* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Apparent Depth
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Light
Properties of Light
Light
Laser
travels in straight lines:
Light
travels VERY FAST –
around 300,000 kilometres per
second.
At this speed it can go around
the world 8 times in one
second.
Light travels much faster than sound.
For example:
1) Thunder and
lightning start at the
same time, but we
will see the lightning
first.
2) When a starting
pistol is fired we see
the smoke first and
then hear the bang.
We
see things because they
reflect light into our eyes:
Homework
Properties of Light summary
1)
2)
3)
4)
Light travels in straight lines
Light travels much faster than
sound
We see things because they reflect
light into our eyes
Shadows are formed when light is
blocked by an object
Image position
You
think in
straight
lines!
The
image is
located
behind the
mirror.
Diffuse vs Specular
Reflection
Diffuse Reflection
– Light incident upon
a rough surface
– Law of reflection
still holds; Normals
are not parallel.
Specular Reflection
– Mirror like reflection
– All Normals are
parallel
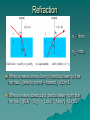
Refraction
In
which medium does light travel
faster? (glass rod appears bent)
Speed of light
n is the absolute index
of refraction. This is a
measure of optical
density. n is defined
as the ratio of the
speed of light in a
vacuum to the speed
of light in a new
medium.
v is the speed of light
in the new medium.
c= 3.0 x 108 m/s
As the index increases
the speed decrease.
Draw a graph for
index vs. speed.
Relative Index of Refraction
n is the relative index of
refraction. If air is not
used, then remember
nrel = n2/n1
What is the relative index
when going from
diamond into lucite?
If nrel < 1 ;
speeds up
If nrel > 1 ;
slows down
Refraction
n(water)=1.33; n(glass)=1.50; n(air)=1.00
Calculate the
speed of light in
water and glass.
Vw = 2.26 x 108m/s
Vg = 2.00 x 108m/s
Refraction
n1- from
n2 - into
When a wave slows down it bends closer to the
normal. {less to more – toward} n2>n1
When a wave speed up it bends away from the
normal. {BLA – Big ―› Little – Away} n2<n1
Refraction
If light rays bend closer to the normal
when slowing down, why does the glass
rod seem to bend away form the normal?
Apparent Depth
R – Real Depth
A – Apparent Depth
Diverging rays
enter your eyes.
You “think” in
Straight Lines.
A virtual image
appears to come
from point y
Apparent Depth
If
the chest is 20 m below the
surface at what depth will the image
appear? Assume nsea water = 1.34
Snell’s Law
n1sinθ1 = n2sin θ2
v1/v2 = λ1 / λ2
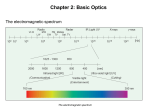
Optics
Mirrors and
Reflection
We
describe the path of light as
straight-line rays
Reflection off a flat surface follows
a simple rule:
– angle in (incidence) equals angle out
(reflection) surface normal
same
exit ray
– angles
measured
from surface
incident ray
angle
reflected ray
“normal” (perpendicular)