* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lect4 Proteins
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
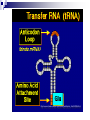
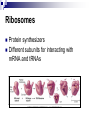
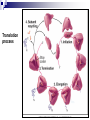
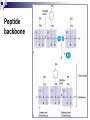
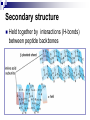
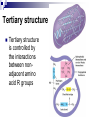
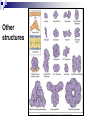
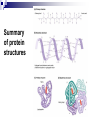
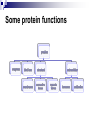
PROTEINS Nicky Mulder Acknowledgements: Anna Kramvis for lecture material (adapted here) Central dogma of molecular biology http://www.cem.msu.edu/~reusch/VirtualText/nucacids.htm Protein building blocks Proteins are made up of amino acids 20 possible amino acids Each specified/encoded by a triplet of bases Messenger RNA transcripts translated into proteins The Genetic Code Each amino acid is specified by a triplet of 3 bases (codons) Codons were elucidated a decade after the discovery of the DNA structure in 1953 If we have the 4 bases A,C,G,T we have 4 x4 x4 = 64 possible codons Actually 61 codons + 3 stop codons The Genetic Code Codon usage varies Open reading frame String of in-frame combinations/triplets of bases that specify an amino acid Starts with ATG (Meth) or Val Ends with stop codon One base insertion or deletion –out of frame/frameshift Translating sequences 6 possible reading frames, 3 in each direction AGTCGGCTGACTGCGTTTACGAATGCGATTACTCCCTT +1 Reverse complement AAGGGAGTAATCGCATTCGTAAACGCAGTCAGCCGACT -1 Translating sequences 6 possible reading frames, 3 in each direction AGTCGGCTGACTGCGTTTACGAATGCGATTACTCCCTT +2 AAGGGAGTAATCGCATTCGTAAACGCAGTCAGCCGACT -2 Translating sequences 6 possible reading frames, 3 in each direction AGTCGGCTGACTGCGTTTACGAATGCGATTACTCCCTT +3 AAGGGAGTAATCGCATTCGTAAACGCAGTCAGCCGACT -3 Getting the final protein Six-frame translation Find longest ORF with initiation site, start codon and ending with stop codon Transcription and translation ATGCGGTGCAACGTGCATCCTAAA UACGCCACGUUGCACGUAGGAUUU W G P Y T A K L http://www.virtualsciencefair.org/2004/mcgo4s0/public_html/t3/RNA.html library.thinkquest.org Ribosomes Protein synthesizers Different subunits for interacting with mRNA and tRNAs Translation process Copyright-Anna Kramvis 15 Amino acid structure The chemistry of R groups distinguishes amino acids and their properties Polypeptide chain Each protein has a unique sequence of amino acids joined into a polypeptide chain Valine Leucine Serine Tyrosine Proline Protein primary structure Proteins made up amino acids joined by peptide bonds between carboxyl group of one and amino group of the next www.columbia.edu commons.wikimedia.org Peptide backbone Primary structure, disulphide bonds Secondary structure Held together by interactions (H-bonds) between peptide backbones Tertiary structure Tertiary structure is controlled by the interactions between nonadjacent amino acid R groups Quaternary Structure More than one protein chain, e.g. hemoglobin Possible bonds in proteins Hydrogen bonds: weak electrostatic attractions between electronegative atom (O or N). Van der Waals forces: can be attractive or repulsive, depends on distance Electrostatic interactions or ionic bonds: weak bonds that form between charged groups in aqueous environments Hydrophobic effects: arise because hydrogen bonded structure of water forces hydrophobic groups into the internal parts of the protein. Other structures Summary of protein structures The function of a protein depends on sequence of amino acids and requires a precise folding of its polypeptide chain Properties of Amino Acids http://www.jalview.org/help/html/misc/properties.gif Name Glycine Alanine Valine Leucine Isoleucine Proline Phenylalanine Tyrosine Tryptophan Cysteine Methionine Serine Threonine Lysine Arginine Histidine Aspartate Glutamate Asparagine Glutamine G A V L I P F Y W C M S T K R H D E N Q Gly Ala Val Leu Ile Pro Phe Tyr Trp Cys Met Ser Thr Lys Arg His Asp Glu Asn Gln R-Group Properties Hydrophobic Hydrophobic Hydrophobic Hydrophobic Hydrophobic, two chiral carbons Cyclic, not terribly hydrophobic Hydrophobic, bulky Less hydrophobic (than Phe), bulky Hydrophobic, bulky (indole ring) Hydrophobic, highly reactive (S-S link) Hydrophobic (start a.a.) Hydrophilic, reactive Hydrophilic, reactive, two chiral carbons Highly hydrophilic, positively charged Highly hydrophilic, positively charged Highly hydrophilic, positive or neutral Highly hydrophilic, negatively charged Highly hydrophilic, negatively charged Uncharged Uncharged Copyright-Anna Kramvis 29 Some protein functions Information from a protein sequence MDITIQHPWFKRALGSLYPSRLFDQFFGEGLFEYDLLPFLSSTISPYYRQSLFR • amino acid composition • molecular weight Information from a protein sequence Single amino acid physical properties MDQHPWFKRAITIVLLGLLPFLSLYPSRLFDQFCGEGLFEYDSSTISCYRQSLF RTVLESG D,E -acidic C,D,E,H,K,N,Q,R,S,T –polar, active sites, metal binding V,L,I,M –hydrophobic, membrane C –disulphide-rich, disulphide bonds Information from a protein sequence Functionally important regions MDQHPWFKRAITIVLLGLLPFLSLYCPSRLFDQFCGEGLFEYDSSTISYRQSLF RTNVLES Active site/metal Hydrophobic region binding Glycosylation site disulphide bond • Transmembrane regions • Signal sequences • Localisation signals (subcellular location) • Targeting sequences • Modification sites Information from a protein sequence FAMILY DOMAIN Conserved sequence Conserved domains MOTIF Properties of regions SITE RESIDUE Physical amino acid properties GKLIANNTRVWVYCGNGKPSDLGGNNLPAKFLEGFVRTSNIKFQDAYN Protein abundance Not all genes are expressed all the time, amount of protein is affected by: gene expression -transcriptional regulation Post-transcriptional regulation Translational regulation Post-translational regulation Transcription regulation Regulators –enhancers and repressors, can be cis- or trans-acting Bind to specific sites Sigma factors, anti-sigma factors DNA unwinding DNA methylation Signalling pathways Post-transcriptional regulation mRNA half-life Antisense RNA RNA splicing siRNAs Translational regulation Ribosomes Translation factors tRNA availability Post-translational regulation Transport to appropriate place Protein folding (chaperones) Post-translational modification: Phosphorylation Acetylation Sugars added…. Summary of main building blocks of biological systems http://jp.senescence.info/thoughts/dna_life.jpg Translation exercise 1. Translate this mRNA using the genetic code table 5’AUGUUUUUGUCGUACUGGUGUCUACCUCAUCAACGU AUUACGAAUAAG3’ Write out the translation using the one letter and three letter conventions. 2. Give the characteristics of each amino acid in the polypeptide chain. 3. How long is the original RNA sequence and how long is the protein sequence? Copyright-Anna Kramvis 41 Additional questions Here is a gene sequence: 5’ AGCAATGCATGCATCGTTATGG 3’ Identify the initiation codon What reading frame is it in? Would translation be affected if the first C was changed to G, if so, what effect? Would translation be affected if the second last C was changed to T, if so, what effect?