* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
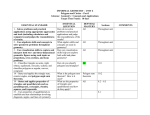
CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN 121 77.5 Unit 1: Tools of Geometry 15 9 How do you find length, area? 2 1 What are the basic tools and concepts of geometry? ow do we measure line segments and angles? 1 3 2 1 0 0.5 How do we use the Distance Formula? ow do we use the Midpoint Formula? How do we identify parallel and perpendicular lines? page 1 of 16 Students will be able to... Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test book Geometry PH 2004 Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site • find area/perimeter of rectangles, triangles, 1.7 circles, composites. 1.2, 1.3 • identify and define the basic tools of geometry (Line, point, plane, etc.) 1.4, 1.5 • measure & construct segments, angles, triangles, bisectors • measure figures, and find midpoint and distance 1.6 on the coordinate plane • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs 2 0.5 • identify and define parallel and perpendicular lines • use slope to determine whether lines are parallel or perpendicular 3.5, 3.6 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions Resources/Assessments other # of Blocks CP HN page 2 of 16 Students will be able to... book Resources/Assessments other Unit 1: Tools of Geometry (continued) Geometry PH 2004 2 2 1 2 How do we prove that lines are parallel? How do we determine angle measure when parallel lines are cut by a transversal? • plan and write paragraph, flow chart and two column proofs, distinguishing between properties, 2.1 - 2.5 postulates and theorems • write conditional statements & their converses • write proofs using the Alternate Interior Angles, 3.2, 3.2 Alternate Exterior Angles, & Corresponding Angle Theorems • determine angle measure when parallel lines 3.1, 3.2 are cut by a transversal • explain the relationship between the types of angles created when parallel lines are cut by a transversal CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN Unit 2: Triangles 25 How do we classify triangles by sides and angle? 1 What are the relationships between the sides and angles of a triangle? What is the Triangle Inequality postulate? 10 0.5 0.5 2 1 page 3 of 16 Students will be able to... Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test • define, identify, and classify triangles by sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral) and angles (acute, equiangular, obtuse). • understand the Side-Angle Postulate • justify the Side-Angle Postulate in informal proofs • solve problems involving the Triangle Inequality Postulate book Geometry PH 2004 3.3 5.5 Resources/Assessments other Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site What is the Triangle Inequality postulate? What are the special segments within a triangle? What are the relationships between the special segments within triangles? How do we determine if triangles are congruent? 4 0.5 1 0.5 5 2 • justify the Triangle Inequality Postulate in informal proofs • identify and solve problems involving midsegments, altitudes, and medians • identify and solve problems involving incenter, orthocenter, circumcenter, and centroid. (Centroid-CP, all else Honors) • understand the “shortcuts” for determining congruency in triangles (ASA/SAA/SAS) • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs 5.1 - 5.3 5.3 4.1 - 4.3, 4.6 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN page 4 of 16 Students will be able to... Unit 2: Triangles (continued) How do we prove that triangles are congruent? book Geometry PH 2004 3 2 7 1 How do we determine if triangles are similar? • write proofs using the congruency postulates • identify similar triangles, and solve problems involving proportion • identify minimum information to know if triangles are similar (AA, SSS~, SAS~) 4.4, 4.5, 4.7 8.1 - 8.5 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions Resources/Assessments other # of Blocks CP HN page 5 of 16 Students will be able to... book Resources/Assessments other Unit 3: Similarity & Trigonometry 13 9 What are the special properties of right triangles? How can we use the Pythagorean Theorem & its converse? 4 2 Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test Geometry PH 2004 • use geometric mean/similarity to solve problems 8.4 • solve with Pythagorean Theorem • deduce obtuse,acute,right with Pythagorean Thoerem 7.2 Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site GSP Demos Ch 09 • use 3,4,5 and 5,12,13 Pythagorean Triples 1 0.5 1 0.5 5 4 What are special right triangles? What are the 3 Trigonometric Ratios? • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs • solve problems involving 45-45-90 and 30-607.3 90 triangles • apply the properties of special right & similar 7.3 triangles to determine the missing side of a given triangle • solve problems with trigonometry & use trig tables & calculators for ratios • connect 9.1 - 9.3 tangent ratio to slope of lines CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions Unit 4: Polygons How can a polygon be classified? How can the sum of a polygon's interior angles be determined when only the number of sides is known? # of Blocks CP HN 16 10 1 0.5 2 1 Trig Ratio Tables p731 IMP 1: Return of the Tree page 195 EGwGSP page 6 of 16 Students will be able to... Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test • classify polygons based on number of sides (quadrilateral, triangle, etc.) concave/convex, regular/irregular • determine the sum of the interior and exterior angles of a polygon book Resources/Assessments other Geometry PH 2004 Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site 3.4 Ch5 Discovering Geometry 3.4 GSP Demos Ch 5 How can the sum of a polygon's interior angles be determined when only the number of sides is known? How can it be determined if two polygons are similar? How can quadrilaterals be classified using properties of sides, angles and diagonals? 2 4 1 1 • decompose polygon into triangles • solve problems using the formulas for interior and exterior angles of polygons to determine the measure of missing angles • apply properties of similar figures to determine 8.2 if two polygons are similar • apply properties of similar figures to determine the length of missing sides and the measure of missing angles in similar polygons using proportions • use knowledge of angles, sides and diagonals in 6.1, 6.2 order to classify quadrilaterals • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN Students will be able to... book Geometry PH 2004 1 1 0.5 1 1 What makes a good definition? EGwGSP page 112-113 Golden Ratio applies to credit cards, business cards GSP Demos Ch 01 CH 4 of EGwGSP page 104-105 EGwGSP, http://www.keymath.com/x19428.xml page 7 of 16 Unit 4: Polygons (continued) 1 http://www.keymath.com/x19426.xml • use properties of quadrilaterals (sides, diagonals, angles, and diagonals) to solve problems involving squares, rectangles, parallelograms, etc. • define classes of quadrilaterals with biconditionals • justify postulates about the special quadrilaterals using informal proof 6.2 - 6.5 Resources/Assessments other How do we prove a conjecture? 2 2 • write proofs of quadrilateral theorems using the properties of congruence, and angle postulates Geometry Midterm Review are the essential elements of 2What blocks 4 3 • complete practice review problems that summarize the terms’ work Geometry? 6.3 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN Unit 5: Circles 10 What types of lines and line segments are associated with circles? 1 What are the special ratios of circles? 1 3 What relationships exist among the measures of central and inscribed angles and arcs? 8.5 1 0.5 2 page 8 of 16 Students will be able to... Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test • classify special segments of circles (radius, diameter, chord, secant, tangent, arc) • demonstrate an understanding of circle ratios: radius-diameter, diameter-circumference, pi • solve problems for the circumference, diameter, and radii of circles • solve problems relating inscribed angles, intercepted arcs, radii, tangent segments, secant segments, chords* • apply proportions to chords, tangents, secants,radii* • demonstrate understanding of the relationships between the measures of central and inscribed angles and arcs book Geometry PH 2004 7.6 7.6 11.1 11.4 Resources/Assessments other Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site What relationships exist among the measures of central and inscribed angles and arcs? • apply mean to vertical angles between intercepted arcs • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs 11.1 11.4 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN page 9 of 16 Students will be able to... Unit 5: Circles (continued) How can the relationship between arcs and angles be used to find the length or measure of arcs? How do we prove circle conjectures? book Geometry PH 2004 2 1 1 2 • solve problems for the measurements of central and inscribed angles, arc angles, the measurements of angles and arcs formed by secants and tangents • write indirect proofs in paragraph and twocolumn format to prove theorems of circles, involving conjectures, tangents, inscribed angles, and parallel lines 11.1 11.4 11.1 11.4 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions Unit 6: Measuring 2D Figures How are triangles measured using properties to deduce missing information? Resources/Assessments other # of Blocks CP HN page 10 of 16 Students will be able to... 8 7 Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test 2 1 • differentiate between perimeter and area book Geometry PH 2004 Resources/Assessments other Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site • deduce altitude of equilateral triangle How are triangles measured using properties to deduce missing information? • solve for the perimeter and area of triangles using triangle formulas (i.e. area, Pythagoras, Special Right Triangles, Trig) 2 3 How are quadrilaterals measured using properties to deduce missing information? How are perimeter and/or area of regular polygons found? How are circles measured using properties to deduce missing information? 1 0.5 1 0.5 • differentiate between perimeter and area • solve for the perimeter and area of quadrilaterals (parallelograms vs. trapezoids) using area formulas • connect mean to trapezoid area formula • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs • solve problems using the lengths of segments and apothems to solve for the perimeter and/or area of regular polygons • solve problems for the circumference and area of circles andcalculate the arc length and area of sectors with proportions • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs 7.1 - 7.4 7.4 7.5 7.6, 7.7 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions Unit 7: Measurement in Space # of Blocks CP HN 10 6 What does 3-D mean? 1 How can polyhedrons be named? 0.5 page 11 of 16 Students will be able to... Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test • differentiate between 2D and 3D figures. identify appropriate measurement units (i.e. units², units³) • differentiate between bases and faces of prisms • explore net diagrams book Geometry PH 2004 10.1, 10.2 Resources/Assessments other Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site How is the lateral surface area of an object found? 2 1.5 What are the formulas used to solve for it? How is the total surface area of an object found? • demonstrate understanding of lateral • surface area as total surface area minus the base area(s) • solve for 10.3, 10.4 the total lateral area of objects in space using lateral surface area formulas • complete real-world modeling problems 2 0.5 What are the formulas used to solve for it? • differentiate between total surface area and lateral surface area of an object • solve for the total surface area of objects in space using surface area formulas • identify and calculate slant height complete real-world modeling problems 10.7 10.3, 10.4 10.7 CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN page 12 of 16 Resources/Assessments Students will be able to... Unit 7: Measurement in Space (continued) How does one measure the space inside 3D figures? Geometry PH 2004 1 1 What is volume? What are the relationships between perimeter scale factors and area/volume ratios? book 2 0.5 • demonstrate understanding of volume as a measurement in cubic units • select 10.5, 10.6 and differentiate between the volume formulas necessary to solve problems 10.7 • complete real-world modeling problems • identify scale factors for given polyhedrons based on perimeter calculations (units) • use the scale factor to calculate the area and volume ratios (units², units³) 10.8 other CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN page 13 of 16 Students will be able to... book Geometry PH 2004 Unit 8: Transformations 7 5 What is a transformation? 2 0.5 • understand the basic concepts of transformations, including image/pre-image, isometry 0.5 • identify and define translation, reflection, and rotation on and off the coordinate plane 12.2, 12.3 0.5 • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs • understand dilation and apply the concept of scale factor to figures • complete real-world modeling problems 12.7 What is an isometry? When do we use dilation? 1 Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test Resources/Assessments other Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site 12.1 ******MCAS Review****** 1 0.5 • understand the concept of composition • identify multiply transformations, including glide reflections, reflections over parallel lines (translation), and reflections over intersecting lines (rotations) How are composite transformations created? CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ 12.4 # of Blocks page 14 of 16 Resources/Assessments Essential Questions CP HN Students will be able to... Unit 8: Transformations (continued) book other Geometry PH 2004 1 1 When are tessellations useful? • identify when tessellations are used in the real world • create tessellations using chosen transformation 12.6 • identify the vertex arrangements of tessellations, note sum of degrees ************NOTE: Alternative Assessment: Tessellation Drawing Project, Geometer's Sketchpad Kaleidoscope (pg 661)*************** CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions Unit 9: Statistics & Geometric Probability # of Blocks CP HN 8 6 Why do we look at data? How can it best be represented? 1 1 page 15 of 16 Students will be able to... Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test • classify different methods of data collection and graphic representation such as frequency tables, box-and-whisker, and stem-leaf plots, scatterplots book Resources/Assessments other Geometry PH 2004 Geometry Activity binder, District Google Documents site 7.6 Skills Handbook 1 1 • classify different methods of data collection and pp. 712 graphic representation such as frequency tables, 714 box-and-whisker, and stem-leaf plots, scatterplots 1 • demonstrate understanding of mean, median, mode, and range of data by solving central tendency problems • select appropriate measures of central tendency to adequately interpret data What are some of the ways quantitative data can be represented? How can one interpret quantitative data? 2 What is a measure of central tendency? What generalizations can you draw from a given set of data? 8.4 • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs 1 0.5 • demonstrate understanding of weighted frequency and line-of-best-fit with graphic representations 3.5 • complete PSAT, MCAS MCQs/SAQs/ORQs CRLS Mathematics Department Geometry Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide Understanding Goals/ Essential Questions # of Blocks CP HN page 16 of 16 Resources/Assessments Students will be able to... Unit 9: Statistics & Geometric Probability (continued) What is the likelihood that an outcome will occur? book Geometry PH 2004 2 1.5 • use lengths, areas to calculate probability pp 723 724 other • find P(dart in bull's eye) • solve problems for the probability of an event occurring Geometry Final Review What are the essential elements of Geometry? 5 4 • complete practice review problems that summarize the year/semesters’ work 7.8