* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution of Populations
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
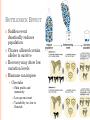
EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS Chapter 23 CLARIFYING EVOLUTION Natural selection ACTS on individuals Evolutionary impact of affects populations over time Grants Finches Drought = large, deep beaks Seeds = large, hard Average beak size increase Population evolved More large in population Beak not change in life Mutations ultimate source of new alleles GENETIC VARIATION Mutation Must be in gametes to be passed to offspring Point mutations Phenotype & environment Wobble bases and introns Altering gene number or sequence Nondisjunction Olfactory receptors Sexual reproduction Allelic reshuffling Crossing over, independent assortment, and fertilization Makes evolution possible POPULATIONS Species interbreeding to produce offspring in an area Genetic makeup is the gene pool Alleles for all loci in all individuals Each allele has a frequency (proportion) HARDY-WEINBERG PRINCIPLE Frequency alleles & genotypes remain constant Determines if evolution is occurring Conditions necessary No mutation Usually not a huge effect anyway Infinitely large, isolated population No movement in or out of population to change allelic frequency Mating is random Neither allele gives reproductive (or early survival) advantage over the other Can apply to some, all or no genes HARDY-WEINBERG EQUILIBRIUM 2 alleles Allelic frequency p+q=1 Genotypic frequency p is more common, q is less common p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 Phenotypic frequency Same or different then genotypic HARDY-WEINBERG PRACTICE Work with examples in section, end of chapter, and study guide to become familiar with equation Wildflowers with 2 alleles (Cr Cw) demonstrating incomplete dominance, what does this mean? 320 red, 160 pink, 20 white 500 individuals, 1000 copies of genes for flower color (2n) Frequencies of each allele, genotype, & phenotype? Blood Type M MN N Genotype LMLM LMLN LNLN Number of Individuals 700 650 150 MICROEVOLUTION Change in allelic frequency in a population over generations 3 mechanisms Natural selection Genetic drift Improves match between individual and environment Chance events that alter allele frequencies Gene flow Transfer of alleles between populations GENETIC DRIFT Chance events cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably Doesn’t work to produce adaptations Founder effect and bottleneck effect are examples FOUNDER EFFECT Isolated individuals form a new population Gene pool differs from source Few members blown to a new island or an earthquake splits a population Chance where some individuals and their alleles, but not others are separated BOTTLENECK EFFECT Sudden event drastically reduces population Chance allowed certain alleles to survive Recovery may show low variation levels Humans can impose Cheetahs Skin grafts and immunity Low sperm count Variability too low to flourish GENE FLOW Transfer of alleles into or out of a population Fertile individuals and their alleles move Reduces genetic differences between populations Significant enough, 2 populations can = 1 Human populations Introduces new alleles to population Natural selection can increase frequency RELATIVE FITNESS Contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of others Natural selection is not survival of the fittest Individuals with most viable, fittest offspring pass on the most genes Survival doesn’t guarantee reproductive success Selection favors individuals with phenotypic traits that provide higher reproductive success than others MODES OF SELECTION Dark rocks Beak size in finches Birth weight SEXUAL SELECTION Certain inherited characteristics enhance finding mates Creates sexual dimorphism Differences (2°) that don’t have direct effect on fitness Include size, color, ornamentation, and behavior Intrasexual selection (within same sex) Males defend status through force or psychologically Intersexual selection (between sexes) Female choice depends on showiness of male Not always beneficial, pose risks by making more visible = tradeoff Females want mates with ‘good genes’ Midshipman Fish Male singers or sneakers Singing induces egg laying Male resumes singing Attract more mates Sneakers hangout and sneak in to fertilize eggs Resemble females NATURAL SELECTION ISN’T PERFECT Selection can only act on existing variations Evolution limited by ancestry Doesn’t scrap existing structure, adapts to new ones Often compromises Interaction of chance, natural selection, and the environment Chance moves 1 organism to new environmentColorado, but not necessarily to best fit environment New species are ‘better than’