* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transmitters
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Ringing artifacts wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
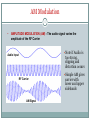
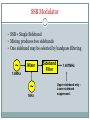
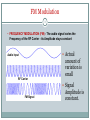
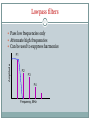
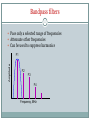
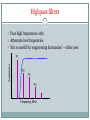
East Kent Radio Society EKRS 1 Intermediate Course (4) Transmitters Karl Davies Transmitters 2 Summary Block diagrams of transmitters Oscillators for generating a carrier Operation of mixers Modulators AM, FM, and SSB modulation Harmonics Filters CW Transmitter 3 Block diagram of CW transmitter Keying stage switches RF on and off Slow rise and fall time of RF envelope will avoid excess bandwidth RF oscillator Keying stage Key Power amplifier Low-pass filter AM Transmitter 4 Block diagram Modulator - the audio modulates the RF amplitude RF oscillator Microphone Modulator AF amplifier Power amplifier Low-pass filter SSB Transmitter 5 Block diagram Modulator produces double-sideband suppressed-carrier Sideband filter suppresses unwanted sideband RF oscillator Mic Balanced modulator AF amplifier Sideband filter Power amplifier Low-pass filter FM Transmitter 6 Block diagram Audio used to modulate frequency of RF oscillator RF oscillator AF amplifier Mic Buffer amplifier Power amplifier Low-pass filter LC Oscillator 7 Circuit of a Colpitts LC oscillator L1 and C1 determine frequency +9V TR1 C2 220pF C3 470pF L1 10uH C1 150pF Output R1 100k C4 680pF R2 330 LC oscillator (VFO) 8 Varying L or C changes frequency Drifts with temperature, supply voltage, output load Nearby objects affect L or C Modulated by supply noise and vibration Requires rigid screened construction Requires regulated & filtered supply Needs to be calibrated Either by adjusting the dial Or by adjusting L & C with trimmers Prevent drift causing operation outside Amateur bands Crystal Oscillator 9 Circuit of a crystal oscillator XL1 determines frequency +9V TR1 C3 XL1 3.756MHz 470pF Output R1 100k C1 22pF C4 680pF R2 330 Crystal Oscillator 10 Crystal determines frequency of oscillation Made out of piezoelectric quartz rock Very stable compared to LC oscillator Little drift with temperature, supply etc Fixed frequency - cannot be tuned Synthesisers are stable frequency sources Use crystal oscillator as a reference Mixers 11 Two frequencies can be combined in a mixer circuit Result is the creation of sum and difference frequencies ~ Mixer 10MHz ~ 1MHz 10MHz+1MHz=11MHz and 10MHz–1MHz=9MHz AM Modulation 12 • AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) - The audio signal varies the amplitude of the RF Carrier Note if Audio is Audio Input too strong, clipping and distortion occurs RF Carrier AM Signal Simple AM gives carrier with lower and upper sidebands Mixer as a Modulator 13 Mixer may be used as an AM modulator AM has carrier and two sidebands Most power is in the carrier signal Excessive audio causes over-modulation ~ Mixer 1.4MHz ~ 1kHz DC offset 1.401MHz Upper sideband 1.399MHz Lower sideband 1.400MHz Carrier DC offset unbalances mixer and causes carrier component. SSB Modulator 14 SSB = Single Sideband Mixing produces two sidebands One sideband may be selected by bandpass filtering ~ Mixer 1.4MHz ~ 1kHz Sideband Filter 1.401MHz Upper sideband only Lower sideband suppressed. SSB Modulation 15 SSB has a number of advantages No carrier, so power is not wasted Half the bandwidth of AM No RF power without modulating audio Smaller PSU Less heat Carrier Lower Sideband Carrier and Unwanted Sideband is suppressed compared to normal AM, reducing bandwidth -3kHz Upper Sideband -300Hz +300Hz SSB: 2.7kHz BW AM: 6kHz BW +3kHz FM Modulation 16 • FREQUENCY MODULATION (FM) - The audio signal varies the Frequency of the RF Carrier - its Amplitude stays constant Actual Audio Input amount of variation is small RF Carrier Signal FM Signal Amplitude is constant. FM Modulator 17 FM can be achieved by varying the capacitance in a VFO Varicap diode – varies capacitance with reverse voltage Apply modulating audio + DC bias to diode Crystal oscillator? FM achieved via phase modulation in following stage Excessive audio causes over-deviation Distorted audio at receiver Interference to adjacent channels FM Modulator 18 Oscillator with Frequency Modulation by Varicap Diode L1 and C1 set nominal frequency, which is varied by CD Diode DC Bias must be positive. Audio varies the bias/Capacitance +9V Diode DC Bias RF Block Audio In L2 DC Block TR1 C2 220pF C3 470pF C5 22pF CD Varicap Diode L1 10uH C1 150pF FM Output R1 100k C4 680pF R2 330 Data transmission 19 Often achieved by modulating two or more audio tones (FSK) Audio tones generated in a modem Tx audio Data Modem Rx audio SSB or FM transmitter Harmonics 20 Harmonics are multiples of the wanted frequency - oscillators, mixers, and amplifiers generate harmonics Harmonics can be radiated and interfere with other radio users Power, dBW F1 F2 F3 F4 Frequency, MHz F1: Fundamental F2: Second Harmonic F3: Third Harmonic F4: Fourth Harmonic 145MHz 290MHz 435MHz 580MHz Lowpass filters 21 Pass low frequencies only Attenuate high frequencies Can be used to suppress harmonics Amplitude F1 F2 F3 F4 Frequency, MHz Bandpass filters 22 Pass only a selected range of frequencies Attenuate other frequencies Can be used to suppress harmonics Amplitude F1 F2 F3 F4 Frequency, MHz Highpass filters 23 Pass high frequencies only Attenuate low frequencies Not so useful for suppressing harmonics! – other uses Amplitude F1 F2 F3 F4 Frequency, MHz