* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
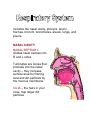
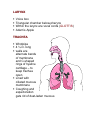
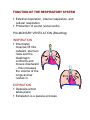
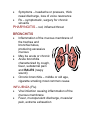
Respiratory System 1H10.01Describe the structure of the respiratory system. A. Nasal cavity (nose) 1. Nasal septum divides nose into R and L sides 2. Cilia – hairs that trap dirt and particles B. Sinuses 1. Cavities in skull 2. Connected to nasal cavity by ducts 3. Lined with mucous membrane C. Pharynx 1. Throat 2. 5” long D. Larynx (voice box) 1. Triangular chamber below pharynx 2. Contains vocal cords 3. Adam’s apple 4. Epiglottis – covers larynx during swallowing E. Trachea (windpipe) 1. 4 ½” long 2. Walls have bands of C-shaped cartilage 3. Lined with ciliated mucous membrane F. Bronchi and Bronchioles 1. Lower end of trachea divides into R and L bronchus 2. Become bronchial tubes and bronchioles as branches enter lungs G. Alveoli 1. Clusters of thin-walled sacs made of single layer epithelial tissue 2. Inner surfaces covered with surfactant 3. Each alveolus surrounded by capillaries H. Lungs 1. Fill thoracic cavity 2. Upper part = apex 3. Lower part = base 4. Lung tissue porous and spongy, it floats 5. R lung larger and shorter, 3 lobes 6. L lung has 2 lobes I. Pleura 1. Membrane that covers lungs 2. Double-walled sac 3. Space is pleural cavity 4. Pleural cavity filled with pleural fluid to prevent friction J. Upper respiratory tract 1H10.02 Analyze the function of the respiratory system. A. Cilia – hair in nose that traps dirt and particles B Sinuses 1. Lined with mucous membrane to warm and moisten air 2. Give resonance to the voice C Pharynx 1. Common passageway for air and food 2. When food swallowed, epiglottis closes over opening to larynx, preventing food from entering lungs D. Larynx 1. Produces sound (voice box) 2. Made of cartilage fibrous plates E. Trachea 1. C-shaped cartilage rings keep trachea open and more rigid 2. Coughing and expectoration get rid of dust-laden mucous F. Bronchi and bronchioles – passageway for air from trachea to alveoli in lungs G. Alveoli 1. Surfactant – keep alveoli from collapsing 2. O2 and CO2 exchange takes place between alveoli and capillaries H. Pleura – pleural cavity filled with pleural fluid to prevent friction I. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) 1. Inspiration (inhalation) a. Intercostal muscles lift ribs outward b. Sternum rises and the diaphragm contracts and moves downward c. This increases the volume of the lungs and air rushes in 2. Expiration (exhalation) a. Opposite action from inhalation b. Passive process J. Respiratory movements 1. 1 inspiration + 1 expiration = 1 respiration 2. Normal adult = 14 – 20 respirations/min 3. Increases with exercise, body temperature, certain diseases 4. Newborn resp = 40 – 60/min 5. During sleep – resps decrease 6. Emotion can change rate of respiration 7. Coughing – deep breath followed by forceful expulsion of air – to clear lower respiratory tract 8. Hiccups – spasm of the diaphragm and spasmodic closure of the glottis 9. Sneezing – air forced through nose to clear respiratory tract 10. Yawning – deep prolonged breath that fills lungs, increases blood O2 K. Control of breathing 1. Neural factors a. Respiratory center located in medulla oblongata b. Increase or decrease of O2 or CO2 in the blood will trigger respiratory center c. Phrenic nerve – stimulates diaphragm 2. Chemical factors a. Depends on level of blood CO2 b. Chemoreceptors in aorta and carotid arteries sensitive to the amount of blood O2 1H10.03 Identify characteristics and treatment of common respiratory disorders. A. Common Cold 1. Contagious viral, respiratory infection 2. Contributing factors – chilling, fatigue, poor nutrition, not enough sleep 3. Rx – stay in bed, drink warm liquids and fruit juice, good nutrition 4. Good handwashing = best prevention B. Pharyngitis – red, inflamed throat C. Laryngitis 1. Inflammation of larynx 2. Symps – sore throat, hoarseness, loss of voice, difficulty swallowing D. Bronchitis 1. Inflammation of mucous membranes of trachea and bronchi 2. Symps – cough, fever, substernal pain and rales (raspy sound) 3. Chronic bronchitis – middle or old age, caused by cigarette smoking E. Influenza (Flu) 1. Viral infection upper respiratory tract 2. Symps – fever, mucopurulent discharge, muscular pain, extreme exhaustion 3. Rx – symptomatic F. Pneumonia 1. Infection of lung 2. Caused by bacteria or virus 3. Alveoli fill with thick fluid 4. Symps – chest pain, fever, chills, dyspnea 5. Diagnosis – x-ray and listening to lungs 6. Rx – oxygen and antibiotics G. Tuberculosis 1. Infectious bacterial lung disease 2. Tubercles (lesions) form in lungs 3. Symps – cough, low grade fever in the afternoon, weight loss, night sweats 4. Diagnosis – skin test, if positive, follow up with chest x-ray and sputum 5. Rx – antibiotics H. Asthma 1. Inflammatory airway obstruction 2. Caused by allergen or psychological stress 3. 5% of Americans have asthma 4. Symps – difficulty exhaling, dyspnea, wheezing, tightness in chest 5. Rx – antinflammatory drugs, inhaled broncholdilator I. Emphysema 1. Alveoli become distended, lose their elasticity, can’t rebound, may eventually rupture 2. Air becomes trapped in alveoli, can’t exhale, forced exhalation required 3. Dyspnea increases as disease progresses 4. Rx – alleviate symptoms, decrease exposure to respiratory irritants, prevent infections Q. Related terms 1. Apnea 2. Dyspnea 3. Tachypnea Includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, lungs, and pleura. NASAL CAVITY NASAL SEPTUM = divides nasal cavities into R and L sides Turbinates are bones that protrude into the nasal cavity – they increase surface area for filtering dust and dirt particles by the mucous membrane. CILIA – the hairs in your nose, trap larger dirt particles SINUSES – cavities in the skull, ducts connect them to the nasal cavity, lined with mucous membrane to warm and moisten the air. Frontal Maxillary Ethmoid Sphenoid Sinuses give resonance to the voice. PHARYNX The throat Common passageway for air and food 5” long When food is swallowed, the EPIGLOTTIS closes over the opening to the larynx, preventing food from entering the lungs. LARYNX Voice box Triangular chamber below pharynx Within the larynx are vocal cords (GLOTTIS) Adam’s Apple TRACHEA Windpipe 4 ½ in. long walls are alternate bands of membrane and C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage – to keep trachea open Lined with ciliated mucous membrane Coughing and expectoration gets rid of dust-laden mucous BRONCHI and BRONCHIOLES Lower end of trachea divides into R and L bronchus As they enter lungs, subdivide into bronchial tubes and bronchioles Bronchi – similar to trachea with ciliated mucous membrane and hyaline cartilage Bronchial tubes – cartilaginous plates (instead of C-shaped rings) Bronchioles – thinner walls of smooth muscle, lined with ciliated epithelium At the end, alveolar duct and cluster of alveoli ALVEOLI Composed of a single layer of epithelial tissue Inner surfaces covered with SURFACTANT – to keep alveoli from collapsing Each alveolus surrounded by capillaries O2 and CO2 exchange takes place between the alveoli and capillaries LUNGS Fill thoracic cavity Upper part = apex Lower part = base Base fits snugly over diaphragm Lung tissue porous and spongy – it floats R lung = larger and shorter (displaced by the liver) and has 3 lobes L lung smaller (displaced by the heart) and has 2 lobes PLEURA Thin, moist slippery membrane that covers lungs Double-walled sac Space is pleural cavity – filled with pleural fluid to prevent friction FUNCTION OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM External respiration, internal respiration, and cellular respiration Production of sound (vocal cords) PULMONARY VENTILATION (Breathing) INSPIRATION Intercostal muscles lift ribs outward, sternum rises and the diaphragm contracts and moves downward – this increases the volume of the lungs and air rushes in. EXPIRATION Opposite action takes place Exhalation is a passive process Respiratory Movements 1 inspiration + 1 expiration = 1 respiration Normal adult = 14 - 20 respirations per minute Increases with exercise, body temperature, certain diseases. Age - newborn = 40-60/min Sleep = respirations Emotion can or rate Coughing – deep breath followed by forceful expulsion of air – to clear lower respiratory tract. Hiccups – spasm of the diaphragm and spasmotic closure of the glottis – irritation to diaphragm or phrenic nerve Sneezing – air forced through nose to clear respiratory tract Yawning – deep prolonged breath that fills the lungs, increases oxygen within the blood Control of Breathing Breathing controlled by neural and chemical factors. Neural Factors Respiratory center located in MEDULLA OBLONGATA on CO2 or O2 in the blood will trigger respiratory center PHRENIC NERVE – stimulates the diaphragm Chemical Factors Depends on the levels of CO2 in the blood (respiratory center in brain) Chemoreceptors in aorta and carotid arteries sensitive to the amount of blood O2 COMMON COLD Contagious viral respiratory infection Indirect causes - chilling, fatigue, lack of proper food, and not enough sleep Rx – stay in bed, drink warm liquids and fruit juice, good nutrition Also called an Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) Handwashing – best preventative measure LARYNGITIS Inflammation of larynx or voice box Often secondary to other respiratory infections Symptoms – sore throat, hoarseness or loss of voice, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) SINUSITIS Infection of mucous membrane that lines sinus cavities Caused by bacteria or virus Symptoms – headache or pressure, thick nasal discharge, loss of voice resonance Rx – symptomatic, surgery for chronic sinusitis PHARYNGITIS – red, inflamed throat BRONCHITIS Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the trachea and bronchial tubes, producing excessive mucous May be acute or chronic Acute bronchitis characterized by cough, fever, substernal pain and RALES (raspy sound) Chronic bronchitis – middle or old age, cigarette smoking most common cause INFLUENZA (Flu) Viral infection causing inflammation of the mucous membrane Fever, mucopurulent discharge, muscular pain, extreme exhaustion Complications – pneumonia, neuritis, otitis media and pleurisy Rx – treat the symptoms PNEUMONIA Infection of the lung Caused by bacteria or virus Alveoli fill with exudates (thick fluid) Symptoms – chest pain, fever, chills, dyspnea Rx – O2 and antibiotics TUBERCULOSIS Infectious bacterial lung disease Tubercles (lesions) form in the lungs Symptoms: cough, low grade fever in the afternoon, weight loss, night sweats Diagnosis – TB skin test If skin test positive – follow up with chest xray and sputum sample RX – antibiotic ASTHMA Inflammatory airway obstruction Caused by allergen or psychological stress 5% of Americans have asthma Symptoms: difficulty exhaling, dyspnea, wheezing, tightness in chest Rx: anti-inflammatory drugs, inhaled bronchodilator EMPHYSEMA Alveoli become over-dilated, lose their elasticity, can’t rebound, may eventually rupture Air becomes trapped, can’t exhale – forced exhalation required Reduced exchange of O2 and CO2 Dyspnea increases as disease progresses Rx – alleviate the symptoms, decrease exposure to respiratory irritants, prevent infections, restructure activities to prevent need for O2