Chapter 1: MEASUREMENT
... 20. The position y of a particle moving along the y axis depends on the time t according to the equation y = at − bt2 . The dimensions of the quantities a and b are respectively: A. L2 /T, L3 /T2 B. L/T2 , L2 /T C. L/T, L/T2 D. L3 /T, T2 /L E. none of these ans: C 21. A particle moves along the x a ...
... 20. The position y of a particle moving along the y axis depends on the time t according to the equation y = at − bt2 . The dimensions of the quantities a and b are respectively: A. L2 /T, L3 /T2 B. L/T2 , L2 /T C. L/T, L/T2 D. L3 /T, T2 /L E. none of these ans: C 21. A particle moves along the x a ...
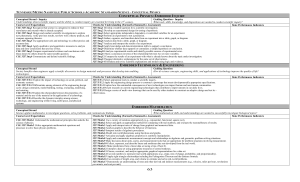
CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS: EMBEDDED INQUIRY EMBEDDED
... 3237.1.3 Explore characteristics of rectilinear motion and create distance-time graphs and velocity-time graphs. 3237.1.4 Investigate the characteristics of centripetal motion and centripetal acceleration. 3237.1.5 Evaluate the dynamics of systems in motion and collisions including friction, gravity ...
... 3237.1.3 Explore characteristics of rectilinear motion and create distance-time graphs and velocity-time graphs. 3237.1.4 Investigate the characteristics of centripetal motion and centripetal acceleration. 3237.1.5 Evaluate the dynamics of systems in motion and collisions including friction, gravity ...
Science Bowl Questions/Answers for Physics
... PHYS-91; Short Answer: A charged particle is moving in a UNIFORM magnetic field. If the direction of motion of the charged particle is parallel to the magnetic field, describe the shape of the charged particle's path. ANSWER: STRAIGHT LINE PHYS-91; Multiple Choice: An infinitely long wire carries a ...
... PHYS-91; Short Answer: A charged particle is moving in a UNIFORM magnetic field. If the direction of motion of the charged particle is parallel to the magnetic field, describe the shape of the charged particle's path. ANSWER: STRAIGHT LINE PHYS-91; Multiple Choice: An infinitely long wire carries a ...
Notes: AP Physics 1
... For AP Physics 1, we are using the textbook Physics Fundamentals, by Vincent P. Coletta (Physics Curriculum & Instruction, Inc., 2010). These notes are meant to complement the textbook discussion of the same topics. In some cases, the notes and the textbook differ in method or presentation, but the ...
... For AP Physics 1, we are using the textbook Physics Fundamentals, by Vincent P. Coletta (Physics Curriculum & Instruction, Inc., 2010). These notes are meant to complement the textbook discussion of the same topics. In some cases, the notes and the textbook differ in method or presentation, but the ...
Persson2006-Contact_mechanics_for_randomly_rough_+
... the theory is (approximately) valid for all squeezing forces. In addition, the theory is very flexible and can be applied to more complex situations such as contact mechanics involving viscoelastic solids [9,11], adhesion [10] and plastic yield [9]. It was originally developed in the context of rubb ...
... the theory is (approximately) valid for all squeezing forces. In addition, the theory is very flexible and can be applied to more complex situations such as contact mechanics involving viscoelastic solids [9,11], adhesion [10] and plastic yield [9]. It was originally developed in the context of rubb ...
MODELING OF IMPACT DYNAMICS OF A TENNIS BALL WITH A
... tennis ball as it comes into contact with a flat surface. The model is supposed to behave as a rigid body in the horizontal direction. The model is used to predict contact of the ball with the ground and applies from start of contact to end of contact. The springs and dampers for both the vertical a ...
... tennis ball as it comes into contact with a flat surface. The model is supposed to behave as a rigid body in the horizontal direction. The model is used to predict contact of the ball with the ground and applies from start of contact to end of contact. The springs and dampers for both the vertical a ...
final exam - PHYSICS57
... 1. At the instant when the traffic light turns green, an automobile starts with a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2. At the same instant a truck travelling with a constant speed of 8.5 m/s overtakes and passes the automobile. (a) How far beyond the starting point will the automobile overtake the tru ...
... 1. At the instant when the traffic light turns green, an automobile starts with a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2. At the same instant a truck travelling with a constant speed of 8.5 m/s overtakes and passes the automobile. (a) How far beyond the starting point will the automobile overtake the tru ...
Resource Guide for Physics and Whitehead
... of Whitehead’s significance.” [Lucas, 1989, p. 199] Unification of geometry and physics – Whitehead’s 1905 Memoir “undertook the unification of geometry and physics by means of …symbolic logic--which was forged by Whitehead and Russell between 1900 and 1910. The paper constitutes a synthesis unique in ...
... of Whitehead’s significance.” [Lucas, 1989, p. 199] Unification of geometry and physics – Whitehead’s 1905 Memoir “undertook the unification of geometry and physics by means of …symbolic logic--which was forged by Whitehead and Russell between 1900 and 1910. The paper constitutes a synthesis unique in ...
1000-Solved-Problems-in-Classical-Physics-An-Exercise
... This work is subject to copyright. All rights are reserved, whether the whole or part of the material is concerned, specifically the rights of translation, reprinting, reuse of illustrations, recitation, broadcasting, reproduction on microfilm or in any other way, and storage in data banks. Duplicat ...
... This work is subject to copyright. All rights are reserved, whether the whole or part of the material is concerned, specifically the rights of translation, reprinting, reuse of illustrations, recitation, broadcasting, reproduction on microfilm or in any other way, and storage in data banks. Duplicat ...
Schaum`s Theory and Problems of Theoretical Mechanics
... with the geometry of the motion, 2. Dynamics, which is concerned with the physical causes of the motion, 3. Statics, which is concerned with conditions under which no motion is apparent. AXIOMATIC FOUNDATIONS OF MECHANICS An axiomatic development of mechanics, as for any science, should contain the ...
... with the geometry of the motion, 2. Dynamics, which is concerned with the physical causes of the motion, 3. Statics, which is concerned with conditions under which no motion is apparent. AXIOMATIC FOUNDATIONS OF MECHANICS An axiomatic development of mechanics, as for any science, should contain the ...