* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Cengage Learning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
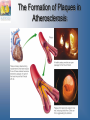
Chapter 11 Diet and Health Nutrition: Concepts & Controversies, 12e Sizer/Whitney Learning Objectives Describe relationships between immunity and nutrition, and explain how malnutrition and infection worsen each other. Compare and contrast the progression and the symptoms of heart disease in men and women. Describe what dietary and genetic factors may affect CVD risks and why higher LDL levels are a health concern. Learning Objectives Develop a general eating plan for a person with prehypertension. Speculate about possible mechanisms by which a diet high in red meat might increase the risk of breast cancer or colorectal cancer. Learning Objectives Develop a healthy eating plan that reduces the intake of trans fat and saturated fat but maintains sufficient intakes of essential nutrients. Describe some recent advances in nutritional genomics with regard to the health of the body through life. Introduction Two types of diseases Infectious and chronic Nutrients and our body’s defenses Hoaxes Leading causes of death Chronic diseases Mixture of factors The Ten Leading Causes of Death in the United States Nutrition and Immunity Well-nourished immune system Provides protection Susceptible groups PEM Malnutrition Effects of Protein-Energy Malnutrition (PEM) on the Body’s Defense Systems The Concept of Risk Factors Risk factors Suspected contributors Show correlation with the disease Disease risk factors Genetic Environmental Behavioral Social Dietary contributions to disease Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships Among Chronic Diseases The Concept of Risk Factors Estimating your risk Search family’s medical history Laboratory tests Cardiovascular Diseases Disease of heart and blood vessels Symptoms of heart attack and stroke Minimizing risks Heart is one of the least regenerative organs Heart disease Men vs. women U.S. Heart Disease Death Rates Atherosclerosis Hardening of the arteries Everyone has signs How advanced is the disease Plaque formation Damaging factors to vessel linings Inflammation Macrophages Mineralization The Formation of Plaques in Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis Plaque rupture Blood clots Abnormal blood clotting Omega-3 fatty acids Blood pressure Risk Factors for CVD Age, gender, and genetic inheritance Nonmodifiable High LDL and low HDL cholesterol Higher the LDL the greater the risk Most atherogenic lipoproteins Higher HDL reduces risk LDL oxidation LDL, HDL, and Risk of Heart Disease Adults Standards for Blood Lipids, Body Mass Index (BMI) and Blood Pressure Risk Factors for CVD Hypertension and atherosclerosis Both worsen CVD Worsen each other Diabetes Physical inactivity Benefits of activity for heart health Smoking Risk Factors for CVD Atherogenic diet DASH eating plan Obesity & metabolic syndrome Cluster of risk factors Inflammation Increased risk of thrombosis Other risk factors Recommendations for Reducing CVD Risk Lifestyle changes Increase physical activity Lose weight Implement dietary changes Reduce exposure to tobacco smoke Recommendations for Reducing CVD Risk Diet to reduce CVD risk Reduce fat intake Saturated and trans fats Limit refined starches and added sugars Eat fruits, vegetables, and whole grains Diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids Other dietary factors Nutrition and Hypertension One of most prevalent forms of CVD No symptoms you can feel Two numbers Systolic pressure Diastolic pressure Prehypertension Blood pressure checks at regular intervals Nutrition and Hypertension Blood pressure Cardiac output Factors causing an increase Peripheral resistance Factors causing an increase Risk factors Salt intake Alcohol The Blood Pressure Nutrition and Hypertension DASH diet Health benefits beyond blood pressure Weight control Physical activity Alteration of hormones Salt or sodium Alcohol Minerals and vitamin C Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Blood Pressure Complementary and Alternative Medicine Complementary vs. alternative Integrative medicine National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) http://nccam.nih.gov/ Accupuncture Herbal medicines Selected Herbs: Claims, Evidence, and Risks Selected Herbs: Claims, Evidence, and Risks Nutrition and Cancer Prevention of cancer Risk factors Lifestyle factors Environmental exposures Diet Dietary components Relation to cancer How Does Cancer Develop? Cancer arises in the genes DNA is damaged by carcinogen Cellular repair or self-destruction Cell loses ability to self-destruct Replicates uncontrollably Mass of abnormal tissue Cancer prevention through tumor development Cancer Development Which Diet Factors Affect Cancer Risk? Energy intake Reduced caloric intakes Cancer prevention only Obesity Depends on site of cancer & other factors Physical activity Alcohol Fat and fatty acids Which Diet Factors Affect Cancer Risk? Red meats and processed meats Cooking Smoking Fiber-rich foods Folate and antioxidant vitamins Calcium and vitamin D Iron Food phytochemicals The DASH Diet: Preventive Medicine Emphasized foods Make only a few dietary changes at a time Start with fruits & vegetables Nutritional Genomics: Can It Deliver on Its Promises? Controversy 11 Nutritional Genomics Research Genome Genetic profile DNA microarray technology DNA mutations SNPs Variation of a nucleotide Epigenetics Epigenome Proteins and other molecules that regulate expression of genes Turning genes “on” and “off” Inherited or altered Regulation Histones Methyl groups Two Epigenetic Factors and Gene Activity Bioactive Food Components and Gene Expression Epigenetics Future generation effects Embryonic development Modifying your epigenome Health implications Bioactive constituents in whole foods Genetic Testing Arguments Merits Demerits Nutritional genomics fraud Genetic Testing: Pros and Cons