* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - SchoolRack
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
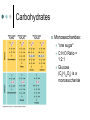
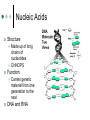
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Introductory Terms Macromolecule = “giant” molecule of living matter Monomer = subunits that serve as the building blocks of a polymer Example: Lego block Polymer = monomers linked together Example: Lego castle Macromolecular Reactions Dehydration Synthesis: 2 molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of water Hydrolysis: Water is used to break up polymers to monomers Macromolecular Diversity Diversity in polymers is due to differing arrangements of monomers… Nearly infinite possibilities… Alphabet analogy Carbohydrates Structure: C:H:O in a 1:2:1 Ratio Example: C6H12O6 Functions: Short-term energy storage • Pasta dinner before the big race, game, etc. Structural Support Carbohydrates Monosaccharides: “one sugar” C:H:O Ratio = 1:2:1 Glucose (C6H12O6) is a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Disaccharides: “double sugar” 2 monosaccharides joined together by a glycosidic linkage (covalent bond) Sucrose = glucose + fructose Carbohydrates Polysaccharides Polymers in which a few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides are linked together Starch and glycogen are examples Carbohydrates Structural Polysaccharides Cellulose • Major component of plant cell walls • Cannot be digested by humans • Fiber! Chitin • Used by arthropods to build exoskeletons • Cell wall of fungi Lipids Structure: Made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Do not dissolve in water Functions: Long-term energy storage Chemical messengers (hormones) Insulation Waxes Lipids Fats Made of glycerol and 3 fatty acids Fatty acid has a long carbon skeleton and a carboxyl group C-H bonds responsible for hydrophobia of fats Lipids Fats Saturated Fat = no double bonds • Saturated with hydrogen Unsaturated Fat = double bonds • Not saturated with hydrogen Lipids Phospholipids Have only 2 fatty acids Instead of 3rd fatty acid, they have a phosphate group Major component of cell membrane Lipids Steroids Made up of 4 interconnected rings Examples: • Cholesterol • Testosterone • Estrogen Proteins *** Most of a cell is made up of proteins Instrumental in almost everything organisms do Structure: All proteins are created from unique combinations of 20 different amino acids C,H,O,N Major Functions: Structure Defense (antibodies) Enzymes Proteins Amino Acids Amino acids are the monomers of proteins Organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups 20 types of AAs that make up 1000s of different proteins AAs are linked together by peptide bonds Amino Acids Proteins A protein is one or more polypeptides precisely twisted, folded and coiled into a molecule of unique shape (3-D) 4 Levels of Protein Structure Primary Structure • Unique sequence of AAs • Example: Tryptophan-leucine-glycine-glycine-lysine-phenylalanine-serine-leucine • Sickle Cell Anemia Proteins Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary Structure: The amino acid chain is folded into unique shapes because of hydrogen-bonding This gives each protein a unique shape Proteins Denaturation: When pH, salt concentration, temperature, and/or other environmental factors are altered, the protein may unravel and lose its shape Biologically inactive Structure + function Nucleic Acids Structure Function Made up of long chains of nucleotides CHNOPS Carries genetic material from one generation to the next DNA and RNA