* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LVD - Renesas e
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
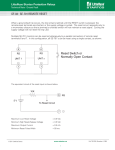
RL78 POC and LVD Renesas Electronics Corporation © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. 00000-A Introduction Purpose This course provides an introduction to the RL78 Power-On-Clear and Low Voltage Detector. Objective Learn about the RL78 POC and LVD features and its capabilities. Content 18 pages (including this page) Learning Time 20 minutes 2 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. POC Power-On-Clear 3 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. Power-On-Clear Circuit Functions Generates internal reset signal at power on Compares supply voltage VDD and detection voltage VPOC VDD >= 1.51V ± 0.03V and generates internal reset signal when VDD < 1.50V ± 0.03V CPU can also be released by LVD, selectable by an option byte Current consumption already included in STOP mode current Block Diagram 4 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. Power-On-Clear Circuit Operation LVD is off VPOC0 to VPOC2 = 0x07 Undefined area The supply voltage enters the undefined area If this may happen in the system, the LVD must be used in combination. 5 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. LVD Low-Voltage-Detector 6 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. Low-Voltage-Detector Circuit Functions Compares the supply voltage VDD with detection voltage VLVIH, VLVIL and generates a reset or internal interrupt Detection voltage is selectable by option byte – 14 levels (1.63V~4.06V) Three different operation modes available – interrupt and reset mode – Reset mode – Interrupt mode Very low power consumption of only 0.1uA LVD is operating is STOP mode 7 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. Block diagram of LVD 8 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. Option byte for LVD Functions of this register Select base operation mode of the LVD Select voltage level of LVD Address : 000C1H/010C1H 7 6 5 4 3 2 VPOC2 VPOC1 VPOC0 1 LVIS1 LVIS0 VPOC2-0,LVIS0,1 9 1 LVIMDS1 LVIMDS0 Set detection voltage by combination LVIMDS1 LVIMDS0 selection LVD operation mode 0 0 Setting prohibited 0 1 Interrupt mode 1 0 interrupt & Reset mode 1 1 Reset mode © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. 0 Low-Voltage Detector levels Detection voltage levels When used as reset mode, or interrupt mode Detection voltage (TYP.) Detection voltage (TYP.) 14 levels can be selected. 10 When used as interrupt & reset mode © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. LVD control register LVIM Functions of this register Write enable for LVIS Status flags for LVD operation LVIM 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 LVISEN 0 0 0 0 0 LVIOMSK LVIF LVISEN Write enable for LVIS 0 Disabling rewriting to LVIS 1 Enabling rewriting to LVIS LVIOMSK 0 1 Mask status flag of LVD detection LVD operation enabled LVD operation waiting LVIOMSK is set to 1 automatically after LVISEN =1. After rewriting LVIS, LVD detection needs stabilization. LVIOMSK =1 during rewriting LVIS and during stabilization. Therefore after clear LVISEN to 0, LVIOMSK is kept 1 during stabilization time of about 200us to 300us . LVIF 0 1 11 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. voltage detection status flag VLVI =< VDD VDD =< VLVI LVD control register LVIS Functions of this register Mode selection (LVIMD) Voltage level selection (LVILV) It is possible to write to LVIS register in interrupt & reset mode if LVISEN =1. In interrupt mode or reset mode it isn't possible to change the value of LVIS. Interrupt & reset mode Interrupt mode Address : FFFAAH After reset : 00H / 01H / 81H Reset mode Symbol 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 LVIS LVIMD 0 0 0 0 0 0 LVILV 12 LVIMD 0 1 Selection of LVD detection mode Interrupt mode Reset mode LVILV 0 1 LVD detection voltage level High-voltage detection level Low-voltage detection level © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. Different LVD modes Different Objectives and the right LVD mode Objective Mode to be used LVD should be used to RESET mode A substitute an external reset IC. Reset generation at the preselected voltage. Switch device in secure B state/standby in case of low voltage. Interrupt mode Interrupt generation at the preselected voltage. Save important data before Interrupt (detection notice) and reset mode reset by low voltage detection. Interrupt generation at the preselected voltage C and finally reset generation at reset voltage. 13 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. Example A: external reset IC Supervise guaranteed voltage range of CPU To avoid operation outside specified area Operation condition frequency Voltage LVD setting : HOCO 32MHz : 5V Option byte 00C1H :“0111 1111B” LVD detection voltage : VLVI5 (rise 2.81V(typ.) fall 2.70(min.)) LVD mode : reset mode LVD reset release. and CPU start operation. LVD POR 2.81V(typ.) Reset by LVD CPU operable 2.7V(min.) CPU inoperable 1.51V ->time CPU state 14 POR reset LVD reset CPU operation © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. LVD reset POR reset Example B: Switch device to standby Supervise guaranteed voltage range of CPU and set device into standby to avoid operation outside specified area Operation condition frequency voltage LVD setting Option byte 00C1H :“0011 1101B” : HOCO 8MHz : 3V LVD detection voltage : VLVI11 (rise 1.88V(typ.)、fall 1.8V(min.)) LVD mode : interrupt mode Reset release by LVD only rising supply voltage. and start operation CPU. LVD 1.88V(typ.) Cause interrupt by LVD. then switching to standby by software. CPU operable 1.80V(min.) Reset by POR. Stopped RTC POR CPU inoperable 1.51V ->time CPU state POR reset LVD reset RTC state POR reset LVD reset 15 CPU operation © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. STOP RTC operation POR reset POR reset Example C: Save data before reset Supervise guaranteed voltage range of CPU and save parameters before enter reset. Operation condition frequency voltage LVD setting Option byte 00C1H : “0101 0110B” : HOCO 8MHz : 3V LVD detection voltage Reset release voltage Reset voltage Interrupt voltage : VLVI6 2.71V(typ.) : VLVI8 2.40V(min.) : VLVI6 2.60V(min.) LVD mode : interrupt (detection notice)& reset mode LVD reset release and CPU operation start. LVD is set to interrupt Cause interrupt by LVD. Then switching LVD to reset automatically. saving important data by software. 2.71V(typ.) 2.60V(min.) LVD CPU operable Reset by LVD 2.40V(min.) CPU inoperable POR ->time CPU state 16 POR reset LVD reset CPU operation © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. saving data LVD reset POR reset Summary Power on Clear Functions Block Diagram Operation For more information, visit: 17 © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved. LVD Functions Block Diagram Option Bytes Registers Operation Modes Renesas Electronics Europe © 2010 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved.