* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proper Nutrition Notes
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Dietary fiber wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
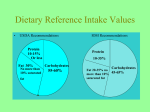
Guidelines for Good Nutrition Obesity Trends http://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/trends.html Food Energy True Calorie=the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1 degree C 1. CALORIES IN = CALORIES OUT 1 GRAM OF FAT = 9 CALORIES 1 GRAM OF PROTEIN = 4 CALORIES 1 GRAM OF CARBOHYDRATES= 4 CALORIES 1 GRAM OF ALCOHOL = 7 CALORIES VARIABLES IN CALORIC INTAKE RESTING METABOLIC RATE ACTIVITY DIETARY THERMOGENESIS RESTING METABOLIC RATE FACTORS: GENES, AGE, GENDER, MUSCLE MASS, WEIGHT DEFINITION: THE NUMBER OF CALORIES NEEDED TO MAINTAIN NORMAL BODILY FUNCTIONS WHILE AT REST Activity How much physical activity do you do in a day? None Very little Moderate A lot Super athlete DIETARY THERMOGENESIS The number of calories that is needed for consumption, digestion and transportation of a meal. 2. DECREASE DIETARY FAT Less than 30% of total caloric intake Essential fatty acids 2-4% of daily calories Body needs these fatty acids but is not capable of making Fat related cancers occur with an average intake of 20-25% fat intake threshold. TYPES OF FAT Saturated- No double bond- animals Poly- Unsaturated – 2 or more double bonds Mono- unsaturated- 1 double bond Increased Saturated fat = Increased Heart disease Keys: Less that 1/3 of total fat should be from saturate fat 2. DECREASE SATURATED FAT No more that 30% of total fat intake Solid at room temperature Butter, lard, margarine. Shortening The more solid at room temperature the more saturated the fat is. AMOUNTS OF FAT Red Meat - ½ saturated Chicken and Turkey- 1/3 saturated Fish- ¼ saturated Whole milk-Dairy Productsup to 2/3 saturated 4. PROTEIN 10-15% of daily intake Anything from an animal Beans, seeds 5. INCREASE COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES +/- 60% Whatever is left after Fats and Protein Pasta, rice, breads, fruits, vegetables Anything not fat or protein 6. DECREASE SIMPLE SUGARS NO MORE THAN 2% OF YOUR DAILY INTAKE Soda, candy, junk foods 7. DIETARY CHOLESTEROL Less than 300mg per day Body does not need cholesterol from outside- it makes it own Anything from animal will have cholesterol CHOLESTEROL LEVELS 240 and Above = High Risk 200-239 = Moderate Risk Below 200 = Ideal Levels These numbers have steadily decreased over the years showing lower and lower safe levels. Total Cholesterol- WebMD Total cholesterol Desirable: Less than 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) Less than 5.17 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) Borderline high: 200–239 mg/dL 5.17–6.18 mmol/L High: 240 mg/dL and greater 6.21 mmol/L and greater LDL’S AND HDL’S LDL’S (low density lipoproteins) Bad cholesterol- adheres to artery walls and creates blockage HDL’S (high density lipoproteins) Good Cholesterol- carry’s bad cholesterol to the liver to be disposed. Healthy diet and exercise will increase these. 8. DIETARY SODIUM No more than 2400 mg per day Check chicken noodle soup label 9. CALCIUM 1000-1500 Mg per day 8oz glass of milk – 300mg 8oz yogurt- 400mg Vitamin D is essential to absorption of Calcium Caffeine will decrease absorption 10. DIETARY FIBER 25 Grams per day Legumes (comes from a plant) Beans Bran cereal Fruits Most vegetables Whole grains FIBER CONTINUED… Insoluble- protects against cancer Wheat Roughage Soluble- protects against heart disease Oats Assignment Keep a Nutrition Journal for 3 days (at least 1 weekday and 2 weekend days) = 30 points Due Monday Record EVERYTHING you consume as you eat and drink it (do NOT rely on memory)…be honest! 15 Extra points if you go to MyPyramid Plan at http://www.mypyramid.gov/pyramid/index.html; answer the questions; and print off your information. Then, type/write 1 page on how this plan compares to your actual nutrition practices. Digestion Food travels 26 ft through the digestive system Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum Digestion Process Chewing—saliva (amylases) Pharynx—triggers swallowing reflex Epiglottis moves—covers trachea Esophagus—peristalsis moves it down to stomach (5-10 s) Sphincter opens to let food into stomach Digestion Process, continued Stomach—gastric juices secreted (Hydrochloric acid and Pepsin) Food stays here for 2-6 hours Moves to small intestine (19.8 ft) Stays here for 3-6 hours Enzymes released to help break food down more (ex: lipases, bile) Digestion Process, continued 2 Small intestine Most absorption of nutrients occurs here Villi—fingerlike projections increase surface area for absorption Wastes moved into large intestine/colon (dead cells, mucus, digestive secretions, bacteria, and yeast) Digestion Process, continued 3 Large intestine/colon Water balance is key to consistency of waste products The Liver Secretes bile (emulsifies fat) Maintains blood glucose levels Monitors production of cholesterol Detoxifies poisons Hepatitis Cirrhosis Lactose Intolerance Stomach and intestinal pain, vomiting, diarrhea result from eating milk products Inability to digest lactose (sugar found in milk) Why? They don’t produce the enzyme lactase Excretion Process that rids the body of toxic chemicals, excess water, salts, and CO2 Maintains osmotic and pH balance 3 organs: lungs, kidneys, and skin Excretion organs Lungs: excrete CO2 and water vapor in exhaled air Kidneys: excrete nitrogen wastes, salts, water, etc in urine Skin: excretes water, salts, nitrogen wastes, etc in sweat Kidneys Regulate the amount of water and salts in blood plasma Each kidney contains 1 million nephrons Nephron=tiny tubes that filter wastes from blood, retain useful molecules, and produce urine Urine Elimination Urinary bladder—hollow, muscular sac that stores urine Urethra—tube that urine leaves the bladder through Kidney Damage Kidney failure: infection, diabetes, high blood pressure, and autoimmune disorders Dialysis Transplantation