympathetic nervous systems also derive from the basal plate. Structural Development: The Developing Ventricular System Develops in the cavity inside the neural tube, contains cerebral spinal fluid Four ventricles: • Lateral ventricles • Third ventricle • Fourth ventricle Cellular Development: Formation of Neurons and Glial Cells A layer of ectodermal cells form on the inner surface of neural tube and divide to form: Ventricular layer which then divides into daughter cells Daughter cells migrate: • between the intermediate and marginal layers to form the cortical plate which develops into the cortex. • to the subventricular layer, becoming either glial cells or interneurons. • daughter cells remaining in the ventricular layer develop into ependymal cells, which form the lining of the four ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord. Cellular Development: Formation of Neurons and Glial Cells Cellular Development: Formation of Neurons and Glial Cells Neurogenesis is the formation of new neurons. • Few neurons are formed after birth • Exceptions are: cerebellar cells, olfactory receptor neurons, hippocampal neurons, and some cortical neurons • These exceptions allow for neuroplasticity. Cellular Development: Formation of Neurons and Glial Cells Migrating cells • Guided by radial glial cells • Glycoproteins allow neurons to bind to other neurons or radial glial cells (a handhold). • Failures of the adequate production of glycoproteins may lead to behavioral deficits. • Cell migration dysfunction is implicated in schizophrenia where abnormal distributions of neurons have been found in the brains of schizophrenic patients. Neural Cell Differentiation Cell-autonomous differentiation is controlled by genetic programming. • A Purkinje cell will develop into its distinctive form even if grown in culture out of its environment. Induction - other cells influence the final form. • The notochord influences new neurons to become a spinal motor neurons. Glial Cell Development Glial cells develop from the ventricular layer. Glial cells develop more after birth. A major function of glial cells is the myelination of neurons: Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system wrap themselves around nerve axons; a single Schwann cell makes up a single segment of an axon's myelin sheath Oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system wrap themselves around numerous axons at once. Formation of Neural Connections Once a cell has differentiated, it must establish connections with other neurons. Neurons grow toward target cells Axon emerges from growth cone Filopodia - consist of spine-like extensions that appear to be searching The Movement of Filopodia and the Growth Cone Formation of Neural Connections: Axonal Growth Guidepost cells serve as a map; when the filopodia reach them, the growth cone adheres to that cell and the guidepost cells redirect axonal growth to target cells. Neurotrophins released by the target cell • Attract the filopodia of developing neurons • Repels others to ensure only appropriate axons move toward the target Target cell determines the neurotransmitter released from the presynaptic neuron The Importance of Neural Activity Neural activity is necessary for establishing appropriate neural connections. Axonal remodeling is the process of axons connecting to the correct place; selectively strengthens the synaptic connection Neural activity “wires” the connections for communication within the nervous system New synaptic connections after birth allow more refined analysis of stimuli and more varied behavioral responses Neural Cell Death Apoptosis - genetically programmed cell death Synaptic pruning Theories of cell death • Neurons compete for connections to target cells and the unsuccessful ones die. • Neurons that receive a sufficient amount of chemical from the target cells survive; neurons that receive less die. Neural development recap Disorders of Development: Down Syndrome Genetic condition that causes delays in physical and intellectual development Most common genetic cause of learning disabilities in children Down syndrome results when one of three types of abnormal cell division involving chromosome 21 occurs Trisomy 21 Mosaic Down Syndrome Translocation Down Syndrome Neuroplasticity: Neural Degeneration Causes • Tumors Seizure Disorders Cerebrovascular Accidents Degenerative Disorders Disorders Caused by Infectious Diseases Types of degeneration Anterograde Retrograde Transneuronal • Chromatolysis - process of breakdown where degeneration occurs Neural Degeneration: Tumors Tumor - Mass of cells whose growth is uncontrolled and that serves no useful function Metastasis - Process by which cells break off a tumor and grow elsewhere in body • Tumors damage brain tissue two ways Compression Infiltration Glioma - Cancerous brain tumor Meningioma - Benign brain tumor Neural Degeneration: Seizure Disorders Seizure - a period of sudden, excessive activity of cerebral neurons Briefly alters consciousnesses, movement, or actions If neurons that make up the motor system are involved, convulsions can occur Convulsion – a violent sequence of uncontrollable muscular movements caused by a seizure • Hippocrates was the first to note that seizures might have a physical cause Classification of Seizure Disorders I. Generalized Seizures A. Tonic-clonic (grand mal) B. Absence (petit mal) C. Atonic II. Partial Seizures A. Simple 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Localized motor seizure Motor seizure with progression of movements Sensory Psychic Autonomic B. Complex – includes 1-5 as above III. Partial seizures evolving to a generalized cortical seizure – starts as IIA or IIB than becomes a grand mal seizure Specific Lobe Seizures Frontal lobe seizures may produce unusual symptoms that can appear to be related to a psychiatric problem or a sleep disorder. Temporal lobe seizures may include having odd feelings such as euphoria, fear, panic and déjà vu. Occipital seizures are often mistaken for migraines because they share symptoms including visual disturbances, partial blindness, nausea and vomiting, and headache. Parietal lobe seizures can involve both sensory and visual sensations. Cerebrovascular Accidents: Stroke Hemorrhagic stroke Caused by the rupture of a cerebral blood vessel Most common cause is high blood pressure Ischemic stroke Caused by the obstruction of blood flow to the brain Thrombus – a blood clot that forms within a blood vessel, obstructing blood flow Embolus – a piece of matter that dislodges from its site of origin and travels through the system until it reaches a vessel to small to let it pass thereby obstructing blood flow Cerebrovascular Accidents: Effects of a Stroke Right Brain Paralysis on the left side of the body Vision problems Quick, inquisitive behavioral style Left Brain Paralysis on the right side of the body Speech/language problems Slow, cautious behavioral style Hindbrain Can affect both sides of the body May leave someone in a ‘locked-in’ state Cerebrovascular Accidents: Risk Factors for Stroke High blood pressure Cigarette smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke High cholesterol Diabetes Being overweight or obese Physical inactivity Obstructive sleep apnea Cardiovascular disease Use of some birth control pills or hormone therapies that include estrogen Heavy or binge drinking Use of illicit drugs Cerebrovascular Accidents: Traumatic Brain Injury Vehicle-related collisions Violence Sports injuries Falls Explosive blasts Traumatic Brain Injury Head Games Degenerative Disorders Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy Parkinson’s Huntington’s Alzheimer’s Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Multiple Sclerosis Degenerative Disorders: Multiple Sclerosis Autoimmune demyelinating disease Myelin protein crosses into general circulation causing an immune system reaction Sclerotic plaques interrupt neuronal signals Disorders Caused by Infectious Diseases Viral Encephalitis Herpes Polio Rabies HIV Meningitis Bacteria Syphilis Lyme Disease Malaria Neuroplasticity: Regeneration of Damaged Neurons Neural regeneration • Occurs in embryonic and neonatal nervous system • In adults usually does not occur in CNS • Occurs in PNS Glycoproteins present in mature PNS promote cell regeneration Oligodendrocytes synthesize a glycoprotein that inhibits axonal growth in CNS Collateral Sprouting – neurons compensate for loss of neural connections in CNS by sending new axonal endings to vacated receptor sites Chromatolysis Neuroplasticity: Transplantation Animal research - Substantia nigra damage has been reduced by implanting fetal tissue from donors into the damaged area. Human research - Parkinson’s disease patients have partial recovery of motor ability from transplanted fetal tissue. Ethics - a major debate over the use fetal stem cells exists, acceptance might be higher for adult stem cell use Neuroplasticity: Stem Cells Embryonic stem cells are found in an embryo, fetus or the umbilical cord blood. Depending upon when they are harvested, embryonic stem cells can give rise to just about any cell in the human body. Adult stem cells - found in infants, children and adults. They reside in developed tissues such as those of the heart, brain and kidney. They usually give rise to cells within their resident organs.