* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 2.1 Continental Drift
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Paleoflooding wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
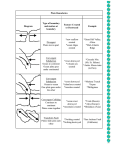
*Refer to Chapter 3 in your Textbook Bellringer: 9/10/15 List 3 ways you think the ocean has changed over time (use things like more/less, bigger/smaller…) Reminder: ALL Unit 1 make-up & late work must be turned in by next Thursday, 9/17! Learning Goals: 1. I can explain evidence for the Theory of Plate Tectonics. 2. I can differentiate between the 3 plate boundaries. 3. I can explain how the ocean was formed. 4. I can identify smaller divisions of the ocean. Theory of Continental Drift: = the movement of the continents across the ocean bed Edward Suess (Late 1800’s) Gondwanaland: South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, & India Alfred Wegener (1915) Laurasia: North America, Europe, & Asia Pangea: combined Gondwanaland with added Laurasia Theory of Continental Drift Convection H. Hess (1960’s) Convection: force that makes magma in Earth’s mantle move, due to heating and cooling Cool- sinks toward core Heat- rises toward upper mantle/crust Theory of Plate Tectonics = Lithospheric/Tectonic plates move across the asthenosphere Lithosphere: crust & upper mantle, rigid Asthenosphere: part of the lower mantle, viscous Lithospheric Plates Theory of Plate Tectonics Types of Plate Boundaries: Convergent: oceanic-to-continental crust come together Old crust is submerged into the mantle and destroyed Form: Trenches Divergent: oceanic-to-oceanic crust move apart New crust is formed via sea floor spreading Form: Mid-ocean ridges Transform: oceanic-to-oceanic crust scrape past each other in opposite directions Form: Faults & Cliffs Types of Plate Boundaries Formation of the Ocean Tethys Ocean: Between Gondwanaland and Laurasia Closed when India moved into Asia Panthalassic Ocean: Huge ocean surrounding Pangea Became the Pacific Atlantic Ocean: Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart Formation of the Ocean MYAM YA Today’s Ocean We have one world ocean broken into 5 artificial components Pacific Atlantic Indian Arctic Southern/ Antarctic Smaller Divisions of the Ocean Sea: a smaller body of salt water that is almost completely surrounded by land Example: Mediterranean Sea Gulf: a smaller body of salt water that is partially surrounded by land Example: Gulf of Mexico Estuary: inlet area where salt water meets fresh water Example: St. Lucie Estuary Lagoon: body of water composed of brackish water- a mixture of salt & fresh Example: Indian River Lagoon