* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt version
Peer-to-peer lending wikipedia , lookup
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Debt settlement wikipedia , lookup
Debt collection wikipedia , lookup
United States housing bubble wikipedia , lookup
Debt bondage wikipedia , lookup
Debtors Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
First Report on the Public Credit wikipedia , lookup
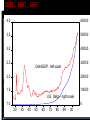
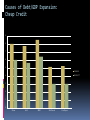
Getting to the Root of the Cause MACROFINANCE CRASH OF 2008 Landmark Events in Crisis Winter 2006-07 Real Estate Prices Fall Summer 2007 Countrywide Mortgage fails Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac in distress Summer-Fall 2007 Northern Rock (British lender) fails Spread between T-Bill and LIBOR grows large Recession begins Spring 2008 Bear Stearns fails Summer 2008 Oil & other commodity prices spike September 2008 Lehman Bros. fails AIG near failure Stock market plunges LIBOR; Commercial Paper markets freeze (“wholesale money markets” Wachovia (bank) fails Fed begins/expands unusual interventions Financial Stress Leading up to Sept 08 TED = T-Bill Rate – LIBOR (usually equal) KCFSI = Kansas City Fed Financial Stress Index 6 5 4 3 6 3.5 5 3.0 1 4 2.5 0 3 2.0 2 1.5 1 1.0 0 0.5 -1 0.0 -2 -0.5 2 -1 07M01 07M07 08M01 08M07 TED 09M01 09M07 KCFSI 90 92 94 96 98 00 TED (Libor -TB3) 02 04 06 KCFSI 08 Relative Size of Financial & Macroeconomic Losses Time Frame Stock Market Change (DIJA) 1907-08 Length GDP Change (Real) Stock Change/ GDP Change Highest Unemp. Rate -40% 13 months -5% 8 8.00% 1919-20 -46% 15 months -23% 2 11.30% 1929-33 -83% 43 months -29% 3 25.20% 1937-38 -49% 15 months -7% 7 19.10% 1946-48 -35% 21 months -5% 7 4.00% 1973-75 -51% 25 months -5% 10 9.00% 1978-82 -37% 48 months -7% 5 10.80% 1987-88 -28% 5 months >0% NA 5.80% 2000-01 -18% 16 months -1% 18 6.10% 2007-2009 -53% 16 months -4% 13 10.10% Key Questions Cause/Effect What was the gasoline, what was the match? Responses Get rid of gasoline? Get rid of matches? Store in safer places? Fuel for the Crash Home Mortgage Debt = 1/3 Commercial Loans Amplified by implied or explicit guarantees to banking/financial system (“moral hazard”) Fed/Fannie-Freddie Amplified by competition for loans Amplified by gov’t push for loans to non-qualifiers DEBT, DEBT, DEBT 4.0 60000 3.5 50000 3.0 40000 2.5 30000 Debt/GDP - left scale 2.0 20000 1.5 10000 U.S. Debt -- right scale 1.0 0 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Mortgage Debt Part of the Story, Commercial Lending a Bigger Part 4.0 3.5 Total Debt/GDP 3.0 2.5 2.0 Non-house-govt/gdp 1.5 1.0 House-debt/gdp 0.5 Govt Debt/gdp 0.0 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 00 05 “Poster” Project for Commercial (nonmortgage) Debt (Artist Image) $11 Billion City Center Project Las Vegas – MGM Mirage Bank Loan/Bond Funded The Real Thing Limits of Debt Constraints Economy-wide Budget Constraint: Income + Debt Value = Debt Payments + Consumption Over the long run: Debt Value = Debt Payment or else “Ponzi Scheme” Implies Consumption must be based on Income (not debt) Why So Much Attention on Mortgage Debt? Mortgage market was the first “on fire” Many interpreted as “the cause” Mortgage debt traded daily in markets Quickly reflecting change in valuations Info on this appearing by 2007 Commercial bank loans not traded in markets Change in value reported slowly by banks over time Info on this not really appearing until into 2009 MATCH FOR THE FUEL Falling real estate prices & mortgage defaults beginning in 2006-2007 Lenders not receiving expected payments Begins chain of financial firms in trouble because not receiving payments from other firms Oil Price (and many other basic commodities) Price Spikes of 2008 Oil from $70/barrel to $145/barrel Oil price spikes leading all but 1 post WWII recession Limiting Future Problems? LIMIT “SYSTEMIC RISK” MANY IDEAS: Stricter regulation including more owner “capital” per loan Limit financial firm size Insurance fees tied to risks of lending Eliminate subsidies to housing lending like Fannie/Freddie Bottom Line: whatever the specifics, systemic risk only reduced through substantially less lending Tradeoff: Benefits of lending-Risks of lending Causes of Debt/GDP Expansion: Cheap Credit 9 8 7 6 5 1990-99 2003-07:7 4 3 2 1 0 Prime AAA BBB Fed Funds ComPaper Causes of Cheap Credit: Public Sector Backing of Debt (Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and others) 9000 GSE Assets + Govt-MBS (in Billions $) 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 90 92 94 96 98 00 02 04 06 08 Cheap Credit: Foreign Investors Liked U.S. .06 Capital Inflows Relative to GDP .05 .04 U.S. .03 .02 .01 .00 Euro Area -.01 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 Causes of Cheap Credit: Expansion of “Wholesale” Money Markets Cheap Credit: Wholesale Market Expansion Cheap Credit: Wholesale Market Expansion Securitization, e.g. CDOs Pooling mortgage (other debt) risk (CDOs, SPVs) Credit Insurance Transferring Risk (CDS) Cheap Credit: Fed Responsible? 20 16 Inflation Rate & Smoothed (HP Filter) 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 00 02 04 06 08