* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
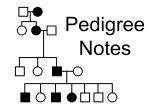
11.1 BASIC PATTERNS OF HUMAN INHERITANCE WHAT YOU WILL LEARN -How to determine if an inherited trait is dom/rec -Examples of DOMINANT/RECESSIVE disorders -Construct / Interpret PEDIGREES READING Q’s 1-IDENTIFY -Check the term that describes the genotype of a person who expresses a recessive trait -HOMOZYGOUS: organism with 2 of the same alleles for a particlular trait -aa READING Q’s 2-CATEGORIZE: The following genetic disorders as RECESSIVE or DOMINANT a-albinism b-Huntington's c-cystic fibrosis recessive dominant recessive dominant recessive dominant READING Q’s 3-EXPLAIN -For what purpose is a genetic pedigree used? -study genetic relationships -trace inheritance of a trait generation to generation READING Q’s 4-DRAW The symbols that are used to represent a male AND female in a pedigree MALE- FEMALE- READING Q’s 5-EVALUATE -Circle the carriers in the second generation READING Q’s 6-CALCULATE -What percentage of the children in this family inherited TaySachs disease? -1/4=25% READING Q’s 7-IDENTIFY -Do any grandchildren in this family have polydactyly? -NO READING Q’s 8-EXPLAIN -Why are recessive traits difficult to study? -Not all people who carry the recessive allele have the trait GROUP WORK: APPLICATION NOTES -As a group complete the areas below using your knowledge from the reading/discussion. MAIN IDEA REVIEW VOCAB RECESSIVE / DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS VOCAB -carrier -pedigree MAIN IDEA -PEDIGREESinheritance of traits over several generations REVIEW VOCAB DEFINE: gene -segment of DNA on chromosome DEFINE: homozygous -2 identical alleles [TT / tt] DEFINE: heterozygous -2 different alleles [Tt] RECESSIVE/DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS COMPARE/CONTRAST: recessive and dominant genetic disorders RECESSIVE -expressed when indv HOMO recessive [tt] DOMINANT -expressed when indv HOMO dominant [TT] or HETERO [Tt] RECESSIVE/DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS EXPLAIN why recessive disorders are more common than dominant disorders. -DOMINANT: only one allele must be inherited to be affected -if DOM trait interferes w/ survival- no pass on -RECESSIVE: carriers do NOT display the disorder -many carriers are unaware they carry an affected gene RECESSIVE/DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS IDENTIFY: the disease for each dominant/recessive disorders -caused by altered genes; results in lack of skin pigmentation -ALBINISM -RECESSIVE -characterized by body’s inability to tolerate galactose -GALATOSEMIA -RECESSIVE -gene found on chromosome 15;characterized by lack of enzyme that breaks down fatty acids -TAY SACHS -RECESSIVE RECESSIVE/DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS IDENTIFY: the disease for each dominant/recessive disorders -affects the nervous system; no treatment; breaks down part of brain -HUNINGTON’S -DOMINANT -affects mucus-producing glands, digestive enzymes, sweat glands -CYCTIC FIBROSIS -RECESSIVE -affects height and body size -ACHONDROPLASIA -DOMINANT RECESSIVE/DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS PREDICT: what are the chances of 2 carriers of cystic fibrosis having a child with cystic fibrosis? F f F FF Ff f Ff ff ¼= 25% RECESSIVE/DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS Positive Exposure Positive exposure video clip Rick Guidotti - PART 2 Positive Exposure Inside Edition Part I - YouTube PEDIGREE BASICS [the FAMILY TREE of genetics] WHAT is it: -diagram explaining genetic history WHO uses it: -scientist -genetic counselors WHY use it: -probability of child having disorder/condition -determine disorder/condition as autosomal/sex linked PEDIGREES SUMMARIZE: pedigree symbols MALE CARRIER -sqaure - -half shaded symbol / FEMALE -circle - PARENTS/OFFSPRING -line down from parent, circles/squares on second row AFFECTED MALE -shaded square AFFECTED FEMALE -shaded circle PARENTS -circle joined to square GENERATIONS -I, II , III, IV,V STEPS for INTERPRETING PEDIGREES 1- DETERMINE if the pedigree chart is showing: AUTOSOMAL or X-LINKED disorder -autosomal: -If it is a 50/50 ratio between men and women -x-linked: -If most of the males in the pedigree are affected 2- DETERMINE if disorder is DOMINANT or RECESSIVE -dominant: -one of the parents must have the disorder. -recessive -neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. Connecting Pedigree Symbols Married Couple Siblings EX- PEDIGREE CHART PRACTICE INTERPRETING 1. Determine if the pedigree chart shows an autosomal or X-linked disease. -If most of the males in the pedigree are affected the disorder is X-linked -If it is a 50/50 ratio between men and women the disorder is autosomal. PRACTICE: Interpreting Is it Autosomal or X-linked? Answer Autosomal Interpreting a Pedigree Chart 2. Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive -If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. -If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. PRACTICE: Interpreting Dominant or Recessive? Answer Dominant PRACTICE: Interpreting • Dominant or Recessive? Answer • Recessive ANALYZING PEDIGREES EVALUATE: the inheritance of achondroplasia shown in the pedigree -parent w/ disorder -father -#children with disorder -1 / 1st born son -genotype of younger son -homozygous recessive / aa ANALYZING PEDIGREES ANALYZE and RESPOND: -RECALL if the trait is rec or dom based on the following information: -individuals I-1 and I-2 are unaffected but have affected child RECESSIVE DOMINANT X -SPECIFIY if parents II-1 and II-2, who have an affected child, are carriers of that trait X CARRIER NOT A CARRIER -TELL whether there is a dominant gene in the genotype of II-4 X NONE A LEAST ONE -Individual II-1is in generation 2 X TRUE FALSE ANALYZING PEDIGREES THINK BACK and RESPOND: -A scientist uses a pedigree to study family history TRUE FALSE X -A pedigree traces the inheritance of a particular trait through only two generations MANY TRUE FALSE X -In a pedigree, one who does not express the trait is represented by a darkened circle/square TRUE FALSE X -In a pedigree, a horizontal like between 2 symbols shows that these individuals are the parents of the offspring X TRUE FALSE ANALYZING PEDIGREES DIAGRAM: Suppose both parents can roll their tongues but their son cannot. [TONGUE ROLLING = DOMINANT / T] DRAW a pedigree showing this trait LABEL each symbol with the appropriate genotype What was the probability that they would have a non-tongue roller offspring? (hint: punnet square) -both parents carry recessive gene -parent genotype Tt -son genotype tt -probability of child tt= 25% PEDIGREE CHART PRACTICE PEDIGREE PRACTICE A PEDIGREE PRACTICE B PEDIGREE PRACTICE C PEDIGREE PRACTICE D INVESTIGATING HUMAN PEDIGREES -USE the information provided in the transcript to construct a pedigree showing hairy earlobes* in a family *HE -DETERMINE the oldest couple in the family -DRAW their pedigree symbols—include names -CONTINUE with other members in the family -DETERMINE genotypes as you gather enough information