* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seamless Handoff Between Heterogeneous Wireless Networks
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
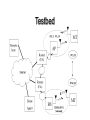
Seamless Handoff Between Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Haipeng Jin and Kameswari Chebrolu, UCSD Aditya Pande and Xiaohua Chen, Stanford University Javad Razavilar, Magis Networks Inc., San Diego Barani Subbiah, 3Com Corp., Santa Clara Introduction Future Wireless systems will be characterized by their heterogeneity. – Multiple access technologies provide access to internet content. Indoor Environment – 802.11, Bluetooth, HomeRF, IrDA etc. Outdoor Environment – GPRS, CDMA2000, Satellite etc. Systems differ in terms of coverage, bandwidth, delay, cost etc. Universal Wireless Communication System Anytime, Anywhere Coverage Three Layers of Coverage – coverage decreases from top to bottom. Topmost Layer – Satellite Systems – Global Coverage Middle Layer – Cellular Networks – Metropolitan Areas Bottom Layer – Local Area Networks – Hot Spot Coverage A common IP based network will connect them to each other. Requirements Multimode terminals Seamless inter-system (Vertical) handoff – Service negotiation across different systems Seamless intra-system (Horizontal) handoff Our Focus Vertical Handoff – Identify issues related to handoff between WLAN and WWAN – Requirements for handoff: small delay, low packet loss – Implement a testbed Network Layer : Mobile IP with extensions Link Layer: Handoff Algorithm Mobile IP IETF standard , handles mobility across IP subnets at the network layer. Mobile Terminal (MT) communicates with other nodes using its home address. MT acquires care-of address and registers with Home Agent (HA). HA intercepts packets destined for the MT and tunnels them. Route optimization - avoids triangle routing – CH learns the MT’s current care-of address and tunnels packets directly. Mobile IP CH Packets destined for mobile Packets in reverse direction HA FA Encapsulated packets MT Architecture Seamless handoff between WLAN (IEEE 802.11) and WWAN (CDMA PCS). Mobile IP based Extensions – Before handoff, MT notifies old Foreign Agent (FA) to stop transmitting and buffer packets. – Connection established to new FA – New FA contacts old FA which passes the buffered packets. – MT communicates with Correspondent Host (CH) through the new FA. Handoff Algorithm Details Based on measurement of WLAN signal strength, Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Connected to WLAN – SNR above CThresh, MT stays connected to WLAN – SNR falls below CThresh, MT scans for WWAN services and makes initial connections – SNR falls below DThresh, MT will switch from WLAN to WWAN Cont… Connected to WWAN – – Searches for WLAN signal periodically SNR above CThresh, MT switches from WWAN to WLAN Two thresholds defined to avoid “Ping-Pong” effect An exponential moving average of the SNR is used. Only SNR of the WLAN is monitored as MT prefers WLAN because of the high data rate Testbed Testbed Testbed built at 3Com Corp A laptop equipped with 802.11 and CDMA PCS network interfaces served as MT. Protocol – Mobile IP with extensions Home Agent was not implemented. Handoff related processes were implemented using C under linux platform. A text based application was used in the demonstration. Results Handoff delay-time elapsed between the last packet received on the old connection to the first packet received on the new connection. Handoff delay was about 600ms when switching from WWAN to WLAN Handoff delay was about 1040ms when switching from WLAN to WWAN. SNR measurement on WLAN Switching from WLAN to WWAN Delay on WLAN Delay while handoff Conclusions A handoff algorithm to provide seamless roaming between WLAN and WWAN was proposed. Field test results show – No unnecessary handoffs – Small packet loss and delay