* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1.2 - Electronic Signal & Switches
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
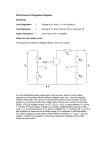
EKT 121 / 4 ELEKTRONIK DIGIT 1 CHAPTER 1.2 : Electronic Signals & Switches Digital Signals Made up of a series of 1s and 0s Represent numbers, letters, symbols, or control signals Timing diagram of a digital signal. Digital Signals Digital system respond to digital state (0 or 1) and not actual voltage In timing diagram, LSB may not always be on the right. Depends on which method is used Clock waveform timing Timing is very important for digital signals. Clock & timing circuits: Periodic clock waveforms: Produce clock waveforms Trigger digital signal at precise intervals Voltage vs time Waveform repetitive, at specific time interval, pulse identical. Frequency: Reciprocal of clock period (tp) f = 1 / tp Serial & Parallel Representation Serial : Use 1 electrical conductor for data to travel Inexpensive but slow Can transmit only 1 bit for each clock period Eg: Internet, computer-to-computer communication. Parallel: Use separate electrical conductor for each bit If system uses 8-bit numbers, 8 lines are required Expensive but fast Eg: computer-to-printer Exercise Sketch serial & parallel representations of 4-bit number 0111. Clock frequency 5 MHz, find time needed to transmit using both method. LSB is transmitted first. Switches in Electronic Circuits Switching from one voltage to another (0 V to +5 V) Cause the transitions between 0 and 1 digital levels Make and break a connection between 2 electrical conductors. Manual switch Diodes Transistors Manual Switch Almost ideal ON and OFF resistance ON : Contacts closed R = 0 ohms OFF : Contacts opened R = ∞ ohms A Diode as a Switch Diode : allows current to flow in one direction only Forward biased Anode voltage more +ve than cathode Allow current flow Reverse biased Anode voltage equal or more –ve than cathode Current cannot flow A Transistor as a Switch Three-terminal semiconductor components that allows an input signal at one terminals to cause the other 2 terminals become short or open circuit. Emitter, base, collector Input signal (1 or 0) applied to base. A Transistor as a Switch For NPN transistor Apply +ve voltage from base to emitter cause collecteremitter junction short (ON transistor) Apply -ve voltage or 0 V from base to emitter cause collecter-emitter junction open (OFF transistor) Emitter, base, collector Input signal (1 or 0) applied to base. END OF Electronic Signal & Switches