* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Statistics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
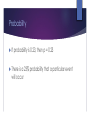
Statistics & Evidence-Based Practice THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING NURSING 200W Objectives Identify the purposes of statistical analyses. Describe the process of data analysis. Describe probability theory and decision theory that guide statistical data analysis. Describe the process of inferring from a sample to a population. Discuss the distribution of the normal curve. Objectives Identify descriptive analyses. Describe the results obtained from inferential statistical analyses. Describe the five types of results obtained from quasiexperimental and experimental study designs. Compare and contrast statistical significance and clinical importance of results. Critically appraise statistical results, findings, limitations, conclusions, and generalization of findings. A Statistical Primer Statistics in Nursing Practice Reading or critiquing published research Examining outcomes of nursing practice by analyzing data collected in a clinical site Developing administrative reports with support data Analyzing research done by nursing staff and other health professionals at a clinical site Demonstrating a problem or need and conducting a study Critically Appraising Statistics Identify statistical procedures used Determine whether statistics used were appropriate or not Evaluate researchers interpretation of statistics Stages in Data Analysis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Prepare data for analysis. Describe the sample. Test reliability of measurement methods. Conduct exploratory analysis. Conduct confirmatory analysis guided by hypotheses, questions, or objectives. 6. Conduct posthoc analyses. Major Statistics in Nursing Studies Descriptive Inferential Descriptive Statistics Describe and summarize the sample and variables Also referred to as summary statistics Inferential Statistics Infer or address the objectives, questions, and hypotheses Descriptive Statistics If a research study collects numerical data, data analysis begins with descriptive statistics Not limited to quantitative research! May be the only statistical analysis conducted in a descriptive study Types of Descriptive Statistics Frequency distributions Measures of central tendency Measures of dispersion Two-Tailedness Ungrouped Frequency Distribution Data in raw form: 1: ☺ 2: ☺☺☺☺☺☺☺ 3: ☺☺ 4: ☺☺☺☺ 5: ☺ Grouped Frequency Distribution Data are grouped into categories: Ages 15 to 20: 12 Ages 20 to 25: 14 Ages 25 to 30: 19…. Example of a Percentage Distribution Housing: 41.7% Textbooks: 8.3% Clothing: 16.7% Food: 8.3% Additional Supplies: 25% How Frequency Distributions are Presented in Research Articles Measures of Central Tendency Mean Median Mode Normal Curve Normal Curve A theoretical frequency distribution of all possible values in a population Levels of significance and probability are based on the logic of the normal curve Mean Is the sum of values divided by the number of values being summed Median Is the value in exact center of ungrouped frequency distribution Is obtained by rank ordering the values Mode Is the numerical value or score that occurs with greatest frequency Is expressed graphically Bimodal Distribution Measures of Dispersion Range Variance Standard deviation Standardized scores Scatterplots Range Is obtained by subtracting lowest score from highest score Difference Scores Are obtained by subtracting the mean from each score Sometimes referred to as a deviation score because it indicates the extent to which a score deviates from the mean Standard Deviation Is the square root of the variance Just as the mean is the “average” value, the standard deviation is the “average” difference score Standardized Scores Raw scores that cannot be compared and are transformed into standardized scores Common standardized score is a Z-score Provides a way to compare scores in a similar process Scatterplots Probability Theory Probability Theory Used to explain: Extent of a relationship Probability of an event occurring Probability that an event can be accurately predicted Probability If probability is 0.23, then p = 0.23 There is a 23% probability that a particular event will occur Inferences A conclusion or judgment based on evidence Judgments are made based on statistical results Decision Theory Decision Theory Assumes that all the groups in a study used to test a hypothesis are components of the same population relative to the variables under study It is up to the researcher to provide evidence that there really is a difference To test the assumption of no difference, a cutoff point is selected before analysis Statistics JUDGING THE APPROPRIATENESS OF THE STATISTICAL TESTS USED Critical Appraisal Factors that must be considered include: Study purpose Hypotheses, questions, or objectives Design Level of measurement Critical Appraisal You must judge whether the procedure was performed appropriately and the results were interpreted correctly. Information Needed 1. Decide whether the research question focuses on differences or associations/relationships. Information Needed 1. Decide whether the research question focuses on differences or associations/relationships. 2. Determine level of measurement. Data Types Nominal Ordinal Interval/Ratio Information Needed 1. Decide whether the research question focuses on differences or associations/relationships. 2. Determine level of measurement. 3. Select the study design that most closely fits the one you are looking at. Information Needed Decide whether the research question focuses on differences or associations/relationships. 2. Determine level of measurement. 3. Select the study design that most closely fits the one you are looking at. 4. Determine whether the study samples are independent, dependent, or mixed. 1. Statistical Tests SOME COMMON STATISTICAL TESTS IN RESEARCH Chi-Square Nominal or ordinal data Tests for differences between expected frequencies if groups are alike and frequencies actually observed in the data Chi-Square Regular Exercise Male 35 No Regular Exercise 15 Total 50 Female 10 40 50 Total 45 55 100 Chi-Square Indicate that there is a significant difference between some of the cells in the table The difference may be between only two of the cells, or there may be differences among all of the cells. Chi-square results will not tell you which cells are different. Example Pearson Product-Moment Correlation Tests for the presence of a relationship between two variables Works with all types of data Correlation Performed on data collected from a single sample Measures of the two variables to be examined must be available for each subject in the data set. Correlation Results Nature of the relationship (positive or negative) Magnitude Testing of the relationship (–1 to +1) the significance of a correlation coefficient Response Question Which are the following are significant? A. r = 0.56 (p = 0.03) B. r = –0.13 (p = 0.2) C. r = 0.65 (p < 0.002) Example Factor Analysis Examines relationships among large numbers of variables Disentangles those relationships to identify clusters of variables most closely linked Sorts variables according to how closely related they are to the other variables Closely related variables grouped into a factor Factor Analysis Several factors may be identified within a data set The researcher must explain why the analysis grouped the variables in a specific way Statistical results indicate the amount of variance in the data set that can be explained by each factor and the amount of variance in each factor that can be explained by a particular variable Regression Analysis Used when one wishes to predict the value of one variable based on the value of one or more other variables Regression Analysis The outcome of analysis is the regression coefficient R When R is squared, it indicates the amount of variance in the data that is explained by the equation R2 = 0.63 Example T-test Requires interval level measures Tests for significant differences between two samples Most commonly used test of differences Example Analysis of Variance ANOVA Tests for differences between means Allows for comparison of groups Example Results A SUMMARY OF THE TYPES OF RESULTS YOU WILL FIND IN EXPERIMENTAL AND QUASI-EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH STUDIES Types of Results Significant and predicted Nonsignificant Significant and not predicted Mixed Unexpected Significant and Predicted Support logical associations between variables As expected by the researcher Nonsignificant Negative or inconclusive results No significant differences or relationships Significant and Unpredicted Opposite of what was expected Indicate potential flawed logic of researcher Mixed Most common outcome of studies One variable may uphold predicted characteristics, whereas another does not Or two dependent measures of the same variable may show opposite results. Unexpected Relationships between variables that were not hypothesized and not predicted from the framework being used Findings, Conclusions, & Implications Findings Results of a research study that have been translated and interpreted Statistically Significant Findings Significant p-values Clinically Significant Findings Practical application of findings Somewhat based on opinion Conclusions A synthesis of findings Researchers should not go beyond what the findings state or interpret too much! Implications The meaning for nursing practice, research, and/or education Specific suggestions for implementing the findings Critical Appraisal QUESTIONS TO ASK Critical Appraisal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What statistics were used to described the characteristics of the sample? Are the data analysis procedures clearly described? Did statistics address the purpose of the study? Did the statistics address the objectives, questions or hypotheses of the study? Were the statistics appropriate for the level of measurement of each variable? Critical Appraisal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What statistics were used to described the characteristics of the sample? Are the data analysis procedures clearly described? Did statistics address the purpose of the study? Did the statistics address the objectives, questions or hypotheses of the study? Were the statistics appropriate for the level of measurement of each variable? Critical Appraisal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What statistics were used to described the characteristics of the sample? Are the data analysis procedures clearly described? Did statistics address the purpose of the study? Did the statistics address the objectives, questions or hypotheses of the study? Were the statistics appropriate for the level of measurement of each variable? Critical Appraisal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What statistics were used to described the characteristics of the sample? Are the data analysis procedures clearly described? Did statistics address the purpose of the study? Did the statistics address the objectives, questions or hypotheses of the study? Were the statistics appropriate for the level of measurement of each variable? Critical Appraisal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What statistics were used to described the characteristics of the sample? Are the data analysis procedures clearly described? Did statistics address the purpose of the study? Did the statistics address the objectives, questions or hypotheses of the study? Were the statistics appropriate for the level of measurement of each variable? Critical Appraisal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What statistics were used to described the characteristics of the sample? Are the data analysis procedures clearly described? Did statistics address the purpose of the study? Did the statistics address the objectives, questions or hypotheses of the study? Were the statistics appropriate for the level of measurement of each variable? The End! QUESTION? COMMENTS?