* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 22 - The University of Texas at Dallas
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
Web analytics wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Semantic Web wikipedia , lookup
Expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) wikipedia , lookup
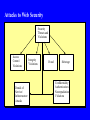
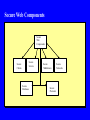
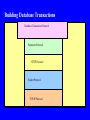
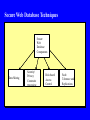
Data and Applications Security Developments and Directions Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham The University of Texas at Dallas Lecture #22 Secure Web Information Management and Digital Libraries March 31, 2005 Outline Web Security Secure Web Data Management Secure Digital Libraries Web Security End-to-end security - Need to secure the clients, servers, networks, operating systems, transactions, data, and programming languages - The various systems when put together have to be secure Composable properties for security Access control rules, enforce security policies, auditing, intrusion detection Verification and validation Security solutions proposed by W3C and OMG Java Security Firewalls Digital signatures and Message Digests, Cryptography Attacks to Web Security Security Threats and Violations Access Control Violations Denial of Service/ Infrastructure Attacks Integrity Violations Fraud Sabotage Confidentiality Authentication Nonrepudiation Violations Secure Web Components Secure Web Components Secure Clients Secure Servers Secure Databases Secure Middleware Secure Protocols Secure Networks E-Commerce Transactions E-commerce functions are carried out as transactions - Banking and trading on the internet - Each data transaction could contain many tasks Database transactions may be built on top of the data transaction service - Database transactions are needed for multiuser access to web databases - Need to enforce concurrency control and recovery techniques Types of Transaction Systems Stored Account Payment - e.g., Credit and debit card transactions - Electronic payment systems - Examples: First Virtual, CyberCash, Secure Electronic Transaction Stored Value Payment - Uses bearer certificates - Modeled after hard cash Goal is to replace hard cash with e-cash - Examples: E-cash, Cybercoin, Smart cards What is E-Cash? Electronic Cash is stored in a hardware token Token may be loaded with money - Digital cash from the bank Buyer can make payments to seller’s token (offline) Buyer can pay to seller’s bank (online) Both cases agree upon protocols Both parties may use some sort of cryptographic key mechanism to improve security Building Database Transactions Database Transaction Protocol Payments Protocol HTTP Protocol Socket Protocol TCP/IP Protocol Secure Web databases Secure data models - Secure XML, RDF, - - - - Relational, object-oriented, text, images, video, etc. Secure data management functions - Secure query, transactions, storage, metadata Key components for secure digital libraries and information retrieval/browsing Secure Web Database Functions Secure Query Processing Secure Transaction Management Secure Storage Management Secure Web Data Security and Integrity Secure Metadata Management Management Secure Data Warehousing Secure Interoperability Secure Web Mining Secure Query Management: Language Issues Query language to access the databases - SQL extensions are being examined - XML-based query languages combined with SQL are emerging Example: XML-QL XML extensions for Multimedia databases such as SMIL (Synchronized Multimedia Interface Language) - Mappings between multiple languages Web rules and query languages developed by W3C Security should be incorporated into all aspects Secure Transaction Management Example transaction on the web - Multiple users attempting to buy a product - Wait for a certain period to get the highest bid i.e., objects are not locked immediately Flexible transaction models for the various types of transactions - Long duration transactions, short transactions, workflow-based transactions - Electronic commerce is a major application Concurrency control protocols - Weak/strict serializability - Fine grained/coarse grained locking Cover channels analysis; E-Commerce Security Security/Integrity Management Support for flexible security policies Negotiations between different database administrators Authorization and access control models such as role- based access control Identification and authentication Privacy Control Copyright protection / Plagiarism Multilevel security: Trusted Computing Base? Maintaining the quality of the data coming from foreign sources Attacks to Web Databases Security Threats for Web Databases Access Control Violations Privacy Violations Integrity Violations Identity Theft Insider Threats Inference Problem Secure Web Database Techniques Secure Web Database Components Data Mining Security/ Privacy Constraint processing Role-based Access Control Fault Tolerance and Replications Secure Digital Libraries Digital libraries are e-libraries - Several communities have developed digital libraries Medical, Social, Library of Congress Components technologies - Web data management, Multimedia, information retrieval, indexing, browsing, -- - Security has to be incorporated into all aspects - Secure models for digital libraries, secure functions Secure Digital Libraries Secure Search Engine Secure Data Manager ••• Secure Knowledge Manager Datasets Secure Communication Network Participating Policy Manager Site N Datasets Documents Tools Secure Information Retrieval Secure Query Processor Secure Metadata Manager Secure Update Processor Secure Browser/ Editor Secure Storage Manager Security/ Integrity Manager Secure Browsing Browser augments a multimedia system to develop a hypermedia system Search space consist of nodes and links with different access control rules and/or classification levels Can a user traverse a link or access the contents of a node? - What authorization does he/she have? Secure Search Engines Secure User Interface Manager: Secure Interface to the client Secure Metadata Manager: Manages the metadata including directory Information and enforces security Secure Query Manager Processes the user request And carries out optimization and search; enforces Security rules Secure Index/Storage Manager: Manages the Indices and Access to Web Servers according to the Security rules Secure Markup Languages Secure SGML Documents Secure HTML Documents Secure XML Documents Secure RDF Documents Future Security Standards Secure Question Answering Secure Question Answering Subsystem Extends Secure Query Processor Secure Query Processor Secure Metadata Manager Secure Update Processor Secure Browser/ Editor Secure Storage Manager Security/ Integrity Manager Summary and Directions End-to-end security - Secure networks, clients, servers, middleware - Secure Web databases, agents, information retrieval systems, browsers, search engines, - - As technologies evolve, more security problems - Data mining, intrusion detection, encryption are some of the technologies for security Next steps Secure semantic web, Secure knowledge management -