* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Functions
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
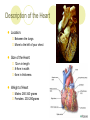
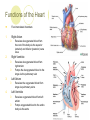
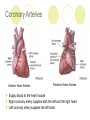
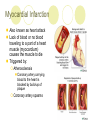
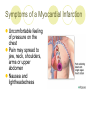
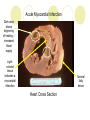
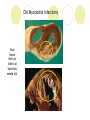
The Heart Description of the Heart Location: Between the lungs More to the left of your chest Size of the Heart: 12cm in length 8-9cm in width 6cm in thickness Weight of Heart Males: 280-340 grams Females: 230-280grams Functions of the Heart Four interrelated chambers 1. Right Atrium 2. Right Ventricle 3. Receives deoxygenated blood from right atrium Pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary vein Left Atrium 4. Receives deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body via the superior (anterior) and inferior (posterior) vena cava Receives the oxygenated blood from lungs via pulmonary veins Left Ventricle Receives oxygenated blood from left atrium Pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body via the aorta Coronary Arteries Anterior Heart Arteries Posterior Heart Arteries Supply blood to the heart muscle Right coronary artery supplies both the left and the right heart Left coronary artery supplies the left heart. Myocardial Infarction Also known as heart attack Lack of blood or no blood traveling to a part of a heart muscle (myocardium) causes the muscle to die Triggered by: Atherosclerosis Coronary artery carrying blood to the heart is blocked by build-up of plaque Coronary artery spasms Symptoms of a Myocardial Infarction Uncomfortable feeling of pressure on the chest Pain may spread to jaw, neck, shoulders, arms or upper abdomen Nausea and lightheadedness Acute Myocardial Infarction Dark area shows beginning of healing – increased blood supply Lightcolored tissue indicates a myocardial infarction Normal fatty tissue Heart Cross Section Old Myocardial Infarctions Scar tissue from an infarct at least two weeks old. Heart Attack Complications Arrhythmias Damaged heart muscle is replaced by scar tissue Damage caused by heart attack increases chance of heart failure Pericarditis (infection around the lining of the heart) Pulmonary embolism (blood clot in lungs)