* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
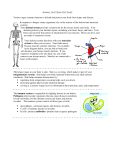
Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term Study Guide Midterm Review Topic List and Study Questions. Disclaimer: This is by no means a comprehensive review and SHOULD NOT be used as a standalone review guide. Student’s should reference their notebook (notes, labs, homework, assignments, quizzes) as well as their textbook for a more thorough review. Anything that has been covered to date is fair game for the Midterm exam Unit 1 – Intro to Anatomy Differentiate between the study of anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in an organism Identify the general functions of the organ systems Explain the process of homeostasis in the human body o Positive vs. Negative Feedback Correctly use the reginal and directional terms Identify the planes/sections of the human body Unit 2 – Histology (Cells and Tissues) Epithelial Tissue o Function o Types o Identify structure o Endocrine vs. exocrine glands Connective Tissue o Distinguish between the types of connective tissue o Explain the extracellular matrix Muscle tissue o Know the 3 types and characteristics of each Neural tissue o Explain the function Tissue Healing o Explain the process of tissue/wound repair Unit 3 – Integumentary Distinguish between epithelial membranes and connective tissue membranes Explain the function of the integumentary system Identify the role of the cells within the integumentary system o Melanocytes o Keratinocytes o Langerhans Cells Distinguish between the structure and function of the different layers of the skin Distinguish between the structure and function of the accessory structures Identify the characteristics of skin disorders Explain the rule of nine and the ABCD rule as it relates to the integumentary system. Unit 4 - Skeletal System Explain the function of the skeletal system Label the microanatomy of the skeleton Differentiate between the axial and appendicular skeleton o Be able to identify the various bones of the skeleton Explain the role of calcium in the onset of osteoporosis Anatomy and Physiology Midyear Review Unit 1 – Intro to Anatomy I. Matching A. Integumentary System B. Muscular System C. Endocrine System D. Lymphatic System E. Digestive System F. Reproductive System G. Skeletal System _____E____ 1. Contains the small and large intestines _____C____ 2. Slow acting system that contains hormones _____H____ 3. Fast acting system that includes the brain ______A___ 4. Contains the skin, hair, and nails _____K____ 5. Includes the bladder, ureters, and urethra _____D____ 6. Picks up fluids leaked from blood vessels ______J___ 7. Contains the trachea ____F_____ 8. Includes the ovaries and uterus ____B_____ 9. Contains tissues that contract _____I____ 10. Includes the heart and blood vessels _____A____ 11. Includes sweat glands _____G____ 12. Includes the skull bones, femur, etc _____G____ 13. Includes joints and cartilage ____J_____ 14. Involved with gas exchange in the body ____H_____ 15. Includes the spinal cord H. Nervous System I. Cardiovascular System J. Respiratory System K. Urinary System II. Use the regional terms in your book as a word bank to complete the following matching. FEMORAL 16. Thigh ORBITAL 17. Eye area PATELLAR 18. Anterior knee SACRAL 19. Between hips CARPAL 20. Wrist CERVICAL 21. Neck region DIGITAL 22. Fingers and toes BRACHIAL 23. Arm III. Use the orientation/direction terms in your book to fill in the blanks. 24. The head is SUPERIOR to the foot. 25. The ribs are SUPERFICIAL to the lungs. 26. The sternum is MEDIAL to the arm. 27. The knee is PROXIMAL to the ankle. 28. The skin is SUPERFICIAL to the bones. 29. The heart is DEEP to the skin. 30. The shoulders are LATERAL to the neck. 31. The ribs are INTERMEDIATE to the sternum and armpits. IV. Draw a simple sketch of the three major planes in the human body V. Fill in the table below: Name of Body Cavity Spinal Dorsal/Ventral Organs SPINAL CORD DORSAL CRAINIAL BRAIN Thoracic Dorsal VENTRAL LUNGS, HEART, ETC ADBOMINOPELVIC VENTRAL Uterus Unit 2 – Histology (Cells and Tissue) I. List the order of organization in the human body starting with cells: Cells TISSUES ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEMS II. Fill in the following table about body tissue: Type of Epithelium Tissue SIMPLE SQUAMOUS Description/Drawing 1 Layer/fish scales or Cobblestone Locations ALEVEOLI OF THE LUNGS Simple cuboidal 1 LAYER/CUBE-SHAPPED KIDNEY SIMPLE COLOUMNAR 1 layer/Tall, column-shaped LINING OF THE STOMACH STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS MORE THAN 1 LAYER (FISH Esophagus SCALES OR COBBLESTONE) PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR 1 LAYER, BUT LOOKS LIKE MORE THAN 1 COLUMNAR LAYER BECAUSE NOT ALL REST ON THE BASEMENT MEMBRANE Trachea Transitional ROUNDED BUT FLATEEN AND ELONGATED WHEN THEY EXPANED URIANARY BLADDER 1. Why are neurons (nerve cells) long and thin? How is their form related to their function? THERE ARE LONG EXTENSIONS THAT ALLOW FOR THE ACTION POTEINTIONAL TO BE CARRIED FROM THE BRAIN TO MUSCLES OR OTHER NEURONS. THE NEURONS CAN SEND SIGNALS OVER LONG DISTANCES BECAUSE OF THE LONG CYLINDRICAL STRUCTURE. 2. What are the three classification of muscle tissue? How are they different from each other? 3. What is the extracellular matrix? A COLLECTION OF FIBRES, PROTEIN, AND INTERACEULLAR FULID THAT ENCAPSULATES THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE CELLLS IN DIFFERENT CONCENTRATIONS. THIS PROPERTY HELPS TO DETERMINE THE TYPE OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE. Unit 3 – Integumentary System I. Questions about the Integumentary System. 1. List the layers of the epidermis from most superficial to deepest STRATUM CORNEUM, STRATUM LUCIDIUM, STRATUM GRANULOSUM, STARTUM SPINOSUM, AND STRATUM BASULE 2. Explain the difference between an eccrine (sweat) gland and sebaceous gland. ECCCRINE – SECCRETE SWEAT EVERYWHERE BUT THE PLAMS AND SOLES OF FEET. SEBACEOUS GLAND – SECRETE CELL FRAGMENTS WITH FATTY ACID AND SEBUM. 3. Why are skin cells that are closest to the surface all dead? 1. TOO FAR AWAY FROM BLOOD SUPPLY 2. TOO MUCH KERATIN KILLS THEM 4. What is the arrector pili muscle and what is its role? THEY ACTIVATE WHEN WE ARE COLD OR SCARED TO MAKE HAIR STAND ON END 5. Explain the rule of nines. What is considered critical? IT ESTIMATES WHAT % OF FLUIDS MAY BE LOST FROM THE BODY DUE TO BURNS. IT DIVIDES THE BODY INTO DIFFERENT % THAT ADD UPTO 100%. 10% IS CRITICAL FOR 3RD DEGREE BURNS OR ANY 3RD DEGREE BURN ON FACE OR HANDS. 6. List the ABCD’s of skin cancer. What does each letter mean? A = ASSYMETRY B = BORDER C = COLOR D = DIAMETER 7. Look at a diagram of the skin cell in your textbook and match the following clues with the correct region/part of the skin: ADIPOSE A. Yellow cells found in subcutaneous layer DERMIS B. Layer where follicle resides SEBACOUS GLAND C. Secretes sebum EPIDERMIS D. Mostly dead skin DERMAL PAPILAE E. Responsible for fingerprints ARRECTOR PILLI MUSCLE F. Responsible for “goosebumps” Unit 4 – The Skeletal System I. Matching the classification of bones: Long bones (L) Short bones (S) Flat bones (F) Irregular bones (I) L 1. Humerus L I 4. Vertebrae L 7. Radius F 10. Sternum 2. Tibia F 3. Occipital S 5. Carpals F 6. Parietal S 8. Patella 9. Ribs F II. Matching Skull Bones/Markings FRONTAL 12. Makes up the forehead SPHENOID 13. Bat shaped bone FORMAN MAGUM 14. Opening for spinal cord EXTERNAL ACUSTIC MEATUS 15. Leads to eardrum LACRIMAL 16. Spot for tear ducts ZYGOMATIC 17. Cheekbone OCCIPITAL 18. Posterior most skull bone III. Label the parts of the long bone: EPHIPHYSIS 1. DIAPHYSIS 2. EPHIPHYSIS 3. SPONGY BONE 4. EPHIPHYSEAL LINE 5. Blood Vessel ARTICULAR CARTILAGE 7. 6.