* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Control of Movement
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
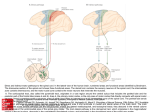
Sensorimotor Control of Behavior: Movement Lecture 9 Motor Systems Functions movement posture & balance communication Guided by sensory systems internal representation of world & self detect changes in environment external & internal ~ Movement & Muscles Movement occurs at joints Contraction & relaxation of of opposing muscles agonists prime movers antagonists counterbalance agonists decelerate movement ~ Dorsal Upper Motor Neurons + Ventral + Alpha Motor neurons + Movement & Muscles Movement control more than contraction & relaxation Accurately time control of many muscles Make postural adjustment during movement Adjust for mechanical properties of joints & muscles inertia, changing positions ~ 3 Classes of Movement Voluntary complex actions reading, writing, playing piano purposeful, goal-oriented learned improve with practice ~ 3 Classes of Movement Reflexes involuntary, rapid, stereotyped eye-blink, coughing, knee jerk graded control by eliciting stimulus ~ 3 Classes of Movement Rhythmic motor patterns combines voluntary & reflexive acts chewing, walking, running initiation & termination voluntary once initiated, repetitive & reflexive ~ Organization of Motor Control Hierarchical & Parallel Parallel pathways active simultaneously e.g. moving arm 1. muscles producing movement 2. postural adjustments during movement Recovery of function after lesion overlapping functions ~ Hierarchical Control of Movement 3 levels of control Cortex Brainstem Spinal cord (SC) Division of responsibility higher levels: general commands spinal cord: complex & specific Each receives sensory input relevant to levels function ~ Hierarchical Control of Movement Association cortices & Basal Ganglia strategy : goals & planning based on integration of sensory info Motor cortex & cerebellum tactics: activation of motor programs Spinal cord execution: activates a motor neurons reflexes rhythmic pattern generators ~ Sensorimotor Cortical System Integration of sensory information and directed movements Anatomy Descending spinal tracts Lateral pathway Pyramidal Motor System Ventromedial pathway Extrapyramidal pathway ~ Cortical Anatomy S1 - postcentral gyrus PPC - Posterior Parietal Cortex M1 - Precentral Gyrus Frontal Lobe somatotopic organization M2 - Secondary Motor Cortex SMA - Supplementary Motor Area PM - Premotor Cortex SMA M1 S1 PM PPC The Descending Spinal Tracts Brain to Spinal Cord Upper motor neurons communication with lower (a) motor neurons Lateral pathway direct cortical control Ventromedial pathway brain stem control ~ The Lateral Pathway Voluntary movement distal limbs 2 tracts Corticospinal tract about 1 million axons Rubrospinal tract small part of pathway ~ Spinal Cord: Lateral Pathway Dorsal Ventral Corticospinal tract Rubrospinal tract Corticospinal tract Motor cortex ---> spinal cord uninterrupted axon 2/3 of axons from motor cortex 1/3 from somatosensory cortex Decussates at medulla Contralateral control movement ~ The Rubrospinal Tract Motor Cortex ---> red nucleus Red nucleus ---> spinal cord inputs from motor cortex bigger role in other mammalian species ~ Lateral Pathway Damage Lesion both tracts no independent movement of distal limbs voluntary movements slow & less accurate Corticospinal only same deficits recovery over several months compensation by rubrospinal tract ~ The Ventromedial Pathway Neurons originate in brainstem Vestibulospinal & tectospinal tracts head & posture posture orienting responses Pontine & medullary reticulospinal tracts originate in reticular formation trunk & antigravity leg muscles tracts are antagonistic ~ Spinal Cord: Ventromedial Pathway Dorsal Vestibulospinal tract Tectospinal tract Medullary Reticulospinal tract Ventral Pontine Reticulospinal tract Major Descending Spinal Tracts Motor Cortex Lateral Red Nucleus Ventromedial Reticular Nuclei Spinal cord Superior Colliculus vestibular nuclei Cortical Control of Movement Primary Motor Cortex Somatotopic organization neurons have preferred direction of movement Motor homunculus ~ M1: Coding Movement Movement for limbs Neuron most active Preferred direction but active at 45 from preferred How is direction determined? Populations of M1 neurons Net activity of neurons with different preferred directions vectors ~ M1: Coding Movement Implications 1. Most M1 active for every movement 2. Activity of each neuron 1 “vote” 3. direction determined by averaging all votes ~ Motor Association Cortex Motor area other than M1 secondary motor cortex (M2) Premotor & Supplemental Motor Areas Active during preparation for movement Planning of movements Stimulation - complex movements motor programs ~ Supplementary Motor Area - SMA Primarily midline cortex Inputs from … PPC S1 Bilateral output to M1 to distal limbs ~ Premotor Area - PMA Anterior to M1 Input primarily from PPC reciprocal connections with SMA Outputs to M1 then proximal limbs ~ SMA M1 S1 PPC PMA Spinal cord Planning Movements Targeting vs trigger stimulus recording activity of neurons active when movement planned for specific direction Different populations of neurons active during planning (targeting) & execution (trigger stimulus) PM active before movement ~ Simple finger flexion only M1 activation Sequence of complex finger movements M1 + SMA activation ~ Mental rehearsal of finger movements only SMA activation ~ Sensorimotor Integration Perceptual development Active interaction required environmental feedback important Held & Hein (1950s) kittens passively moved depth perception deficits & related responses, blinking, looming ~ Sensorimotor Integration Sensory inputs guide movement visual, auditory, tactile location of objects in space Proprioceptive & vestibular position of our body Critical for planning & refining movements ~ Generation of Rhythmic Motor Patterns Central Pattern Generators Half-center Model alternating activity in flexor & extensor Step-cycle has 2 phases swing phase foot off ground & flexing forward stance phase foot planted & leg extending Each limb has own pattern generator ~ Half-center Model Flexor a + Tonic input + + + + a + + Extensor + Rhythmic Patterns: Sensory Feedback Not necessary for locomotion but slower, less coordinated Stumble correction reaction during swing phase tactile stimulus on dorsal foot ---> flexion Reflex reversal override during extension flexion would cause collapse ~ Goal-directed Locomotion Requires intact supraspinal systems Coordination of antigravity muscles Brainstem motor nuclei modulation of contraction strength Reticulo-, rubro-, corticospinal Balance Vestibulospinal tract (Ventromedial) Also cortical & subcortical areas ~