* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry PowerPoint
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
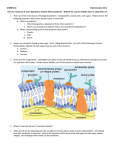
10/20 – Q of D Intro to Biochemistry 1. What do you think is meant by “you are what you eat” Biochemistry Vocab 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Monomer Polymer Macromolecule Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Disaccharide Polysacchaide Lipid Fatty acid Triglyceride 11. Oil 12. Protein 13. Amino acid 14. Peptide bond 15. Enzyme 16. Substrate 17. Active site 18. Nucleic acid 19. Nucleotide Organic Compounds Exs: coal, wool, wood, oil, sugar Over 2 million compounds All organic compounds contain CARBON Exceptions: CO and CO2 Carbon Has an atomic number of 6 Which means it has 6 e Can form 4 covalent bonds Carbon Bonds with other C or with H,O,N,S,P Can bond in straight chains, branched chains, or rings Carbon Ring Branched chain Carbon variety Carbon Video Main idea of part 1: Main ideas of part 2: Main ideas of part 3: Main ideas of part 4: Main ideas of part 5: (on back of notes ) CARBON VIDEO Functional Groups Can influence the characteristics and chemical reactions Ex: adding an OH functional group makes an alcohol. Ethane becomes ethanol ETHANE C2H6 COLORLESS, ODORLESS GAS PART OF NATURAL GAS ETHANOL C2H5OH LIQUID MADE DURING FERMENTATION USED IN ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES USED AS AN ANTISEPTIC Functional Group Examples Building Molecules Monomer each individual molecule, a building block Polymer made by joining monomers together Macromolecule a large polymer Condensation (Dehydration Synthesis) The process of joining monomers to make polymers Must remove 1 water for every bond formed Hydrolysis The process of breaking apart polymers Must add 1 water for every bond that is broken Chemical/Molecular Formula Ex: C6H12O6 Structural Formula Isomer Same chemical or molecular formula but different structural formula i.e.…same parts but put together differently Isomer Example: Simple Sugar C6H12O6 Can be glucose, fructose or galactose (look at picture page) GLUCOSE GALACTOSE FRUCTOSE 4 Organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Sugars, Starches, Fiber Carbohydrates Composed of C H O Ratio of 1C:2H:1O 60% of diet End in – ose Quick energy, #1 fuel source for body Examples: Carbohydrates Monosaccharides – simple sugars Are the building blocks (monomers) of bigger carbohydrates 3 most common: 1. Glucose ○ Main energy source ○ Dextrose ○ Blood sugar, IV fluids 2. Fructose in fruit and veggies sweetest 3. Galactose milk/dairy The 3 Monosaccharides Glucose Fructose Galactose The formula for all 3 monosaccharides is C6H12O6 but they are all structurally different so they are isomers. Disaccharides – double sugars Formed by condensation Sucrose Lactose Maltose Sucrose – table sugar ○ Glucose + fructose Lactose – milk sugar ○ Glucose + galactose ○ Lactose intolerant Maltose – brewer’s sugar ○ Glucose + glucose Disaccharides Formula C12H22O11 WHY? C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 C12H24O12 H2O C12H22O11 Glycosidic Linkage Disaccharide Picture Glycosidic linkage MALTOSE Polysaccharides complex sugars 100’s of sugars all bonded in same direction 100’s of sugars – but they are bonded in alternating directions 100’s of sugars in branched chains. Starch Plant starch Sugars bonded in the same direction Examples: Glycogen Animal Starch Highly branched chains Stored in liver and muscles Cellulose Bonded in opposite directions Humans cannot digest for ENERGY Eat for vitamins and minerals Cellulose Is insoluble (doesn’t dissolve). Also called fiber. Your body is lacking the enzyme to break the bonds apart and get out the energy. Polysaccharides complex sugars 100’s of sugars all bonded in same direction 100’s of sugars – but they are bonded in alternating directions 100’s of sugars in branched chains. Getting Energy from Polysacccharides Must be broken apart using the process of hydrolysis and then the monosaccharides can be used The bigger the carb the longer it takes to break down – more sustained energy Carbs and Nutrition Simple Carbs Mono and disaccharides Sugars Very quick burning Spike in energy level Followed by a crash Make you want more of them Need less in diet Complex Carbs Polysaccharides Starch and fiber Take longer to break apart and burn Provides a steadier/more constant energy source Whole grains, seeds Need more in diet •The goal behind carb loading is to help our body store glycogen. •The more glycogen stored, the more energy is available to us on race/game day. •Accomplished by increasing carb consumption and decreasing exercise intensity/duration. Carb Pit Stop 1. The monomer of a carbohydrate is ______ 2. The most common monosaccharide is ___ 3. The sweetest monosaccharide is _____ 4. The monosaccharides have the formula___ 5. They all look different so they are ________ 6. Table sugar is called ____________ 7. Milk sugar is called ______________ 8. The bond between monosaccharides is ___ 9. The formula of a dissacharide is _____ 10. The polysaccharide that can’t be broken down by humans is ___________ 11. Excess sugar in humans is stored as ____ 12. The type of carb found in plant cell walls is __ Fats, Oils, Waxes Large amounts of C, H - little O Fats, oils, waxes Insoluble in water - nonpolar Uses for Lipids Energy storage – long term Insulation Padding for vital organs Cell membranes Waterproofing Buoyancy Healthy hair and skin Absorption of Vitamins A and D Monomers Fatty acids and glycerol (a type of alcohol) Can have 1, 2 or 3 fatty acids Are called monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides Types of Fatty Acids 1. Saturated – solid, bad Exs: lard, butter, animal fat, fat on meat The Bad Fat Brothers Polyunsaturated – several CC double bonds, Exs: sunflower and corn oil Monounsaturated – one C-C double bond, liquid, better for health, Exs: olive oil, canola oil Types of Fatty Acids Saturated Polyunsaturated Omega-3 fats Best fat to eat Protects against heart disease, acts as an anti- inflammatory, eases muscle aches, helps the brain Lack of this fat is linked to depression Found in tuna fish, salmon, walnuts Trans-Fatty Acids Chemically processed Worst type of fat to consume Lead to heart disease and high cholesterol Found in stick margarine, commercially fried foods, packaged baked goods Many companies are now changing their “formulas” to get rid of these fats The Bad Fat Brothers Types of Lipids Triglycerides 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol Fats – solid Types of Lipids Oils – lipids that are liquid at room temperature Waxes – waterproofing Steroids Cholesterol 2 types – ○ LDL – bad ○ HDL - good Steroid Cholesterol Proteins Composed of C,H,O,N and S Are: Structural building materials (ex: muscles) Functional chemical compounds (enzymes) Foods such as eggs, cheese, meat, nuts Proteins Made from amino acids There are only 20 different amino acids Amino acids used in different numbers and combinations to make millions of proteins (like letters making words) Central Carbon glycine “R” valine “R” leucine “R” alanine “R” Each individual is unique because of their proteins which is determined by your DNA Non-essential amino acids – body can make these Essential amino acids – body cannot make – must be obtained through food 10 essential – children 8 – adults These are “recycled” throughout body and ecosystem. (fish example) Proteins are joined together by condensation 2 together – dipeptide Many together - polypeptide Chains have 30-3000 amino acids Special bond between amino acids is called peptide bond Enzymes Catalysts – speed up reactions so they can occur at normal body conditions Substrate – what is being catalyzed Active site –where enzyme and substrate interact Enzymes Lactase Enzyme Enzymes Can denature – unfold the protein Examples: Sucrase Lactase Lipase Nucleic Acids Master molecules 2 types: DNA – have directions (blueprint) for making proteins RNA – transfers information 3 billion nucleotides to make up DNA in every cell in your body Monomer is nucleotide 3 parts ○ Phosphate ○ Sugar ○ Nitrogen base REVIEW Macromolecule Polymer Carbs Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Monomer Bond Uses