* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
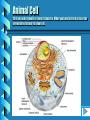
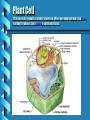
The Cell An internet laboratory on the cell, created by Wendy M. Rounds 5/3/00 The Cell Cells are the basic unit of life. Cells carryout all the necessary functions for life such as: reproduction, taking in nutrients and excreting wastes. Cells are made up of chemicals and molecules. Human cells contain mostly water. The Cell Cells are classified as prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells lack a well-defined nucleus and many organelles. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells include the protists, fungi, plant and animal cells. We will study these cells during this lab. The Cell Animal Cells Have centrioles Store glucose as glycogen Do not have a cell wall Contain mitochondria Plant Cells Lack centrioles Store glucose as cellulose or starch Have a cell wall Have large vacuoles Contain chloroplasts as well as mitochondria The Cell Animal Cell Click on the cell to study it in more detail Plant Cell Click on the cell to study it in more detail Animal Cell Click on each organelle to learn its function. When you have finished click on the arrow button to study the plant cell. Plant Cell Click on each organelle to study its function. When you have finished click here to study the animal cell or here to continue this lab. Cell Extensions Two types of cellular extensions are cilia and flagella. Cilia are small hairlike projections which beat to move substances. The respiratory tract is lined with cilia which only beat in one direction to move substances up from the lungs. (then we swallow them) Flagella (flagellum is the singular) are cellular projections which help the cell to move. A flagellum is found on sperm cells and helps them to swim to fertilize the egg. Lab Report Once you have reviewed the organelles of the animal and plant cells. Open the Lab Report which you downloaded from WebCT with this file. Nucleus Back The nucleus is the controller of the cell. It is surrounded by the nuclear envelope which controls what substances may exit/enter the nucleus. It contains DNA and the nucleolus. DNA is termed the “genetic blueprint” and directs all protein synthesis. The nucleolus makes ribosomes. Nucleus-Plant Back The nucleus is the controller of the cell. It is surrounded by the nuclear envelope which controls what substances may exit/enter the nucleus. It contains DNA and the nucleolus. DNA is termed the “genetic blueprint” and directs all protein synthesis. The nucleolus makes ribosomes. Ribosomes Free floating and fixed: Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Ribosomes are protein factories. All protein synthesis occurs within the ribosome. They may be fixed (attached to the endoplasmic reticulum) or free floating in the cytoplasm They are composed of rRNA and proteins. Back Ribosomes-Plant Free floating and fixed: Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Ribosomes are protein factories. All protein synthesis occurs within the ribosome. They may be fixed (attached to the endoplasmic reticulum) or free floating in the cytoplasm They are composed of rRNA and proteins. Back Endoplasmic Reticulum Back The endoplasmic reticulum or ER is a network of channels which assist in the synthesis and transport of cellular products. There are two types: smooth ER which is involved in the synthesis of lipid products such as steroid hormones. Rough ER which has ribosomes attached to it & is involved in protein synthesis. Endoplasmic Reticulum-Plant Back The endoplasmic reticulum or ER is a network of channels which assist in the synthesis and transport of cellular products. There are two types: smooth ER which is involved in the synthesis of lipid products such as steroid hormones. Rough ER which has ribosomes attached to it & is involved in protein synthesis. Golgi Apparatus This organelle consists of tubular channels which function to assemble, and check proteins coming from the rough ER. The golgi apparatus also ensures that the completed proteins go to the appropriate area of the cell. (that proteins for the cell membrane get to the membrane, proteins hormones exit the cell etc.) Back Golgi Apparatus-Plant This organelle consists of tubular channels which function to assemble, and check proteins coming from the rough ER. The golgi apparatus also ensures that the completed proteins go to the appropriate area of the cell. (that proteins for the cell membrane get to the membrane, proteins hormones exit the cell etc.) Back Lysosomes Back Lysosomes contain powerful digestive enzymes which break apart anything that gets inside it. They are important in protection (splitting bacteria) as well as, old organelles. Lysosomes are able to release the end products for reuse in the cell. It is important that the lysosome doesn’t rupture or the enzymes would digest the cell. Mitochondria Back Mitochondria are the “powerhouses” of the cell. They are responsible for carrying out aerobic cellular respiration. This process forms ATP from the food we eat and requires oxygen. Mitochondria-Plant Back Mitochondria are the “powerhouses” of the cell. They are responsible for carrying out aerobic cellular respiration. This process forms ATP from the food we eat and requires oxygen. Cytoskeleton Back The cytoskeleton functions as the “muscles and bones “of the cell. It consists of: Microfilaments: which help the cell to move (muscle contraction) Intermediate Filaments: which prevent the cell from being pulled apart. Microtubules: function in maintaining the cell shape. Cell Wall Only found in plant cells Surrounds cell membrane Composed of lignin and cellulose Function to strengthen and protect plant cells. Back Central Vacuole Large organelle Comsists of mostly water, plant pigments, and toxins. Functions for storage of nutrients and pigments, and retains waste products. The pigments which give a flower its color are stored in the vacuole. Back Chloroplasts Contain green pigment termed chlorophyll. Function in photosynthesis Back