* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Insides3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
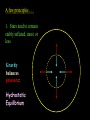
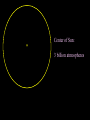
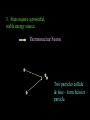
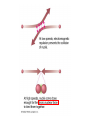
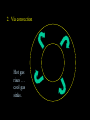
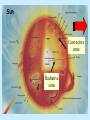
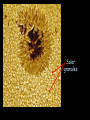
Contraction to a normal hydrogen-burning star Birth out of the interstellar medium Expansion to red giant Contraction to white dwarf OR . . . Collapse to neutron star OR black hole . . .supernova explosion Stellar Insides Stellar Insides: How are stars constructed? Atmosphere Core Envelope A few principles . . . 1. Stars tend to remain stably inflated, more or less. Gravity balances pressure: Hydrostatic Equilibrium Center of Sun: 3 billion atmospheres 2. Stars must be hotter on the inside. Center of Sun: 16 million K High temp, pressure gas completely ionized: Plasma 3. Stars require a powerful, stable energy source. Thermonuclear Fusion Two particles collide & fuse – form heavier particle. Net reaction in main sequence stars: 4 protons (hydrogens) helium + neutrinos + energy Proton-proton (PP) chain + 1H 2H + positron + gamma ray + neutrino 2 1H 2 1H + 2H 3He + gamma ray 3He + 3He 4He + 1H + 1H 2H Deuterium Alternative: CNO Cycle * Energy comes from conversion of mass into energy: mass (41H) mass(4He) m (> 0) E = mc2 gamma rays, neutrinos, positrons + energy of motion * Fusion requires high temp & density: collisions must be frequent & violent * Important consequence: creation of elements that did not previously exist! Nucleosynthesis Sun’s luminosity = 3.9 1026 Watt Sun converts 4 million tons hydrogen to energy per second! Stars lose mass over time! Transporting energy from core to surface 1. Via photons (radiative transfer): ‘random walk” Net heat flow 2. Via convection Hot gas rises . . . cool gas sinks. Sun Convective zone Radiative zone Solar granules