* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
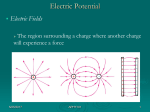
Forces Introduction Why do objects speed up or slow down? Forces: push, pull, friction, etc. Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) • Laws of motion, law of gravitation, telescopes, properties of light, calculus, etc. 5/22/2017 APHY101 1 Forces Force Contact (push) and field (gravity) • A vector quantity Net force = sum of all the force vectors • This causes an acceleration or maintains equilibrium 5/22/2017 APHY101 2 Forces Newton’s First Law An object remains at rest or moves at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net external force. This applies in a non-accelerating reference frame such as this room. Newton’s laws don’t apply in your car as it accelerates. 5/22/2017 APHY101 3 Forces Mass (m) The property of an object to resist changes in its velocity. • Inertia • Unit: kg 5/22/2017 Mass ≠ Weight APHY101 4 Forces Gravitational Force or weight A force directed toward the center of the Earth (or other object) Weight = m g • Unit: Newtons (N) or Pounds (lbs) 5/22/2017 APHY101 5 Forces Newton’s Second Law Acceleration is proportional to the net force applied and inversely proportional to the mass. or 5/22/2017 APHY101 Fnet = m a 6 Forces Newton’s Third Law Action and reaction • Forces come in pairs and involve two objects You and the Earth • Are the forces equal in magnitude? accelerations equal in magnitude? 5/22/2017 APHY101 Are the 7 Forces Normal Force Perpendicular to the surface between two objects. • A cup sitting on a table • Leaning your back against a wall • A car parked on a hill 5/22/2017 APHY101 8 Forces Friction A force that resists sliding motion • Depends on the materials in contact and the normal force between the materials. Reduction of friction – lubricants (ie. engine oil) When is friction a good thing? 5/22/2017 APHY101 9