* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download F 1 generation
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
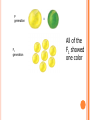
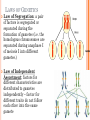
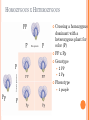
GENETICS! GREGORY MENDEL Born 1822; Died 1884 Monk and a teacher Work not recognized until 1900 Studied heredity by studying pea plants What is heredity? MENDEL’S PEA PLANTS Observed seven characteristics of pea plants with two different traits Controlled how each plant was pollinated Self-pollination or cross-pollination What’s the difference? MENDEL’S EXPERIMENTS Grew true-breeding plants What does it mean to be true breeding? Starting strain called parent generation or P generation Cross-pollinated P generation to produce offspring called the first filial generation or F1 generation F1 generation self-pollinated and produce the second filial generation or F2 generation P generation x P generation F1 generation x All of the F1 showed one color P generation x F1 generation F2 generation F2 produced plants about ¾ one trait and ¼ the other trait RESULTS Factor was controlling the traits since there were two traits there were two factors Alleles: represent the factors - dominant CAPITAL LETTERS; recessive lower case letters; They are alternate forms of genes. Dominant trait: Able to repress the other trait Recessive trait: repressed by the dominant Homozygous: same alleles; RR or rr – also called purebred or true breeding Heterozygous: one of each allele forming a hybrid Rr Genotype: allele pairs/actual DNA: RR, Rr, or rr Phenotype: physical appearance; red, yellow, green, tall, short, etc. *You only see the recessive phenotype when there are two of the recessive alleles. Whenever you see the dominant phenotype, you cannot tell the genotype.* Lead to the modern study of molecular genetics, the study of chromosomes and genes. Y y LAWS OF GENETICS Law of Segregation: a pair of factors is segregated or separated during the formation of gametes (i.e. the homologous chromosomes are separated during anaphase I of meiosis I into different gametes.) Law of Independent Assortment: factors for different characteristics are distributed to gametes independently – factor for different traits do not follow each other into the same gamete PROBABILITY Probability that a specific event will occur; expressed as a decimal, fraction, or percent Probability = Number of times an event happened Number of possible opportunities The predicted results are more likely to occur the more trials that are performed MONOHYBRID CROSSES Monohybrid cross: between individuals with one pair of contrasting traits ( mono = one) Punnett squares are used to help predict the probability of a trait HOMOZYGOUS X HOMOZYGOUS Crossing two plants homozygous for color (P) One dominant one recessive PP x pp Genotype 4 Pp Phenotype 4 purple HOMOZYGOUS X HETEROZYGOUS Crossing a homozygous dominant with a heterozygous plant for color (P) PP x Pp Genotype 2 PP 2 Pp Phenotype 4 purple HOMOZYGOUS X HETEROZYGOUS Crossing a heterozygou plant with a homozygou recessive for color (P) Pp x pp Genotype 2 Pp 2 pp Phenotype 2 purple 2 white HETEROZYGOUS X HETEROZYGOUS Both heterozygous for color (P) Pp x Pp Genotype 1 PP 2 Pp 1 pp Phenotype 3 purple 1 white TESTCROSS Used to determine the genotype of a individual with an unknown genotype Must use an organism of an known genotype hence use a homozygous recessive