* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Branches of this artery as I said when it reaches to
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
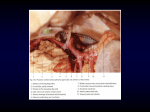
SORRY : A PROBLEM IN PRINTING THIS FILE CONTACT MALEK IN MORE DETAILS page 1 08 04 Heart Vascular supply نبيل خوري.د أماني خصاونه 5002-3-52 page 2 Anatomy lec #4 Dr.nabeel khoori Blood supply to the heart firstly bcz this lec is the 2nd anatomy lecture in the same day ,the doctor start it by completing what he start about defect in the valves so be sure that you study the lec #3 b4 study this lecture yyyyyy And practically as the blood come back into the ventricle after the contraction of ventricle ,these valves are filled &they close to each other preventing the blood from going back into the ventricle so those are called semilunar valve . The other 2 valves that guarding atrioventricular chamber of the heart are one in the left & one in the right these valve are leaflet like shape –like the leafs of the treat –they have adherent margin that adhere to something called cytoskeleton of the heart What is the function of this cytoskeleton (fibrous ring )in the heart ?? In the beginning we talked about the muscular(myocardial) aspect of the heart ,and as any muscle in the body the heart muscle must be originated & inserted somewhere , so those fibrous rings which we call it cytoskeleton of the heart are incirculating these opening whether it is atriovenricle opening or semilunar opening into the aorta & pulmonary trunk and provide origin for the muscle of the heart ,so the muscle of the heart originated from these ring outsides ,inside they will provide the attachement for these cap *cup like shape *in the semilunar valve or leaf like shape in tricuspidic and mitral valve . As we know that there are four valves within your heart. They are the mitral, tricuspid, aortic and pulmonic valve. The mitral valve and tricuspid valve lie between the atria (upper heart chambers) and the ventricles (lower heart chambers). The aortic valve and pulmonic valve lie between the ventricles and the major blood vessels leaving the heart. As blood leaves each chamber of the heart, it passes through a valve. Your heart valves make sure that blood flows in only one direction through your heart. page 3 F igure 1 :the mitral (bicuspidic )valve & tricuspidic valve You can see the opening ,and you can see that these (the arrow ( what we call it ring . ) attach to this ( )which And u can see also fibrous skeleton of the heart ,in addation to that we see the muscle-labeled as papillary muscle - inserted to the outer aspect of this ring and go back in to the same direction to be inserted to the origin &inserted into the same areas or the same fibrous ring in the different direction . Now the fibrous skeleton that is represented over here has a shape ,and you can see the shape of this if you take out ,you will be able to see it as this structure –Figure 2-. Figure2 this is the fibrous skeleton of the heart AS labeled in the figure above :that is the ring of bicuspidic valve ,that is the ring of tricuspidic valve ,and you can observe that the rings of the aortic & pulmonary trunk are more taller ,more longer if you compare it with the rings in mitral & tricuspidic valves which are tortuous & small page 4 so the rings in the mitral and tricuspidic valves are tortuous and small while the rings in the aortic pulmonary trunk are more taller and more longer now in the lower or toward the septal –the intravenricular septum of the heart ,there is expansion of this fibrous ring & this is what we call it the membranous part of intravenricular septum that will provide the insertion and the origin of the muscle that are located below,–at lower level-of the intravenricular septum ….so these rings which are connected to the fibrous skeleton have an outer surface ,this outer surface is there to provide insertion & origin for the myocardial muscle ,the inside surface of these rings provide attachement for the flap- like structures which we call them the valves the membranous part of IV septum is the part of the septum which is located below the valve which is oval and round . Figure3:this is the tricuspidic valve over here , you see 3 valves(cusps ) over here orientated anteriorly ,posteriorly & medially . page 5 Figure 4:this is the bicuspid valve ,observe that these are chordae tendinae that come out from papillary muscle that over here ,this is the left ventricle & these are the valve ,observe that these valve insert into this fibrous skeleton . Figure 4 this is an opening of the left ventricle ,you can see the atrium over here ,you can see the pectinate muscle above ,you can see the wall of the ventricle which is thicker, you will see that 3 edges of these flap like structure which is mitral valve(I don’t think that they are 3 edge ,it think to be 2 edge???? ) is inserted to chordae tendinae whenever the papillary muscle contract , it will push these toward the atrium closing the opening between the atrium & ventricle. Figure 5 : this is a bicuspidic close ,appereance of the mitral valve Figure 6 :this is oblique cut of the heart ,you will able to see the right ventricle & left ventricle ,also you can see the 2 openings –valves, leaflet- that formed bicuspidic(mitral) valve you can see the opening of the pulmonary vein ,the pulmonary valves &the aortic valves as well . page 6 Figure 6:oblique section of the heart. We said that the pulmonary &the aortic valve are those valve that are cup-like shape ,these cup-like shape structure that they are closed preventing the return of the blood when the blood come over here(in either pulmonary artery or aortic artery) ,then the cup-like structure are filled with blood closing the entrance, preventing the return of the Venus blood into right ventricle . Figure 7:pulmonary valve,&aortic valve This is the difference between mitral valve & tricuspid valve 4 u 2 study Mitral Valve • • • • • 2 triangular leaflets Larger, thicker, stronger than tricuspid Anterior leaflet (aortic or septal ) Posterior leaflet (ventricular) Papillary muscle – contraction occurs during systole to shorten Cordae Tendinae – prevent MR during ventricular systole page 7 Tricuspid valve • 3 triangular shaped leaflets • Names – Anterior – Septal – Posterior • Papillary muscles & chordae tendinae are present but play a more important role in the high pressure chamber of LV This is the aortic valve versus the pulmonary valve in this section Pulmonary valve • 3 Semi-lunar cusps • Semi lunar shape • Attached to a fibrous ring within Aortic valve 3 Similar to pulmonary Leaflets - 3 Semi lunar shape Attached to a fibrous ring within the wall of the wall of pulmonary trunk wall of aortic artery • Orientation: Orientation – Left anterior – Right anterior – Posterior Anterior Left posterior right Posterior page 8 Figure 8that is the normal pulmonary valve ,observe that this disective area of the connection between the right ventricle& pulmonary trunk that the right ventricle entrance over here & that is the beginning of what we call it the pulmonary trunk The ring that is called the fibrous ring of pulmonary trunk extend from here( ) into this area ( ) ,observe that even the color of this area is totally different that made from this fibrous ring that attached to fibrous skeleton of the heart , - Figure 7- Figure 8 Figure 8: If you look carefully at the pulmonary valve you will be able to see that this valve is located immediately below the origin of what we call it the pulmonary arteries Figure9 Figure 9: now this is operation aspect of the aortic valve that cause return of the blood from aorta into the left ventricle ,that there a defect in this aortic valve that cause return of the blood from the aorta into the left ventricle,the anterior ,posterior ,middle one (which is medial one)(that is what the doc said laterally but I think he mean anterior page 9 ,posterior left and posterior right )valves or cusps have practically similar shape which cup-like shape; only the anterior and the medial(he meant the left posterior) one practically provide 2 openings for the coronary artery ok??? As the figure below(Figure 10) ,you can observe that in each of those valve we have what we call it the nodules of the valve & this nodule cut or make division between what we call it the lanula . This is a depression over here This is a depression over here Figure 10 So the lanula =3 surfaces of the valve where in the middle of this we have a ridge &elevation ,this elevation is called nodules ,posterior to this valve you will see a depression over here -look above-; the left posterior &the right posterior,these valve adhere or fix to the wall &this wall with this depression is called aortic sinus In the aortic sinusof the aortic valve in the left posterior & in anterior you have 2 openings there are nothing but origin of coronary artery This is the opening of the coronary artery ,this is the elevated ridge in the valve which what we call it nodules &that what we call it the free edge surface as lunula Lunula in latin mean moon so it is moon like shape that why we call it semilunar valve Now observe over here we have the fibrous ring extending downward &that the fibrous ring extend from here to here &over here you will able to see that we have the myocardial muscle or the cardic muscle as you see . the doc here talked about aortic valve (figure 9 ):This is the finger with a gloves ,if you look and see it carfully you will see a finger with a glove showing this valve open in size the valve showing you how this valve will function as the blood comes this way ,it will fill these gaps so if you bring these gaps ,fix the artery together ,these gaps will be orienated as anterior, posterior left, and posterior right and therefore they will filled with blood preveting the returning of the blood from the aorta . page 1 0 The blood supply to the heart We talked about the aorta having nodules ,having sinus &from the sinuses we have 2 opening in the anterior and posterior left these 2 openings represent the origin or the beginning of the two coronary arteries the arteries that are supplying the myocardial ,& pericardium of the heart with oxygenated blood ,now observe that most of the heart attacks that occur in the human being if you look to these defect of these arteries & that what we call it sinuses (plate) accumulation within the wall ,so the coronary arteries originate at the base of ascending part of aorta and they will go within the or will find within the intraventricular sulcus in the right and the left …that is why we call them left and right coronary arteries …..we will see what will happen to these arteries. RIGHT CORNARY ARTERY:The coronary artery in the right side originated from the beginning of aorta ,the base of ascending aorta from right aortic sinus & goes into intraventricular sulcus in the right side for a long distance then immediately reach the margin which is the inferior border of the heart ,at the meeting between the left border and the inferior border of the heart ,it will be bifurcating into 2 arteries these arteries are called the marginal artery &the posterior descending(or interventricular) artery . THE LEFT CORNARY ARTERY : is masked somehow ,you can’t see it over here because of the presence of the origin of the pulmonary trunk &then it will appear &immediately after it appear ,it will be divided into 2 arteries ,one artery goes down into intraventricular sulcus-anterior interventricular artery- &the other one is called circumflex artery **circumflex artery because they goes around the heart &in circumflex way . The left coronary artery ,this artery practically located in coronary grooves or coronary sulcus- the intravenricular sulcus- which is separation between the atrium &the ventricle in the left side , and it masked by pulmonary trunk and practically it somehow overlap by the auricles , the auricles are nothing but pouch-like structure that come either from the left or from the right atrium ,they are called to be reservoir of an excess of blood on both chambers page 1 1 Figure 11: Very importan t to know how much supply &where these arteries goes. . The left artery supplies the1 left atrium in total ,2most of the left ventricle because of the presence of anterior descending artery in the intraventricular groove ,3part of the right ventricle supply by this artery &4intraventricular septum is supplied by this artery (the 2third anterior including the intraventricular bundle that is found within this septum is irrigated by this artery)and the other 1/3 is supplied by the posterior intervenricular artery which is branches of right coronary artery (RCA). SO “how the supply of the intraventricular septum of the heart?” you see only the anterior two third of the septum is supplied by the anterior intervenricular artery & this division of the left coronary artery and the other one which is posterior one “ the posterior descending aretery”-branch of RCA –supply the other 1/3 part of IV septum . Branches of this artery as I said when it reaches to the level of intraventricular sulcus , this artery will divdide into one circumflex which is posterior aspect and will be continue in the sulucus between the atrium and ventricle in the left side and the other one anterior intervenricular sulcus goes to the 2 ventricles and supply them as we mentioned before. in 40% of people this artery supply the 5sinoatrial node (SA node)that pump in the in the atrium and the ventricles in interventricle sulcus between the right atrium and the right sulcus Figure 12:this is the drawing showing the circumflex artery &the anterior interventricular or descending artery & this is the coronary artery in the left ,we cut the pulmonary trunk practically ,major part of this artery is masked by this artery ,the auricle which is located over here covers the circumflex ,mostly of this arteries ,small portion of this artery can be appearing if we looked in the anterior aspect of the heart mainly this artery give one very important division anteriorly and this division is called the anterior intervenricular artery &the other one is the circumflex which goes and being in the middle into the atriaventricular sulcus in the left side what happen to this artery ??it will goes around and comes and makes a branch or terminal branch or continuing branch of the right one and make together with the right page 1 2 side the posterior descending artery which is the artery that irrigate the posterior one third of intervevtricular septum. Figure 12 SO the posterior intraventricular artery is made mainly by the right coronary artery with the contribution of the circumflex artery which is the branch of the left side . practically as I said ,you can see it totally because it isn’t masked by anything ,it located below the right atria &at the begging you can see it coming out from descending aspect of aorta and it supplies the right atrium in totally it will supplies part of the right ventricle that that practically is not supplied by anterior descending artery, it supply the posterior aspect of interventricular septum ,and practically 80%of people have this supply in AV node within introventricular septum . THE RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY : the sinoatrial node ,it is supplied 60% from this artery ,observe that the sanitoatrial node is mainly supplies by the right side &the right artery is somehow little could be or less can be defected if we compare It with the left one ,the left one is more defected ,you see the santioarial node is more important because it regulator of electricity stimulate the heart ,it supplied mainly of this artery & the AV node as well to complete the innervations of the heart ,most of this santioarial node is supplied by the right coronary artery . so practically we knew that these artery that left and right artery ,they are distributed differently in the human body these are the branches of the coronary artery in the right side ,the sanitoatrial node branches ,the marginal branch *the marginal branch meaning that when you see it over here you can recognize it . this is the marginal artery & this marginal artery goes into the lower or inferior border of the heart & as I said this part mainly this very important bifurcation give more irrigation to the right ventricle & the other one goes posterior continue as the posterior descending artery (PDA)as we see over here posterior( intervenricular) descending artery ,if the continuation of the coronary artery in the right side & that part (the doc page 1 3 means circumflex with PDA)will give santioatrial node because the sanitoatrial node is found in the posterior aspect of AV . This is the angiogram showing the normal coronary circulation : angiogram mean: that we have injected the human arteries or the coronary arteries through the mammary artery with dye &we take X-ray for those arteries to see whether these arteries are fatal or not . Figure13: Now these coronary circulation observe over here ,you can see that you have the right coronary artery over here the heart in this case of this picture is straight forward it isn’t in claim so you will see the left and the right one &this is circumflex & this LAD artery (left anterior descending artery ),and that the right coronary artery & this is the marginal artery ,observe that these 2 bifurcation of the left coronary artery which are important and they are very tortuous ,they are located within intraventricular sulcus,they are irrigating mainly ,see how much the irrigating of the left ventricle if we compare it with the right ventricle the right ventricle will require less blood because the wall of the right ventricle is thinner than the wall of the left one Now when we have the heart in the lab how do we start see its structure? Firstly we should put it in anatomical position how?? The apex is positioned toward the left &the base is straight line that practically to the right . Now-look to the right side of figure above- this is what we call it epicardial fat above epicardium and this is what we call it the serous aspect of the epicardium,this shinning area is pariatel layer of pericardium. This is the left ventricle compare it with the right ventricle whenever you see big amount of fat you will guess that this interventricular septum ,now if we look carfully to this septum we can see arteries which are coronary arteries The dominance of cornary arteries ,what does this mean?? Usually you see that the left artery is more irregatable comparing with the right artery ,the right coronary artery supply both right & left sides but the left one is supplied page 1 4 mainly than the right one ,it will supplied the left side as well as the part of the right side ,& then it will supply two third of the anterior aspect of the septum so therefore it dominant if we compare it with the right side .*this is V.IMP as the doc.said,you should know the meaning of dominance of cornary the artery * Because the doctor concerned on this point ,so I found these useful information: We have 2 artery ,one posterior descending artery and postlateral artery ,if these 2 arteries supplied by right coronary artery then we call this situation rightdominant but if they supplied by circumflex artery (which is branch from left coronary artery )then it is called left –dominant if both of RCA and circumflex artery supply these arteries then it is called co-dominant artery . http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coronary_circulation Within the endocardium we have small arteries which are very important ,why do we study them ??,because there are no maneuvers of doing angioplasty without the surgical intervention or within bypassing , And we are concerned with these plexuses that they are no thing but an arterial plexuses that are found within the subendocardial that take blood from the blood that is found within the chambers of the heart , you will see later on how these technique of angioplasty will be done but practically we have epicardium(mean it is found in epicardium) artery , subepicardial artery (endocardial artery). This is the histological aspect showing over here that the submyocardial artery , over here& over here you have 2 arteries ,see the internal elastic lamina as endocardium occur immediately after the lumen . Angina….. What causes the angina ?? Angina is a narrowing or destruction of some way of the flow of the blood into the myocardial,the atherosclerosis is one of the most important aspect of this destruction ,the atherosclerosis is nothing but when we have a plague &accumulation of blood clot above this plague that reduce the amount of the opening site of coronary artery thus reduce the quantity of blood that are supplying to certain area within the myocardial and this will cause ischemia . Now high blood level ,high cholesterol level ,smoking are the most 3 important causes that participate in forming atherosclerosis. page 1 5 If we look to the coronary artery you can see that this artery is very small therefore any plague in it will affect the area that immediately after the area where is the stenosis or sclerosis,now observe over here the shape or the appearance of myocardial are less appearing to to be ischemitic if we compare it with the nomal appearance of myocardial of the rest of the heart over here. Ok so angina is when the artery don’t provide oxygenated blood to the certain area of the heart &therefore we have ischemic heart ,now the ischemia overhere can be in different kind as well the angina could be stable or unstable . What is the stable and unstable angina ? S TABLE ANGINA when we have pain which is followed by narrowing whether spasm or atherosclerotic of coronary artery , where it is constant pain ; septum pain ,chest pain ,abdominal pain ,teeth pain that radiate toward left upper limb . Now this pain can be very shallow or can be consistent when they are shallow &consistent and the patient will complain of heaviness on his /her chest. The another form of angina which is UNSTABLE ANGINA is that every time the pain will come in different way ,sometime it come as a pain in the neck ,sometime in the shoulder or in the back ,joint but without constant complain of the patient . How we differentiate between them ?? we have 2 ways ,one method which is clinical method ,we use what we call it sub lingual medication which is vasodilator medication , IN STABLE ANGINA put it under the teeth &dissolve v.quickly under the tongue ,these medication will open the coronary circulation & provide less ischemic damage to the heart. In UNSTABLE ANGINA the patient does not follow this rid if they are taking isosorbid(inguinal medication)he does not have benefit cause the pain come in different way so that stable angina when we have coronary blockage somewhere fixed in the heart where in the unstable angina sometime we see it more than one place in the heart or within the coronary artery which is harm . How we examine it ?? Immediately X-ray Exercise electrography( or what I found Exercise ECG) Nuclear(stress)test Coronary arteriography(angiography) page 1 6 Coronary arteriography Procedure :a catheter introduce in femoral artery ,and we will go all the way into the left side of the heart and to the aortic arch & go into the sinuses where we can find them above semilunar valve, you can see the coronary opening and when a catheter enter into it the dye will be injected in these coronary arteries & 3D picture will be taken by X-ray machine to show you this practically ,how this dye is flowing inside the coronary artery circulation ,as in the picture there is a spasm (narrowing)which is caused by atherosclerosis ,and these narrowing can be measured ,it can be 20%,40%,100% ,if it is 100%narrowing or spasm we have for sure serious ischemic changes after the spasm of coronary artery Figure 14 People after age of 40-50 they have less deadly angina pectoris &heart attack than young people why??because of the prescence of the cololateral circulation which occur after the age of 40 years old ,that why old ppl has less deadly heart attack due to coronary blockage and death than youg ppl This is angiogram ,the narrowing of one artery here due to spasm . Figure 15 page 1 7 Nuclear (stress )test:new technique This is image which is taken at the rest ,during exercise ,and these images will show you after we inject the dye in he patient ,then we introduce the patient into MIR machine that take picture(3 dimensional pic) to the chest area,and take a picture in more detail 3 dimensional pic to the pulmonary artery that has a dye inside it,and show what we call hollow image of these artery we can see a cut to the heart see where the narrowing occur within the heart ,it will take along time but you will able to see where the narrowing happen if we see that the hollow is not completed Figure 16 Treatment of angina We introduce this catheter, in the top of the catheter we have a balloon & sometime the ballon is more thinner to open the closed coronary artery so practically,when we reach the coronary artery we inject the dye ,we will know that at this area we have a spasm so we will go with this catheter &inflate the balloon over here ,and thus it will make the diameter of the coronary artery suitable to let the blood going through this artery when ballooning as we see over here ,plague will remove or will squeeze toward the wall make the artery more fatting but this isn’t sufficient resolution for angina this is temporary way that some people ,if they follow the diet of low cholesterol &more exercise and less smoking ,they will be ok but in other cases the plague is big so we have to introduce stent ,stent is nothing but metal mash from specific material that introduce into the spasm ,if we have no result of ballooning way that make this respective area of those coronary artery open &that stent introduce after the balloon & the stent over here allow the coronary artery to be good &that is longer period of time ,it could last for years,10,20 years if the patient again control his cholesterol ,smoking and do a lot of exercises,………. balloning stent metal page 1 8 This is a site where I found good animation 4 this technique http://files.totalhealth.ivillage.com/ivth/files/ivth/animationfiles/flash_ content/clientNF.html But when the 2 previous ways are insufficient Or when we have unstable angina at the same time what should we do?????? We will go to the surgical method which is bypass that when we replace one blocked artery within the heart by artery or vein which is from the patient own veins or arteries , practically coming out from aorta into major respective part of area which is ischematic area , we can do 2 or more bypassing in the heart &it depend on how many bypassing it will take longer time . Nowadays we have what we call it transmyocardial laser revascularization therapy &this therapy practically is allowing the blood in the heart especially in the left side by opening channels between the left ventricle with subendothelial vascularization &subendocardial vascularization these laser channels are introduce without open heart surgery , we just introduce a prop into the right ventricle &open channel between the right ventricle & the wall of the ventricle allowing the blood to come out from right ventricle into the wall and irrigate this area which is ischematic ,so that is a creating of what we call it a channels between left ventricle and that area which is ischemaic area . page 1 9 That is a new technique that has a broad use not in Jordan ,in jordan we have only one machine and it is very expensive ……… THE END OF THE LECTURE firstly I want to apologize by the end of the lecture ,I apologize for any mistakes I did without attention ,I really did my best in listening ,writing ,and reorganization this lecture ,I hope u find it easy and well-understood with best wishes Amani ali khasawneh page 2 0