* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force - Eastside Physics
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
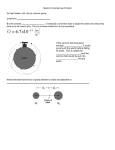
Force • Force is a push or pull on an object • The object is called the System • Force on a system in motion causes change in velocity = acceleration • Force is a vector, it has direction • External World = everything around the system that exerts a force Types of Forces Forces Contact • When the external world is in contact with the system and exerts a force ex. Hand that pushes, Rope that pulls Field Forces • A force exerted on a system without touching the system ex. Gravity, Magnetic force, Interaction between charged particles Agent • An agent is the item in the external world that causes the force to act on the system • ex. The hand that holds The rope that pulls The earth The magnet Free Body Diagram • A diagram representing the System, Agent and the Forces acting on the system • System is represented by a dot • Forces represented by arrows pointing in the direction of the force, away from system • Label each force with a subscript • Choose direction of +ve usually towards stronger force String Positive Direction Ball Ft (force of tension) Fg (force of gravity) Combining Forces • As forces are vectors they can be added just as vectors ex.1 Fa + Fb = F net ex.2 Fa + Fb = Fnet Nonlinear non perpendicular forces are added by adding x and y components of the force vectors Newton’s First Law • An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted on by an external net force • Also known as the Law of Inertia • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist change in motion • Equilibrium = if the net force on a system is zero the system is in equilibrium speed and direction is unchanged. Common Types of Forces • Friction F = Contact force opposing motion of two surfaces, parallel to the surface and opposite to the direction of motion • Normal F = Contact force exerted by system’s surface perpendicular to and away from surface • Spring F = A restoring force- push or pull of spring exerted on system opposite to displacement f N sp • Tension F = pull exerted by a rope on a system, away from the system and parallel to the rope • Thrust F = a force that moves a system in the same direction as the acceleration • Weight F = a field force on a system due to gravity directed to the center of the earth T THRUST g Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is equal to the net force acting on it divided by the mass of the object a = F/m or F = ma • The larger the force the greater the acceleration The greater the mass with the same force the lower the acceleration • Force of 1N = 1kg * 1m/s.s Newton’s Third Law • All forces come in pairs equal and opposite in direction • ex. A ball on a table and the table on the earth. Forces-ball on table / table on ball -table on earth/ earth on table - ball on earth/ earth on ball Net free body diagram ball table earth F table on ball F earth on ball Drag Force and Terminal Velocity • Drag Force is the force exerted on an object as it moves the a fluid ex. Air and water • as the speed of the object through the fluid increases so does the drag • Drag is effected by the fluids viscosity and temperature • Terminal velocity is when the drag force equals the force due to gravity no acceleration constant velocity app.(60m/s) Tension • Is a force exerted by a string or rope on a system • It is assumed the rope has no mass • Tension within all points of the rope is equal and opposite to the force exerted by the system’s weight Example of bucket on rope F T F g =mg Normal Force • Is a contact force exerted by a surface on an object. This force is perpendicular to the surface of contact N Fg Gravitational Force • Gravitational force is the mutual attraction between any two bodies in the universe • Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation =every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them • F g = Gm1m2/r2 where G = the universal gravitational constant = 6.67*10-11N.m2/kg2 Gravity • As weight = mg then w = GMEm/r2 • Then g = GME/r2 • Therefore the larger the mass of an object the larger the effective gravity it generates Forces of Friction fs and fk • An object moving on a surface or passing through a fluid experiences resistance to motion = friction • F f = forces of static friction = the force that prevents movement of an object that is being subjected to an external force • When movement is about to occur fs is at max. s fs and f k • When a force F exceeds Ffs max then movement will occur and the new friction force is less. This new friction force is called the Force of kinetic friction fk • When F-fk= positive value there is acceleration • Both fs and fk are proportional to the normal force; fs=usn and fk=ukn • us is the coefficient of static friction • Uk is the coefficient of kinetic friction Solving Friction Problems • Draw a free body diagram making sure to label all forces