* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BN22 hormonal control
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
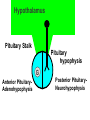
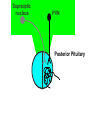
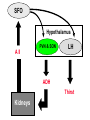
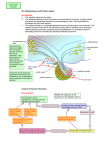
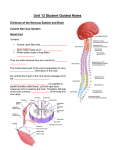
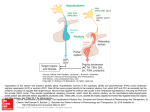
Hormonal Control of Behavior Lecture 22 Chemical Control of Brain Point-to-point control closed-circuit synapse fast, short-lived, local ~ Chemical Control of Brain Diffuse control widespread control slower, longer lasting Diffuse modulatory systems Neuroendocrine system ~ Hormones & Behavior? Responses to a changing environment detect stimulus make response Effectors muscles glands Autonomic N.S. Homeostasis ~ 2 Types of Glands Exocrine ducts sweat, tears, etc. Endocrine ductless hormones released into blood ~ Neurohormones Interact with nervous system Chemical message Neurotransmitters (NTs) Hormones Pheromones What’s the difference? ~ Neurohormones Similarities chemical messengers act at receptors influence behavior Differences medium distance traveled time course ~ Neurohormone Properties Neurons release molecules into blood Long distances Slower Longer lasting effects Widespread ~ Function Developmental sex differentiation testosterone, estradiol Regulatory Insulin, CCK, etc. Vasopressin, Oxytocin ~ Types of Neurohormones Amino acid-derived hormones e.g. epinephrine released from adrenal medulla Protein & Peptide Hormones Bind to membrane receptors Activate the 2nd messenger system ~ Types of Neurohormones Steroid Hormones Derived from cholesterol Soluble in lipids Bind to cytoplasmic receptors regulates gene expression e.g. sex hormones ~ Neuroendocrine System Brain Hypothalamus Releasing Hormones Pituitary gland Anterior: tropic hormones Posterior: neurohormones Glands - Hormones ~ Pituitary Gland 2 parts different developmental origins Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) no axons from hypothalamus parvocellular neurosecretory cells portal system Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) axons from hypothalamus magnocellular secretory cells ~ Hypothalamus Pituitary Stalk Pituitary hypophysis G Anterior PituitaryAdenohypophysis Posterior PituitaryNeurohypophysis Supraoptic nucleus PVN Posterior Pituitary Posterior Pituitary: Neurohormones Magnocellular neurosecretory cells Supraoptic & Paraventricular Nuclei Neurons fire Neurohormones released Transported down axons to posterior pituitary Peptide Neurohormones Oxytocin Vasopressin ~ Oxytocin Induces uterine contractions child birth orgasm during sex Triggers lactation “letdown reflex” triggered by touch, sight, sound ~ Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) AKA: Vasopressin Responds to blood pressure Induces vasoconstriction Promotes water retention Kidney: Renin release Angiotensin I Angiotensin II to kidneys & subfornical organ ~ Subfornical Organ Subfornical organ - SFO Dorsal 3d ventricle lacks blood-brain barrier A II receptors Output to Supraoptic & paraventricular nuclei ADH release lateral hypothalamus (LH) thirst drinking behavior ~ SFO Hypothalamus PVN & SON A II LH ADH Thirst Kidneys ADH (Vasopressin) Alcohol suppresses ADH release Damage diabetes insipidus Symptoms • copius urination • intense thirst ~ Anterior Hypothalamus Primordial tissue from roof of mouth No axons from hypothalamus Parvocellular neurosecretory cells Releasing hormones triggers release of tropic hormones Tropic hormones various glands gonads mammary adrenal thyroid ~ Hypothalamopituitary Portal System Portal Systems Capillary beds Connected by a vein e.g. hepatic portal vein Hypothalamus Anterior Pituitary ~ PVN RH G PVN TH RH TH G TH TH TH Cortisol Regulation Adrenal glands medulla: NE & E cortex: cortisol Regulation of cortisol steroid fight/flight & immunosuppression stress response Receptors widely distributed ~ Cortisol Regulation Hypothalamus Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) Anterior pituitary Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) Adrenal cortex Cortisol Negative feedback to hypothalamus cortisol inhibits own release ~ Sex Hormones Hypothalamus Gonadotropin-releasing hormone - GRH isolated from pig hypothalami Anterior Pituitary Gonadotropins • Follicle stimulating hormone - FSH • Lutenizing hormone - LH ~ Gonadotropins: Target Cells Gonads Testes Androgens -Testosterone Ovaries Estrogens Estradiol and Progesterone ~ Gonadotropin Release Patterns Sex differences FSH & LH both sexes Males steady Females cyclical Transplant male pituitary into female? ~