* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DIGESTION and ABSORPTION
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Cholesterol wikipedia , lookup
Low-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
High-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
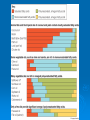
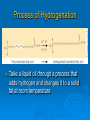
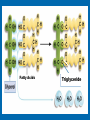
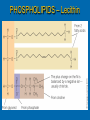
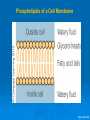
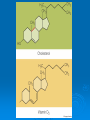
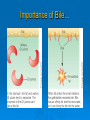
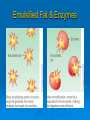
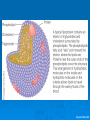
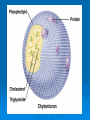
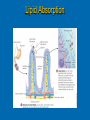
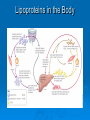
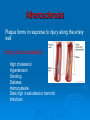
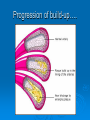
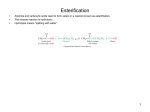
LIPIDS Ch. 5 Triglycerides, Phospholipids, and Sterols LIPIDS Learning Objectives: • Understand lipid terminology and classifications • Understand digestion and absorption of lipids Understand transport of lipids in body Learn about function of lipids in the diet, and how they relate to health issues – Heart Disease (Ch 18) • • Heart Attack GrillMonument to Greasy Gluttony https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dDDbXh1MYc Daily Consumption in the US 47 million hotdogs 2,250 cattle eaten as Big Mac’s 13 pizzas the size of Roman Coliseum 3 million gallons of ice cream 6 million pounds of chocolate WHAT ARE LIPIDS? • Organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen • Hydrophobic – “water-fearing” *Insoluble in water • Lipophilic – “fat loving” • Fats and Oils p. 146 3 CLASSES of LIPIDS Triglycerides • Made up of 3 Fatty Acids and Glycerol • “Fats and Oils” Phospholipids • Made of 2 Fatty Acids & phosphate bound to glycerol • Emulsifiers • Make up cell membranes Sterols • Hydrocarbon ring structure • Cholesterol, Bile acids, some hormones, Vit D Building Blocks: FATTY ACIDS Key building blocks for lipids/triglyceride Chains of carbon atoms Methyl group at one end (CH3) Carboxyl group at the other (COOH) CHEMISTRY OF FATTY ACIDS Influence characteristics of fat in food & health effects in our bodies Solid or liquid @ room temp Spoilage factors (oxidation) “Free” 3 or attached to another compound Characteristics of Fatty Acids Chain length Degrees of saturation Where first double bond is located FATTY ACIDS CHAIN LENGTH *Naturally occurring FAs contain even numbers of carbons • Short chain = less than 6 carbons *Dairy Products • Medium chain = 6-10 carbons *Dairy Products, Tropical Oils • Long chain = 12 or more carbons *Most common in the diet *Meat, fish, vegetable oils FATTY ACIDS 2 Classifications: • SATURATED FATTY ACID = Fully loaded with hydrogen atoms and contains only single bonds between its carbon atoms FATTY ACIDS 2 Classifications: • UNSATURATED FATTY ACID = Lacks hydrogen atoms and has at least one double bond between carbons UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS 2 Types: • Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) = Has one double bond • Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) = Has two or more double bonds Mono vs Poly Unsaturated Unsaturated FA Food Sources MUFA PUFA Olive Vegetable oil Canola oil Peanut oil Avocados Safflower Sesame Soy Corn Sunflower Nuts Seeds oils Lipid Chemical Model Activity Creating Fatty Acids Face-to-face class: * 6 groups * Create an 8-carbon fatty acid 3 groups will make saturated FA’s 3 groups will make unsaturated FA’s 2 polyunsaturated FA’s, 1 monounsaturated FA FATTY ACIDS Consistency Long-chain saturated fatty acids stack tightly Solids at room temp Animal fats Monounsaturated & polyunsaturated fatty acids don’t stack compactly… Liquid at room temperature Vegetable oils Short-chain saturated fatty acids are also liquid at room temperature Characteristics of Fat at Room Temperature p134 UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS TWO TYPES OF BOND FORMATION: • CIS - hydrogens on carbons joined by double bond are on same side = the carbon chain is bent • TRANS – hydrogens on carbons joined by double bond are on the opposite side = the carbon chain is straighter Comparing Cis and Trans Trans Fatty Acids • HYDROGENATION: chemical process where hydrogens are added to mono- or polyunsaturated fats to reduce the number of double bonds. • Results: • Fats are more saturated (solid) Resistant to oxidation (rancidity). Hydrogenation produces trans-fatty acids. Process of Hydrogenation Take a liquid oil through a process that adds hydrogen and changes it to a solid fat at room temperature FATTY ACIDS Essential Fatty Acids Body cannot make C-C double bonds before the 9th carbon from the methyl end Omega-3 Omega-6 Must get them from our diet Vegetable oils, seeds, nuts, fish, and other marine foods FATTY ACIDS • Omega-3: ALA - Alpha-Linolenic Acid EPA - Eicosapentaenoic Acid DHA - Docosahexaenoic Acid • Omega-6: Linoleic Acid Arachidonic Acid Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Linolenic Acid - ALA EPA and DHA Flaxseed Fatty oil Flaxseeds Soybean/Canola Oil Chia/Hemp Seeds Walnuts fish: Salmon Sardines Mackerel Fish oils Sources of Omega-6 Fatty Acids Linoleic Acid Arachidonic Acid Seeds Meats and nuts Vegetable oils Corn Safflower Sunflower Soybean FATTY ACIDS EICOSANOIDS Made from arachidonic acid (Omega 6) and EPA/DHA (Omega 3) Hormone-like compounds - more localized effect, different effects on different cells Important in the… Inflammatory process Blood vessel dilation & constriction Blood clotting EICOSANOIDS Omega-6s Linoleic acid -> arachidonic acid -> eicosanoids formed Overall effect: Constricting blood vessels Promote inflammation Blood clotting EICOSANOIDS Omega-3s Linolenic acid –> EPA and DHA -> eicosanoids formed Overall effect Dilating blood vessels Discouraging blood clotting Reducing inflammation Support Heart Health Table 5-H1 p162 3 CLASSES of LIPIDS Triglycerides • Made up of 3 Fatty Acids and Glycerol • “Fats and Oils” Phospholipids • Made of 2 Fatty Acids & phosphate bound to glycerol • Emulsifiers • Make up cell membranes Sterols • Hydrocarbon ring structure • Cholesterol, Bile acids, some hormones, Vit D TRIGLYCERIDES STRUCTURE: Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol Diglyceride: 2 fatty acids + glycerol Monoglyceride: 1 fatty acid + glycerol Condensation reactions – make triglycerides Fatty Acids Triglyceride Condensation Reactions Form Triglycerides Loss of water Triglycerides are the main form of fat consumed in the _________ (95% as fats and oils) Triglycerides are the main form of fat stored in the __________ (99%) TRIGLYCERIDES FUNCTIONS Stored fat supplies much of energy needs during rest – compactly Insulates the body and keeps it warm Protects bones & organs as a natural shock absorber Sensory qualities – flavor and texture PHOSPHOLIPIDS Glycerol bonded to 2 fatty acids & phosphate Phosphate (hydrophilic) = dissolve in H2O Fatty acids (lipophilic) = soluble in fat Ideal emulsifier to mix or transport fats in water Perfect structure for cell membranes PHOSPHOLIPIDS – Lecithin Functions of Phospholipids Cell Membranes Major component of cell membranes Lipid Transport and Emulsifier In the stomach, intestine, bloodstream and the lymphatic system Phospholipids of a Cell Membrane Figure 5-9 p136 Phospholipids as Emulsifiers • • • • Combine foods that wouldn’t normally mix Reduce fat separation (mayo) Increase shelf-life Prolong flavor release Phospholipids in Foods Lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) Major phospholipid Found in: Liver Eggs Soybeans Peanuts Wheat germ Liver produces lecithin as well. 3 CLASSES of LIPIDS Triglycerides • Made up of 3 Fatty Acids and Glycerol • “Fats and Oils” Phospholipids • Made of 2 Fatty Acids & phosphate bound to glycerol • Emulsifiers • Make up cell membranes Sterols • Hydrocarbon ring structure • Cholesterol, Bile acids, some hormones, Vit D STEROLS Hydrocarbons with a multiple ring structure • Contain no fatty acids • Cholesterol is the best-known sterol, found ONLY in animal food products CHOLESTEROL: Functions Major component of cell membranes (abundant in nerve and brain tissue) Precursor molecule: Examples - Vitamin D, testosterone, cortisol (adrenaline hormone) Important in the synthesis of bile acids CHOLESTEROL: Synthesis Liver manufactures most of the cholesterol in our bodies = 800 -1500 mg per day ~90% of the body’s cholesterol is found in the cells Sterols in Plants Similar in structure to cholesterol Interfere with cholesterol absorption Diets rich in plant sterols lower blood cholesterol levels Plant sterols & stanols are found naturally in small amounts in: • • • • • Grains Vegetables Fruits Legumes Nuts & Seeds LIPIDS Learning Objectives: • Understand lipid terminology and classifications • Understand digestion & absorption of lipids • Understand transport of lipids • Learn about function of lipids in the diet, and how they relate to health issues – Heart Disease (Ch 18) LIPID DIGESTION Lipid Digestion Mouth Chewing mixes fats with saliva Some hard fats melt Lingual lipase found in saliva Minimal fat digestion here Except in infants – lipase plays active role Lipid Digestion Stomach Muscular actions mix fat with watery chyme Exposes food to gastric lipase Works in acidic conditions Little digestion of fats occurs here Lipid Digestion Small Intestine Fat: CCK → gallbladder → bile Secretin → pancreatic juice → pancreatic lipase Chyme: Villi: Intestinal lipases Break down TG’s to monoglycerides & free FA’s Importance of Bile… Emulsified Fat & Enzymes Digestion of Large Triglycerides Form monoglyceride & 2 Free LCFA’s LIPID DIGESTION Mouth: chewing, lingual lipase Stomach: strong muscular contractions, gastric lipase Small Intestine: CCK → gallbladder → bile Secretin → pancreatic juice → lipase Micelles: tiny emulsified fat packets that can enter intestinal cells (enterocytes) Contain monoglycerides and LCFAs Lipid Absorption Small Intestine: duodenum or jejunum Small lipid molecules glycerol and short/medium chain fatty acids DIFFUSE easily into enterocytes (intestinal cells) Absorbed directly into blood stream Lipid Absorption Small Intestine: duodenum or jejunum Micelles – emulsified fat packets carry monoglycerides & long chain fatty acids to the brush border diffuse into enterocytes Once in the enterocytes, monoglycerides and free fatty acids are reformed into triglycerides LIPID ABSORPTION CHYLOMICRONS Transport lipids from intestine cells to rest of body Consist of: Newly-formed triglycerides Cholesterol Phospholipids Protein carriers Figure 5-16b p142 LIPID ABSORPTION Short-chain fatty acids Medium-chain fatty acids Glycerol → Absorbed directly into bloodstream to liver Chylomicrons enter the lymphatic system Bypass liver, blood to body cells for immediate use or storage Lipid Absorption Lipid Digestion/Absorption Review LIPIDS Learning Objectives: • Understand lipid terminology and classifications • Understand digestion & absorption of lipids • Understand transport of lipids • Learn about function of lipids in the diet, and how they relate to health issues – Heart Disease (Ch 18) Transport of Lipids in the Body Lipoproteins - combine lipids and proteins Chylomicrons Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Lipoproteins in the Body Chylomicrons Largest of lipoprotein Transport dietary lipids (triglycerides & cholesterol) from SI to rest of body Cells remove TG’s Become Liver chylomicron remnants collects and recycles what’s left Very Low Density Lipoprotein VLDL Lipids made in liver + chylomicron remnants make -> VLDL Shipped to rest of body TG’s are removed by body’s cells VLDL becomes smaller and more dense → LDL Low-Density Lipoprotein LDL Contain mostly cholesterol Distributes contents to cells: new cell membranes hormones store for use later LDL receptors on liver Control amount of blood cholesterol by removing LDL from circulation High-Density Lipoprotein HDL Made by liver Removes Delivers cholesterol from cells it back to the liver for recycling or disposal Has anti-inflammatory properties Prevents atherosclerotic plaques from breaking apart & causing heart attacks Size and Compositions of the Lipoproteins Figure 5-16 p142 Lipoproteins in the Body Lipid Transport Review LIPIDS Learning Objectives: • Understand lipid terminology and classifications • Understand digestion & absorption of lipids • Understand transport of lipids • Learn about function of lipids in the diet, and how they relate to health issues – Heart Disease (Ch 18) Cholesterol in the Body “Good” vs. “bad” cholesterol ↑ LDL - ↑ risk of heart attack ↑ HDL – protective against heart attacks Cholesterol Differences is all the same between LDL & HDL reflect proportions & direction of movement of cholesterol, not type Dietary Cholesterol Overall diet can affect the amount absorbed Dietary long chain saturated fat increases cholesterol absorption Fiber (especially soluble fiber) decrease cholesterol absorption Saturated Fats in the U.S. Diet Milk, yogurt, and cheese 20% Added fats and oils 34% Other 2% Eggs 2% Nuts and legumes 2% Meat, poultry, and fish 40% Fruits, grains, and vegetables are insignificant sources, unless saturated fats are intentionally added to them during preparation. Heart Disease Nearly 1 million people die each year in the United States related to CVD Heart Disease (heart attack) = leading cause of death in American men and women Heart Disease Elevated blood cholesterol Saturated fat – may increase LDL? Dietary choices – whole foods vs American diet, low fiber Trans-fats – increase LDL decrease HDL Dietary cholesterol? Atherosclerosis • “Hardening and narrowing of the arteries” • Accumulation of soft, fatty streaks along inner arterial walls • • Most people have well-developed plaques by age 30 Slow, progressive disease - takes decades to advance Atherosclerosis Plaque forms in response to injury along the artery wall Injury can be caused by: High cholesterol Hypertension Smoking Diabetes Homocysteine Diets high in saturated or trans fat Infections Progression of build-up…. Atherosclerosis Video Artery Explorer: http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=GBf59Z8tgA0 What Are Risk Factors for CVD? Potentially: High LDL Cholesterol Low HDL Cholesterol But actually depends on the subtypes of these lipoproteins An atherogenic diet: High in… Highly processed foods Trans-fatty acids Too many refined carbohydrates • Refined grains and sugar Low in veggies, fruits, whole plant foods Comparing Types of Fats in Meals Animal fats (in moderation) are fine, focus on whole-plant food fats • Minimally processed animal products are fine in the diet when the diet is plant-based as a whole • I do recommend consuming all of the foods in the righthand column regularly Other CVD Risk Factors Age & Gender Men - age 45 Women - age 55 More women will die from heart disease Family History More members, earlier age of onset - ↑ risk Other CVD Risk Factors Smoking More you smoke, ↑ risk Damages heart, ↑ BP Damages platelets – ↑ blood clots Damages blood vessels, ↑ atherosclerosis Diabetes Blood vessels blocked, ↓ circulation ↑ infections, rapid atherosclerosis ↑ risk of death from CVD Other CVD Risk Factors Physical inactivity & Obesity…abdominal obesity Contributes to ↑ LDL, ↓ HDL, HTN, diabetes Exercising & weight loss – ↓ LDL, ↑ HDL, ↓ BP, improves insulin sensitivity Metabolic Syndrome Includes 3 of 5 factors indicating metabolic disorders 1. abdominal obesity 2. ↑ TG’s 3. ↓ HDL 4. ↑ BP 5. ↑ fasting glucose Associated with many chronic diseases Overeating and physical inactivity contribute to this Factors that Lower LDL and/or Increase HDL Weight More Control mono & polyunsaturated fats Soluble dietary fibers Phytochemicals Moderate (whole-food plants) alcohol consumption PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Trans Fats & Health Effects Trans Fatty Acids Raise total blood cholesterol Raise LDL cholesterol Lower HDL cholesterol FDA mandates grams trans fats included on the Nutrition Facts panel (2006) Food Sources: pages 148, 162 How to Detect Trans-fat Other Dietary Considerations Homocysteine – high levels may promote atherosclerosis, excessive blood clotting, or blood vessel rigidity Omega-3 Fatty Acids – support heart health Soluble Fiber – help lower cholesterol levels Antioxidants – clean up free-radicals (Vitamin E, Vitamin C, etc) Coconut Oil Composed mostly of MCTs (MCFAs) MCTs may help protect against heart disease Other health benefits: Kills bacteria, viruses, fungi, yeast, parasites Improves digestion/absorption of vit/min Reduces inflammation Aids immune system function May aid in weight loss Keeps skin & hair healthier Recommended Intakes of Fat DRI and 2010 Dietary Guidelines recommend fat at 20-35% of energy intake (400 - 700 calories of a 2,000-kcalorie diet) FDA: 10% of energy intake from saturated fat 30% of energy intake total fat Heart Healthy Eating with Fats Reduce trans fats and other artificial fats Reduce refined polyunsaturated vegetable oils Soybean, canola, corn oils Increase whole-food plant sources of fats Nuts, seeds, avocados, olives, etc. Consume healthy saturated fats Coconut, macademia nut, grass-fed butter Consume unrefined, extra virgin monounsaturated oils (olive, avocado) Focus on omega 3-rich foods