* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Changes - Down the Rabbit Hole
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
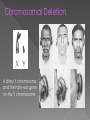
Mutations are a result in a change in DNA sequence › A protein with a different AA sequence could be produced. › Germ Cell - If mutations occur in sex cells they may be passed on to the next generation. › Somatic- A mutation occurring only in body cells may be a problem for the individual but will not be passed on to the offspring. Mutations may be classified as chromosomal alterations or gene mutations › Chromosomal alterations are generally more severe because many genes are usually involved. Significance of Mutations Most are neutral • Eye color • Birth marks • Some are harmful • Cystic Fibrosis • Down Syndrome • Some are beneficial • Sickle Cell Anemia to Malaria • Immunity to HIV • What Causes Mutations? There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: – Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child – Mutations can be acquired. Environmental damage Mistakes when DNA is copied Silent mutation › any mutation that is not expressed because it does not cause a change in amino acid chain. Point mutation base-pair substitution › 1 base is replaced by a different base › • Point mutation • Only one nucleotide changes, but it makes a different protein Gene Mutations Point Mutations – changes in one or a few nucleotides – Substitution THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT THE FAT HAT ATE THE RAT – Insertion THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT THE FAT CAT XLW ATE THE RAT – Deletion THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT THE FAT ATE THE RAT • Frameshift • Causes every codon in the DNA sequence to be changed after the mutation: • Insertion- one or more bases are added • Deletion- one or more bases are removed A Deletion - part of chromosome is left out. Duplication - part of chromatid breaks off add attaches to the sister chromatid creating a duplication of genes on the same chromosome. › Deletion and duplication mutations are errors that occur during crossing over in Meiosis I. Translocation - when part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome. Inversion - when part of a chromosome breaks off and is reinserted backwards. Chromosome Mutations Changes in number and structure of entire chromosomes Original Chromosome ABC * DEF Deletion AC * DEF Duplication ABBC * DEF Transposition ACB * DEF Inversion AED * CBF Translocation ABC * JKL GHI * DEF Chromosomal Deletion A dinky Y chromosome and the hairy ear gene on the Y chromosome