* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Parental investment wikipedia , lookup
Spawn (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive suppression wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial insemination wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Fish reproduction wikipedia , lookup
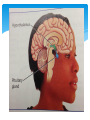
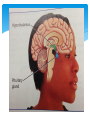
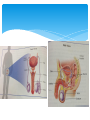
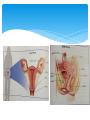
Endocrine System Endocrine System Help regulate activities Produces chemicals that control many of the body’s daily activities Regulates long-term changes such as growth and development Made up of glands: an organ that produces or releases chemicals Endocrine glands: produce and release their chemicals directly into the bloodstream Hormones Chemical product of an endocrine gland Like a chemical messenger Regulate activities in tissues and organs Production: nerve impulses from brain signal for endocrine glands to produce hormones Action: hormones cause a slower, but longer lasting response than the nerve impulses Target cells: the cells the hormones interact with, they recognize the hormone’s structure Functions of Endocrine Glands Each gland releases different hormones Endocrine glands: Hypothalamus: links nervous and endocrine systems Pituitary: regulates growth, blood pressure, and water balance Thyroid: controls release of energy from food molecules Parathyroid: regulate amount of calcium in blood More endocrine glands… Adrenal Adrenaline triggers response to emergencies Salt and water balance in kidneys Sugar in the blood Thymus Immune system development Pancreas Insulin and glucagon control glucose level in blood Ovaries (in females) Estrogen controls changes in female body Trigger egg development Testes (in males) Testosterone controls changes in male’s body Regulates sperm production Hypothalamus Tiny part of the brain near the middle of your head Link between nervous system and endocrine system Sends out never messages and produces hormones Controls pituitary gland Pituitary Gland Just below hypothalamus Size of a pea Communicates with the hypothalamus to control body activities Responds to hypothalamus by releasing hormones Some hormones trigger other glands to produce hormones Negative Feedback Process in which a system is turned off by the condition it produces When the amount of a particular hormone in the blood reaches a certain level, the endocrine system send signals that stop the release of that hormone. The Reproductive System Asexual Reproduction Reproduction where offspring arise from a single parent Inherit the genes of that parent only Offspring will be exact genetic copies of parent Reproduction for single cell organisms Bacteria Protists Many fungi Sexual Reproduction Involves the production of eggs by the female and sperm by the male Egg is the female sex cell Sperm in the male sex cell Fertilization: process by which male and female living things produce offspring Zygote: a fertilized egg Chromosomes Carry information that controls inherited characteristics Cells have 46 chromosomes Except sex cells only have 23 chromosomes 23 chromosomes of sperm join the 23 of the egg Zygote then contains the 46 need to produced offspring Male Reproductive System Specialized to produce sperm and testosterone Testes Organ that produces sperm and testosterone Located in the scrotum External pouch of skin Keeps testes about 2C to 3C below body temp Sperm need slightly cooler condition for development Sperm Composed of a head containing chromosomes and long tail Path: Sperm mix with fluids produced by glands Mixture is called semen Contains about 5-10 million sperms per drop Fluid allows for sperm to swim Contains nutrients that sperm use as energy Leaves body through penis Tube is call urethra (same tube urine travels through) Female Reproductive System Specialized to produce eggs and nourish a developing baby Ovaries Produce eggs and estrogen Egg released about once a month Fallopian tubes (or oviducts) Passageway for eggs to travel from ovary to uterus Fertilization usually occurs in fallopian tube Female Reproductive System Uterus Hollow muscular organ Fertilized egg attaches to wall Egg not fertilized breaks down and leaves uterus through opening called cervix Vagina (birth canal) Muscular passageway leading to the outside of the body Baby leaves mother’s body Menstrual Cycle Monthly cycle of changes in female reproductive system Egg develops in ovary while uterus prepares for arrival of an embryo Stages of cycle: Egg matures, uterus walls thicken Mature egg is released (ovulation) Unfertilized egg enters uterus to breakdown Thickened walls break down Extra blood and tissue of thickened walls leave through vagina (menstruation) Last 4-6 days New egg starts to mature