* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Address of the Electrons
Density functional theory wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
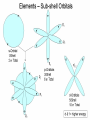
The Address of the Electrons Each electron has a set of four numbers, called quantum numbers Each electron has a different set of numbers ¡ No 2 electrons in the same atom can have the same 4 quantum number ¡ Pauli exclusion principle. Attraction between protons in nucleus and electron in cloud. Takes energy for electron to pull away from nucleus Lower energy levels closer to nucleus Higher energy levels farther from nucleus Described by integers ¡ 1 is closest to nucleus (lowest enegry Show the shape of the area that a electron is most likely moving around. 4 types ¡ s, p, d, and f ¡ Each requires a different amount of energy for an e- to remain ¡ Lowest energy is s ¡ Highest energy is f Described by their energy level number and their subshell type level Example ¡ S orbital in energy level 2---2s An area of high probability where an electron is located The specific orientation of the shape of the subshell S ¡ Has one orbital, holds 2 electrons P ¡ Has three orbitals, holds 6 electrons D ¡ Has five orbitals, holds 10 electrons F ¡ Has 7 orbitals, holds 14 electrons The arrangement of electrons in an atom 3 methods of writing electron configuration ¡ Boxes and arrows ¡ Spectroscopic notation ¡ Noble gas notation From the German word "Aufbauen" which means "to build” Electrons will first occupy orbitals of the lowest energy level. Aufbau Principle Hund’s Rule ¡ Electrons are placed in their own orbitals before doubling up Pauli ¡ In Exclusion Principle order for electrons to share an orbital, they must have different spin ¡ One spin up ¡ One spin down Number of electrons in the sub level 2,2,5 2 1s 2 2s 5 2p Sublevels Use the last noble gas that is located in the periodic table right before the element. Write the symbol of the noble gas in brackets. Write the remaining configuration after the brackets. Ex: Fluorine: [He] 2s2 2p5