* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
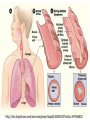
Download Asthma
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
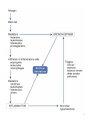
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
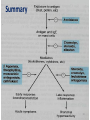
Drugs Used in Asthma Dr. Sasan Zaeri (PharmD, PhD) Department of Pharmacology 1 Asthma A chronic inflammatory disorder of bronchial airways that result in bronchospasm in response to external stimuli (pollen, cold air, tobacco smoke etc.) 2 Symptoms of asthma • Asthma produces recurrent episodic attack of – Acute bronchoconstriction – Shortness of breath – Chest tightness – Wheezing – Rapid respiration – Cough 3 Pathophysiology of Immunologic Asthma 4 5 http://link.brightcove.com/services/player/bcpid236059233?bctid=347806802 6 Aims of Anti-asthmatic Drugs • To relieve acute episodic attacks of asthma (bronchodilators, quick relief medications) • To reduce the frequency of attacks, and nocturnal awakenings (anti-inflammatory drugs, prophylactic or control therapy ) 7 Anti-asthmatic Drugs Bronchodilators (Quick relief medications) Anti-inflammatory Agents (control medications or prophylactic therapy) treat acute episodic attack of asthma reduce the frequency of attacks • • • 2-agonists Antimuscarinics • Corticosteroids •Mast cell stabilizers • Leukotrienes antagonists Methylxanthines •Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody 8 - adrenoceptor agonists • Mechanism of Action Direct 2 stimulation stimulate adenyl cyclase Increase cAMP bronchodilation 9 Classification of agonists Non selective agonists epinephrine - isoproterenol Selective 2 – agonists (Preferable) Salbutamol (Albuterol) Terbutaline Salmeterol Formeterol 10 Nebulizer Inhaler 11 Selective 2 –agonists Short acting ß2 agonists (salbutamol, terbutaline) Drugs of choice for acute attack of asthma Long acting ß2 agonists (salmeterol, formoterol) Used for nocturnal asthma (long acting relievers) Combined with inhaled corticosteroids to control asthma (decreases the number and severity of asthma attacks) 12 • Adverse effects of selective 2 –agonists – Skeletal muscle tremor – Tachycardia and arrhythmia – Tolerance and tachyphylaxis 13 Muscarinic antagonists Ipratropium Act by blocking muscarinic receptors Given by aerosol inhalation Quaternary derivatives of atropine Do not enter CNS Does not diffuse into the blood Minimal systemic side effects 14 Effects Inhibit bronchoconstriction and mucus secretion Less effective than β2-agonists Uses Main choice in chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) In acute severe asthma combined with β2agonists & steroids 15 Methylxanthines Theophylline - Aminophylline • Mechanism of Action Phosphodiestrase (PDE) inhibition cAMP bronchodilation Adenosine receptor antagonists 16 17 • Uses Second line drug in asthma (theophylline in nocturnal asthma) For status asthmatics (aminophylline is given as slow infusion) 18 • Side Effects CVS: arrhythmia GI: nausea & vomiting, ↑ gastric acid secretion CNS: tremors, nervousness, insomnia, convulsion Kidney: ↑renal blood flow, weak diuretic action 19 • Drug interactions Metabolized by Cyp P450 enzymes in liver Enzyme inducers e.g. phenobarbital, rifampin, tobaco smoke → ↑metabolism of theophylline Enzyme inhibitors e.g. erythromycin→ ↓ metabolism of theophylline 20 Anti - inflammatory Agents (control medications / prophylactic therapy) By reducing inflammation, they reduce bronchial hyper-reactivity and bronchospasm 21 Anti-inflammatory Agents Glucocorticoids Leukotrienes antagonists Mast cell stabilizers Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody (Omalizumab) 22 Glucocorticoids • Mechanism of action – Inhibition of phospholipase A2 → ↓ prostaglandin and leukotrienes – Mast cell stabilization →↓ histamine release – Upregulation of β2 receptors 23 24 Routes of administration Inhalation Budesonide, Fluticasone, Beclomethasone Less side effects Oral Prednisolone Parenteral Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone Status asthmaticus (IV infusion) 25 Glucocorticoids Are not bronchodilators Given as prophylactic medications, used alone or combined with beta-agonists 26 Side effects of systemic corticosteroids – – – – – – – – – – Adrenal suppression Growth retardation in children Osteoporosis Fluid retention, weight gain, hypertension Hyperglycemia Susceptibility to infections Glaucoma Cataract Fat distribution, wasting of the muscles Psychosis 27 Inhalation therapy has less side effects – Oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush) – Dysphonia (voice hoarseness) Withdrawal – Abrupt stop of corticosteroids should be avoided and dose should be tapered (adrenal insufficiency syndrome) 28 Mast cell stabilizers Cromolyn - Nedocromil Act by stabilization of mast cell membrane Have poor oral absorption Given by inhalation 29 Mast cell stabilizers Not bronchodilators Not effective in acute attack of asthma Prophylactic anti-inflammatory drugs Children respond better than adults 30 Uses Prophylactic therapy in asthma especially in children Allergic rhinitis Conjunctivitis Side effects Bitter taste minor upper respiratory tract irritation (burning sensation) 31 Leukotrienes antagonists Leukotriene B4 chemotaxis of neutrophils Leukotrienes C4 and D4 bronchoconstriction 32 Leukotriene receptor antagonists Zafirlukast, Montelukast Taken orally Are bronchodilators Are NOT effective to relieve acute attack of asthma Have anti-inflammatory action 33 Uses Prophylaxis of Mild to moderate asthma Aspirin-induced asthma Antigen and exercise-induced asthma Can be combined with glucocorticoids (low dose of glucocorticoids can be used) 34 Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody Omalizumab A monoclonal antibody directed against human IgE It binds to the IgE on sensitized mast cells and prevents activation by asthma triggers and subsequent release of inflammatory mediators Expensive-not first line therapy 35 Summary 36