* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
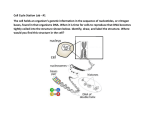
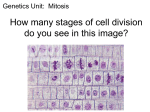
CELL DIVISION Cell Division/Reproduction Why? Cells divide for many reasons: In order to stay small Diffusion occurs at a faster, more efficient rate in smaller cells. Why would diffusion rate matter in cells? Remember what materials need to enter and exit the cell. DNA limits their size DNA can only control cells up to a certain size. Repair/replace old or damaged cells. Growth and Development We start out as one cell, mitosis allows that 1 cell to turn into billions of cells. Cell Cycles Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus No membrane bound organelles (ex. mitochondria, vacuole, chloroplast) A.) Cell division takes place in 2 steps: 1.) DNA is copied 2.) Cell splits by binary fission Cell Cycles Eukaryotic Cells Contain a nucleus and organelles. Repeating sequence of growth and division Occurs in two cycles for two purposes Mitosis Occurs in somatic (ordinary body cells) for growth and repair Creates 2 identical cells Meiosis Occurs in germ cells (ovaries and testes) to make gametes (sex cells). Creates 4 similar cells. Eukaryotic Cell Cycle 3 Stages Interphase G1: First growth phase S: Synthesis phase G2: Second growth phase Mitosis nuclear division Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Division of cytoplasm Centromere Interphase G1 – first growth phase: The cell doubles in size and the organelles double S – synthesis phase: the DNA that makes up the chromatin is copied (DNA replication) this is the longest phase of interphase. G2 – second growth phase: Growth and preparation for mitosis, second checkpoint. This is when the cell is preparing to divide. The LONGEST phase of the cell cycle 90% of the cell’s life is spent in Interphase. Interphase (G1, S, G2) Terms to know: (Start a VOCAB page) DNA related terms Chromosome Single piece of coiled DNA Diploid A cell that contains a set of chromosomes from mom and dad. (46 in Humans) Replicated Chromosome A single piece of DNA that has been copied through DNA replication Sister Chromatids 2 identical strands of DNA Non-Replicated Chromosome Single strand of DNA before it is copied Structural Terms Spindle Fibers Fibers that are attached to centrioles to help pull apart chromosomes Centrioles Organelles that aid in pulling apart chromosomes Centromere Structure that holds the replicated chromosomes together Mitosis (PMAT) Mitosis The nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei with the same number of chromosomes. Cell Stays diploid Consists of 4 phases Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Mitosis Step1: Prophase Longest phase of MITOSIS Chromatin coils and forms chromosomes Nuclear envelope breaks down Spindle fibers form and stretch from one end of the cell to the other They attach to the centrioles They help to pull the cell apart Mitosis Step2: Metaphase Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Mitosis Step3: Anaphase Centromere of each chromosome splits Two sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles Each chromatid becomes separate (non-replicated) chromosome in each daughter cell. Mitosis Step4: Telophase Last stage of Mitosis Chromosomes at each pole uncoil and become chromatin Nuclear envelope reforms Spindle fibers break down Cytokinesis NOT part of mitosis The cytoplasm divides into two cells Cell membrane reforms In plant cells the cell wall reforms