* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
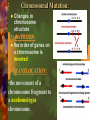
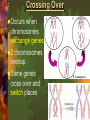
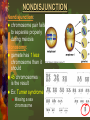
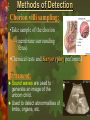
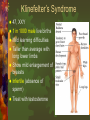
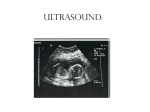
Mutations & Genetic Disorders Headings Vocabulary Important Information Mutations Mutation: Any mistake or change in the DNA sequence Point mutation: Change in one nitrogen base in DNA Ex: albinism Chromosomal Mutation: Changes in chromosome structure 1) INVERSION: the order of genes on a chromosome is inverted 2) TRANSLOCATION: •the movement of a chromosome fragment to a nonhomologus chromosome 3. DELETION Loss of a few bases Loss of large regions of a chromosome 4. DUPLICATION Duplication of a few bases Duplication of large regions of a chromosome Crossing Over Occurs when chromosomes exchange genes. 2 chromosomes overlap. Some genes cross over and switch places NONDISJUNCTION Nondisjunction: chromosome pair fails to separate properly during meiosis Monosomy: gamete has 1 less chromosome than it should 45 chromosomes is the result Ex: Turner syndrome Missing a sex chromosome Trisomy: Gamete has 1 more chromosome than it should Result is 47 chromosomes Ex: Down’s Syndrome Extra #21 chromosome Methods of Detection Chorion villi sampling: •Take sample of the chorion –(membrane surrounding fetus) •Chemical tests and Karyotyping performed Ultrasound: Sound waves are used to generate an image of the unborn child. Used to detect abnormalities of limbs, organs, etc. Amniocentesis: • Fluid surrounding the fetus is drawn out by needle • Fetal cells are collected and grown in a lab. • Chromosomes can be then Karyotyped Autosomal Disorders Down’s Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Patau’s Syndrome (Trisomy 13) Edward’s Syndrome (Trisomy 18) Down’s Syndrome (DS) Excess # 21 chromosome Prenatal testing can be done Result of chromosomal mutation 1 in 900 people born with this Likelihood of having a child with DS increases with advancing maternal age Symptoms: mental retardation, upward slant to eyes, small mouth, abnormal ear shape, decreased muscle tone No cure Patau’s Syndrome & Edward’s Syndrome Cardiac abnormalities Very severe conditions Most affected infants die during first few weeks of life Deletion Disorders Angelman Syndrome Prader-Willi Syndrome Angelman Syndrome Inappropriate laughter with convulsions Poor coordination Mental retardation Prader-Willi Syndrome Extremely floppy Obesity (constantly hungry) Mild mental retardation Sex Chromosome Disorders Klinefelter’s Turner’s Fragile Syndrome Syndrome X Syndrome Klinefelter’s Syndrome 47, XXY 1 in 1000 male live births Mild learning difficulties Taller than average with long lower limbs Show mild enlargement of breasts Infertile (absence of sperm) Treat with testosterone Turner’s Syndrome 45, X Low incidence Look normal Ovarian failure Normal intelligence Short stature Estrogen therapy Fragile X Syndrome Most common inherited cause of mental retardation 1 in 2000 males High forehead, prominent jaw, autism Gap in X chromosome Single Gene Disorders Cystic Fibrosis Hemophilia Sickle Cell Anemia Phenylketonuria Cystic Fibrosis (CF) Recessive disorder Mutation stops production of protein in lung cells, pancreas Thick mucus, bacterial infections in lung “sweat test” Most common in Caucasians (1 in 3300) Chest percussions, diet supplements Shortened life expectancy Hemophilia Sex-linked Failure of blood to clot Rare in females Injections with clotting factors to stop bleeding episodes $350,000 a year in treatment Sickle Cell Anemia Mutation in blood protein “sickle” shape to RBC Screening tests Most common in African-Americans (1 in 375) Pain associated with blocked vessels, causes anemia (fatigue) Common where mosquito-borne malaria is present PKU Mutation disrupts function of enzyme Leads to high phenylalanine levels in brain (poisons) Mental retardation, epilepsy Screening newborns (heel prick) 1 in 10,000 Caucasian births Extremely rare in African-Americans Look normal Need low-protein diet, smelly formulas Self Quiz: Quick Check for Understanding 1. Which of the following is an X-linked disorder? b. heel prick c. X-ray A. testosterone injections b. chest percussions 4. Turner’s Syndrome is A. amniocentesis 3. How are CF patients treated? c. Down syndrome 2. How is PKU tested for? A. Angelman B. hemophilia A. 45, X b. 46, XX c. 47, XXY 5. Patients with Klinefelter’s Syndrome are A. all male b. all female c. male or female