* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objective Recovery Packet Unit 2
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
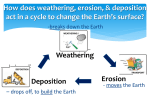
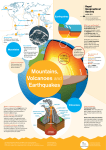
Objective Recovery Packet Unit 2: The Lithosphere, the Rock Cycle, and Weathering/Erosion Step 1 (Star 1): Objective 2.1.1: EEn.2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the lithosphere. A) Re-state the objective in your own words (using an “I can” statement) B) Vocabulary for success: lithosphere, rock cycle, metamorphic, igneous (intrusive and extrusive), sedimentary, cementation, weathering, erosion, physical weathering, chemical weathering, deposition, bedding, foliation (foliated vs. non-foliated rock), magma, lava. Step 2 (Star 2): You have two options (just pick one!): Draw the rock cycle, including each of the three different types of rock and the forces that drive the rock cycle; OR write a paragraph as if you are a rock, who has lived a long life and been transformed into each different type of rock over time. Write a story of your life, using at least 4 complete sentences (again include the three different types of rock and forces that drive the rock cycle). Step 3 (Star 3): Essential Question: What is the composition of Earth and how does that affect the lithosphere? In your answer, include the forces that drive the rock cycle (for example: heat, pressure, gravity), and include a drawing of the layers of the lithosphere, including the composition (what it’s made of) and depth of each layer! Step 4 (Sun) QUIZ: TIME TO SHOW WHAT YOU KNOW! 2.1.1 Quiz: 1. The rock cycle describes how rocks change form over time. Magma deep within the mantle rises towards the crust due to convection. If the magma cools inside the Earth, ___________ igneous rock is formed. If lava cools quickly outside the Earth, ___________ igneous rock is formed. If that rock breaks into small pieces over time, and those sediments become cemented together, ________________rock is formed. Extreme heat and pressure will change any rock to ________________. a. b. c. d. intrusive, metamorphic, sedimentary, extrusive extrusive, intrusive, metamorphic, sedimentary intrusive, extrusive, sedimentary, igneous intrusive, extrusive, sedimentary, metamorphic 2._________________ weathering changes the shape or size of a rock without chemical reactions while ________________weathering breaks down rocks by chemical reactions. a) chemical, physical b) physical, chemical c) acid rain, mechanical d) none of the above 3. The three main forces that drive the rock cycle are ________________, _____________, and ____________________. a. b. c. d. Heat, pressure, magma Heat, weathering, magma Heat, pressure, weathering/erosion Heat, magma, weathering/erosion 4. Pieces of weathered rock (sediment) settle over time to form new rock. The piling up of eroded sediments, called___________________, occurs before the layering of rocks, called _______________. If the rock layers are even (formed by an even amount of pressure causing a banded appearance), this sedimentary rock is ________________. a) deposition, foliation, bedded b) deposition, bedding, non-foliated c) bedding, deposition, foliated d) deposition, bedding, foliated 5. Waves that push and pull (like a slinky) are called _____________ waves and the waves that move up and down are called ___________ waves. In an earthquake, the starting point for waves underneath Earth’s surface is the ____________. a. S, P, epicenter b. S, P, focus c. P, S, focus d. P, S, surface waves 6. Which structure can form as a result of a divergent plate boundary? a) b) c) d) a continental volcano due to the collision of two plates a continental mountain due to the collision of two plates mid-ocean ridge due to the separation of two plates ocean trench, due to the separation of two plates 7. Which would produce the most severe earthquake damage along Earth’s surface? a. b. c. d. earthquake with a deep focus and magnitude 2.5 earthquake with a shallow focus and magnitude 2.5 earthquake with a deep focus and magnitude 4.5 earthquake with a shallow focus and magnitude 4.5 8. Which of the following is not a fault type involved in earthquakes? a. Normal fault b. Strike slip fault c. Hanging wall fault d. Reverse fault 9. How can water be an agent of physical weathering? a) b) c) d) by absorbing material from the atmosphere and the ground to interact chemically by seeping into the soil and dissolving the minerals in rocks by absorbing sulfur oxides and creating acid precipitation by seeping into the cracks of rocks and freezing 10. How are convection currents that move magma underneath Earth’s crust similar to density currents that move water in Earth’s oceans? a. b. c. d. Both types of currents occur in the same place Both types of currents move magma Both involve a cycle wherein hot magma/water rises and cooler magma/water sinks Both involve a cycle wherein cooler magma/water rises and hot magma/water sinks Step 1 (Star 1): Objective EEn.2.1.2: Predict the locations of volcanoes, earthquakes, and faults based on information contained in a variety of maps. A) Re-state the objective in your own words (using an “I can” statement) B) Vocabulary for success: theory of plate tectonics, 3 types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, transform-fault; three types of faults: normal, reverse, strike-slip fault; and 3 types of stress that create those faults: compression, tension, shear stress, epicenter, magnitude, S-wave, P-wave. Step 2 (Star 2): Draw the three types of boundaries: arrows that show how plates are coming together, and list the natural disasters and landforms that may occur at each type of boundary (volcanoes, earthquakes, seafloor spreading, and mid-ocean ridges). BE DETAILED! Step 3 (Star 3): Essential Question: Earthquakes result in faults or cracks in the Earth’s crust. Describe the 3 different types of faults and 3 types of stresses that create those faults. In your answer, include the location on Earth’s surface of the greatest damage from this earthquake! Step 4 (Sun) QUIZ: TIME TO SHOW WHAT YOU KNOW! Quiz 2.1.2: 1. All of the following can form/occur at convergent plate boundaries EXCEPT: a. Earthquakes b. Volcanoes c. Seafloor spreading d. Mountains 2. San Fransisco, CA is located along a transform-fault boundary. What type of seismic activity can be expected in this city? a) Volcano b) Earthquake c) Earthquakes and volcanoes d) Landslide 3. What type of landform will most likely result from the divergent boundary in the Northern Atlantic Ocean? a) Volcano b) Seafloor spreading c) Continental mountain range d) Mud flow volcano 4. Plate boundaries are shown above. If you are a homeowner, which boundaries do you believe volcanic activity might occur? a) Nazca-South America plates b) North American-Pacific plates c) Eurasia-Pacific Plate d) A and C 5. Faults are fractures in the Earth’s crust due to an earthquake. Under tension stress, _____________ fault forms, where the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. Alternatively, under compression stress, ___________ fault forms because the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall. The most common form of fault, strike-slip, occurs due to ________________ stress. a) normal, reverse, tension b) reverse, normal, compression c) normal, reverse, shear d) reverse, normal, shear 6. Seafloor spreading occurs at divergent plate boundaries. Which of the following is NOT true of seafloor spreading? a) New seafloor is created as two plates move apart b) Seafloor spreading occurs at a subduction zone c) Seafloor spreading is also known as ridge push d) A mid-ocean ridge can form 7. Scientists are studying a graph that shows the time differences between seismic P-wave and S-waves as they travel through Earth. Which information do they learn from the graph? a. b. c. d. magnitude of the earthquake duration of the earthquake epicenter of the earthquake earthquake intensity 8. Which of the following instruments do scientists use to measure earthquake intensity? a) b) c) d) Richter scale telegraph seismograph magnetometer 9. The theory of plate tectonics states that the lithosphere is divided into 7 plates that interact with each other at plate boundaries. Which of the following is NOT true of the tectonic plates? a) b) c) d) Plates move because of convection currents in the mantle The theory of plate tectonics is well-accepted Moving plates result in earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains The theory of plate tectonics is less accepted than continental drift theory 10. Active volcanoes can be found: a) b) c) d) Along the Ring of Fire In the middle of a continental plate where magma lies relatively close to the crust At convergent plate boundaries only A and B Step 1 (Star 1): Objective EEn.2.1.3: Explain how natural actions such as weathering, erosion (wind, water and gravity), and soil formation affect Earth’s surface. A) Re-state the objective in your own words (using an “I can” statement) B) Vocabulary for success: sand, silt, clay (compare the three using a chart), physical (mechanical) weathering, chemical weathering, erosion, and list the 4 different agents of erosion. Step 2 (Star 2): Part I: Create a chart that shows three examples of physical weathering (mechanical) and three examples of chemical weathering. Include one sentence per example that summarizes why that weathering is physical versus chemical. Part II: Create a diagram that shows the relative sizes of each type of particle found in soil (sand, silt, clay). In your diagram include the water-holding (retaining) capacity of each particle. Step 3 (Star 3): Essential Question: Contrast (describe the difference between) erosion and weathering. In your answer, include the 4 agents of erosion! Finally, explain how soil is formed over time from both sediments (weathering) and particles transferred by erosion. [Recall: The three major factors that affect the rate of weathering are: rock composition (what it’s made of), local climate, and local topography (i.e. steepness of landforms).] Step 4 (Sun) QUIZ: TIME TO SHOW WHAT YOU KNOW! Quiz 2.1.3: 1. Soil is made of weathered rocks and minerals. The three major components of soil, in order according to how much water they retain are (lowest to highest): a) silt, sand, clay b) sand, silt, clay c) sand, minerals, clay d) clay, silt, sand 2. Rocks weather at different rates. Which of the following does NOT affect the rate of weathering? a. Topography b. Climate c. Amount of sunlight d. Rock composition (what a rock is made of) 3. Erosion differs from weathering because it involves movement. In coastal areas, the two most common forces of erosion are: a) ice, glaciers b) wind, weathering c) wind, waves d) waves, weathering 4. Water can act as both a physical and chemical weathering agent. Along the road, potholes caused by water freezing/thawing in the cracks of rocks and breaking those rocks into pieces, is due to __________ weathering. Alternatively, acid rain hitting rock causes ________ weathering. a) mechanical, chemical b) chemical, mechanical c) slow, fast d) glacial, fast 5. The lithosphere, the uppermost layer of Earth, is made up of the upper _______ and the _____, and divided into 7 plates. These plates move due to ___________ currents, which are created as magma rises towards the crust, cools, and cycles back towards the core. a) core, crust, heat b) mantle, crust, heat c) mantle, crust, convection d) core, crust, convection 6. Physical weathering (also called mechanical weathering) does NOT involve changes in: a) size b) shape c) chemical composition 7. Which features of topography increase the rate of weathering? a) steep gradient (slope) b) direct sunlight c) local climate of low winds and light precipitation d) none of the above 8. Compare: What is the underlying force of all agents of erosion (wind, water, ice, gravity)? a) magnetism b) gravity c) friction d) light 9. 10. Step 1 (Star 1): Objective EEn.2.1.4 I can explain the probability of and preparation for geohazards such as landslides, avalanches, earthquakes and volcanoes in a particular area based on available data. A) Re-state the objective in your own words (using an “I can” statement) B) Vocabulary for success: geohazard, earthquake, tsunami, volcano, landslide, avalanche, floods, sinkhole Step 2 (Star 2): Make a public service announcement (PSA) on one geohazard: define it, identify the cause, identify major effects, and include (2) ways to prepare for that geohazard! Where should we choose to live or put buildings to minimize damage from this geohazard? Name two precautions we can take to increase safety for humans involving this geohazard. Step 3 (Star 3): Essential Question: An earthquake of magnitude 8.2, along with a tsunami, occurred off the coast of Japan this past year. Explain the causes (plate boundaries) and negative effects (loss of life, buildings, environmental damage) of this earthquake and tsunami. In the future, where should we choose to live or put buildings to minimize damage from earthquakes? Step 4 (Sun) QUIZ: TIME TO SHOW WHAT YOU KNOW! Quiz 2.1.4: 1. All of the following can result from an earthquake EXCEPT: a) landslide b) tsunami c) flood d) aftershock 2. Levees are one precaution that can be put in place to reduce damage from floods. Which of the following is the best precaution against sinkholes? a) determine limestone content in bedrock b) determine granite content in bedrock c) determine the amount of groundwater in bedrock d) both limestone content and the amount of groundwater in bedrock (A and C) 3. One long-term effect of global warming is that sea level may rise. If all global ice caps were to melt, the resulting rise in sea level could cause ___________. a) the loss of Florida, Louisiana, and New York City b) barrier islands may disappear c) increased flooding d) all of the above 4.True or False: Volcanic Ash contains gases and affects atmospheric composition with pollutants such as dust, rock particles, and ash. a) True b) False 5.Which of the following geohazards are not correctly matched? a. b. c. d. Sinkholeresults from dissolved limestone underground Earthquake results from plates moving at their boundaries Volcanoesresult from hot water pushing up through the crust Tsunamiscan occur after a large earthquake 6.Which is most likely a prevention strategy for flooding? a) building artificial levees b) reducing water consumption c) recycling bottled-water containers d) building waste landfills for metals and other contaminants 7. Which of the following conditions make a landslide less likely? a) deforestation (removal of trees) along a hillside b) steep gradient (slope) c) little vegetation to hold soil in place d) none of the above (all make a landslide more likely) 8. Contrast (describe the difference between) a foreshock and an aftershock: a) a foreshock must be higher in magnitude than an aftershock b) a foreshock may result in greater damage than an aftershock c) both foreshock and aftershock result from seismic activity d) timing, foreshock occurs prior to the earthquake and aftershock occurs after the earthquake 9. Which theory explains why the earth vibrates in an earthquake? a. Elastic rebound theory b. Strike slip theory c. Seismatic theory d. Theory of relativity 10. Objective 2.2.1: EEn.2.2.1: I can explain the consequences of human activities on the lithosphere (such as mining, deforestation, agriculture, overgrazing, urbanization, and land use) past and present. Step 1: (Star 1): A) Re-state objective in your own words (“I can…”). B) Vocabulary for Success: mining, deforestation, agriculture, overgrazing, urbanization, population growth, carrying capacity, conservation. Step 2 (Star 2): Create a chart that (briefly) describes the a) need and b) environmental consequences of human activities that impact the lithosphere: mining, deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization. Step 3 (Star 3): Essential Question: Pick one of the major human activities that impact the lithosphere to describe in detail. Describe that activity’s effects on the lithosphere, why we need it (what do we gain from it), and consequences (negative impacts on the environment). Finally, explain how population growth increases the need for that activity! Step 4 (Sun): Time for the Quiz! 2.2.1 QUIZ: 1. Which of the following human activities does NOT contribute to erosion (and the loss of fertile topsoil)? a) agriculture b) deforestation c) overgrazing d) planting vegetation 2. a) b) c) Which of the following is NOT a potential negative effect of agriculture/farming? habitat loss soil erosion increased biodiversity d) wasteful water consumption 3) Which of the following is NOT a consequence (negative impact) of mining? a) b) c) d) mine collapse contaminated water supply increased energy supply mountain-top removal 4) Sustainable practices can be maintained over time. Choose the non-sustainable practice below: a) b) c) d) wind energy solar energy fossil fuels factory farming 5) Aquaculture involves growing fish and plants underwater under controlled conditions. Why is aquaculture more sustainable than traditional agriculture? a) provides more fish to prevent over-fishing in wild habitats b) provides greater total supply of fish c) pollutes the water supply more quickly d) none of the above Objective 2.2.2: EEN 2.2.2: I can explain compare the various methods humans use to acquire energy (peat, coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear fission, and wood). Step 1 (Star 1): A) Re-state objective in your own words. B) Vocabulary for Success: population growth, carrying capacity, renewable energy, non-renewable energy, sustainable, conservation. Step 2 (Star 2): Create a chart (started below for you) to characterize the major energy sources. Energy Source Renewable or Non (R or N) Negative Impacts (think environment, economic) Wind Solar Natural Gas Petroleum Coal Gasoline Hydroelectric power Wave/tidal power Nuclear fission Step 3 (Star 3): Essential Question: Oil is formed over millions of years from dead/decaying plant/animal remains. In the United States, we have enough oil resources to last until the year 2100 if we keep using it at the same rate. Knowing what you know about oil resources, explain whether oil is a renewable or non-renewable resource and why. Then, list some good alternatives to using oil (alternatives that we can use to generate electricity). Step 4 (Sun): Time for the Quiz! QUIZ 2.2.2: 1. Knowing what you know about oil, which of the following best characterizes our use of oil: a) Renewable, limited supply b) Non-renewable, unlimited supply c) Renewable, unlimited supply d) Non-renewable, limited supply 2. Which of the following is a renewable resource (can be replaced/replenished quickly over time)? a) Wave/tidal power b) Nuclear fission c) Natural Gas d) Oil 3. One potential negative environmental impact of wind power is: a) Wind turbines are expensive b) Wind turbines can interrupt migratory birds c) Wind turbines are relatively inexpensive d) Wind power can only be harnessed in certain regions of the US 4. One economic cost of solar power is: a) Solar panels can only be used in certain weather b) Nothing, the sun’s energy from nuclear fusion is free c) Solar panels are expensive d) Solar powers are relatively inexpensive 5. Burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) emits greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. How does burning fossil fuels impact the environment? a) Increased air pollution b) Global warming c) Acid rain d) All of the above 6. Wind and solar power share a major advantage over other energy resources: a) inexpensive b) wildlife can be harmed c) relatively low air pollution d) relatively low air and water pollution 7. To conserve natural resources, people are encouraged to reduce, reuse, recycle! Which of the following would do the MOST to conserve resources over time: a) Reduce the total amount of plastic bottles you buy b) Buy 1 liter bottles instead of 24-pack cans of soda c) Recycle all bottles from 24-pack of soda d) Buy more sodas and cans so that you can recycle them 8. Which of the following activities would reduce your carbon footprint? a) Take public transportation instead of driving a car b) Carpool with 2-3 friends c) Drive at a slower speed d) Ride a bike or walk to work